Summary
Background: The study's aim was to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of celecoxib combined with chemoradiotherapy (CRT) for locally advanced oesophageal cancer (OC).
Methods: CRT comprised of 5FU (1000 mg/m2/day, days 1–4, weeks 1 & 5), cisplatin (75 mg/m2, days 1 & 29) and radiotherapy (50 Gy in 25 fractions or 50.4 Gy in 28 fractions). Celecoxib was given daily during CRT at one of five doses (200 mg bd to 600 mg bd). Three to six patients were assigned per dose.
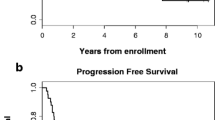
Results: Thirteen patients were recruited before trial closure due to external safety concerns regarding celecoxib. Median follow up was 17 months (95% CI 9 – >39). The highest administered dose was 400 mg bd (n=4) with one dose-limiting toxicity at this level: grade 3 rash. Five (38%) and 8(62%) patients had grade 3 non-haematological and haematological toxicities respectively. No grade 4 toxicities occurred. Radiological response rate was 54% (n=7: all CR). Six patients had resection with one pathological CR. Median progression-free and overall survival were 8.8 (95% CI 5.1 – >24.8) and 19.6 months (95% CI 7.3 – >39) respectively.
Conclusions: A MTD was not reached. The regimen was tolerable, indicating that celecoxib can be safely administered with CRT for locally advanced OC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Refaely Y, Krasna MJ (2002) Multimodality therapy for esophageal cancer. Surg Clin North Am 82:729–746
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:2241–2252
al-Sarraf M, Martz K, Herskovic A et al (1997) Progress report of combined chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with esophageal cancer: an intergroup study. J Clin Oncol 15:277–284
Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A et al (1999) Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Jama 281:1623–1627
Stahl M, Stuschke M, Lehmann N et al (2005) Chemoradiation with and without surgery in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol 23:2310–2317
Walsh TN, Noonan N, Hollywood D et al (1996) A comparison of multimodal therapy and surgery for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 335:462–467
Berger AC, Farma J, Scott WJ et al (2005) Complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal carcinoma is associated with significantly improved survival. J Clin Oncol 23:4330–4337
Williams CS, Mann M, DuBois RN (1999) The role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development. Oncogene 18:7908–7916
Shamma A, Yamamoto H, Doki Y et al (2000) Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in squamous carcinogenesis of the esophagus. Clin Cancer Res 6:1229–1238
Wilson KT, Fu S, Ramanujam KS, Meltzer SJ (1998) Increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in Barrett's esophagus and associated adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 58:2929–2934
Zimmermann KC, Sarbia M, Weber AA et al (1999) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Res 59:198–204
von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Puhringer F et al (2005) Coexpression of cyclooxygenases (COX-1, COX-2) and vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF-A, VEGF-C) in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 65:5038–5044
Souza RF, Shewmake K, Beer DG et al (2000) Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 60:5767–5772
Morgan G, Vainio H (1998) Barrett's oesophagus, oesophageal cancer and colon cancer: an explanation of the association and cancer chemopreventive potential of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Cancer Prev 7: 195–199
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT et al (2000) Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res 60:1306–1311
Sweeney CJ (2003) Why cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition plus chemotherapy? Am J Clin Oncol 26:S122–S125
Ratnasinghe D, Daschner PJ, Anver MR et al (2001) Cyclooxygenase-2, P-glycoprotein-170 and drug resistance; is chemoprevention against multidrug resistance possible? Anticancer Res 21:2141–2147
Uchida K, Schneider S, Yochim JM et al (2005) Intratumoral COX-2 gene expression is a predictive factor for colorectal cancer response to fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 11:3363–3368
Kishi K, Petersen S, Petersen C et al (2000) Preferential enhancement of tumor radioresponse by a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Cancer Res 60:1326–1331
Milas L, Kishi K, Hunter N et al (1999) Enhancement of tumor response to gamma-radiation by an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:1501–1504
Choy H, Milas L (2003) Enhancing radiotherapy with cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme inhibitors: a rational advance? J Natl Cancer Inst 95:1440–1452
Greene FL et al (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual. Springer-Verlay, New York
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Bombardier C, Laine L, Reicin A et al (2000) Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med 343:1520–1528, 1522 p following 1528
FitzGerald GA, Patrono C (2001) The coxibs, selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2. N Engl J Med 345:433–442
Silverstein FE, Faich G, Goldstein JL et al (2000) Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: A randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. Jama 284:1247–1255
Harris RC Jr (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition and renal physiology. Am J Cardiol 89:10D–17D
Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H et al (2005) Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med 352:1092–1102
Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA et al (2005) Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med 352:1071–1080
Mukherjee D, Nissen SE, Topol EJ (2001) Risk of cardiovascular events associated with selective COX-2 inhibitors. Jama 286:954–959
Lorenz M, Slaughter HS, Wescott DM et al (1999) Cyclooxygenase-2 is essential for normal recovery from 5-fluorouracil-induced myelotoxicity in mice. Exp Hematol 27:1494–1502
Leese PT, Hubbard RC, Karim A et al (2000) Effects of celecoxib, a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on platelet function in healthy adults: a randomized, controlled trial. J Clin Pharmacol 40:124–132
Govindan R, McLeod H, Mantravadi P et al (2004) Cisplatin, fluorouracil, celecoxib, and RT in resectable esophageal cancer: preliminary results. Oncology (Williston Park) 18:18–21
Enzinger PC et al (2004) Phase II trial of cisplatin, irinotecan, celecoxib and concurrent radiotherapy followed by surgery for locally advanced esophageal cancer. ASCO GI Symposium
Acknowledgments
Juliana Di Iulio for her assistance with data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This trial has been presented in part at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Symposium January 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dawson, S.J., Michael, M., Biagi, J. et al. A phase I/II trial of celecoxib with chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the treatment of patients with locally advanced oesophageal cancer. Invest New Drugs 25, 123–129 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-006-9016-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-006-9016-5