Abstract
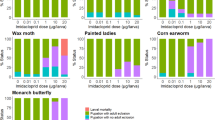
In the present study we investigated the potential relative effects of bisphenol A (BPA) and RH-5992 (tebufenozide) on the development and metamorphosis of the corn stalk borer, Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). A number of morphological and molecular factors were examined in order to identify the toxic and the endocrine-relative action of these two chemicals. We observed that BPA, RH-5992 and the combination of BPA/RH-5992 caused a developmental delay by extending the transition period between larval and pupal instars. These chemicals also reduced adult emergence and caused molting malformations during development and metamorphosis. In the corn stalk borer, BPA exhibits ecdysteroid activities in a fashion similar to that of the ecdysone agonist RH-5992. These results suggest that exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of BPA during the early stages of the corn borer’s life cycle can result in various disorders that may be a consequence of endocrine disruption. The molecular mechanism by which BPA interferes with the physiological processes was also investigated. A significant induction was observed in the expression levels of the ecdysone-induced genes SnEcR and SnUSP, after injection of BPA and RH-5992. Additionally, we found that BPA acts as a very weak agonist of ecdysteroids in Bombyx mori derived Bm5 cell lines. From these cellular and molecular assays, our results brought evidence that BPA, like RH-5992, interferes with the ecdysteroidal pathways of the lepidopteran insect species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander HC, Dill DC, Smith LW, Guiney PD, Dorn P (1988) Bisphenol A: acute aquatic toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:19e26
Andersen HR, Andersson AM, Arnold SF, Autrup H, Barfoed M, Beresford NA, Bjerregaard P, Christiansen LB, Gissel B, Hummel R, Jorgensen EB, Korsgaard B, Le Guevel R, Leffers H, McLachlan JA, Moller A, Nielsen JB, Olea N, Oles-Karasko A, Pakdel F, Pedersen KL, Perez P, Skakkeboek NE, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM, Sumpter JP, Thorpe SM, Grandjean P (1999) Comparison of short-term estrogenicity tests for identification of hormone-disrupting chemicals. Environ Health Perspect 107:89–108
Atlı E, Ünlü H (2012) Developmental and reproductive effects of bisphenol A (Bpa) in Drosophila Melanogaster. Hacettepe J Biol Chem 40:61–68
Biddinger D, Hull L, Huang H, McPheron B, Loyer M (2006) Sublethal effects of chronic exposure to tebufenozide on the development, survival and reproduction of the tufted apple bud moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J Econ Entomol 99:834–842
Colborn T, vom Saal FS, Soto AM (1993) Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ Health Perspect 101:378–384
Commission of the European Communities (1996) Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances. In: Part II; Environmental Risk Assessment. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Crain DA, Eriksen M, Iguchi T, Jobling S, Laufer H, LeBlanc GA, Guillette LJ (2007) An ecological assessment of bisphenol-A: evidence from comparative biology. Reprod Toxicol 24:225–239
Debernard S, Bozzolan F, Duportets L, Porcheron P (2001) Periodic expression of an ecdysteroid-induced nuclear receptor in a lepidopteran cell line (IAL-PID2). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:1057–1064
Dhadialla TS, Carlson GR, Le DP (1998) New insecticides with ecdysteroidal and juvenile hormone activity. Annu Rev Entomol 43:545–569
Dinan L, Bourne P, Whiting P, Dhadialla TS, Hutchinson TH (2001) Screening of environmental contaminants for ecdysteroid agonist and antagonist activity using the Drosophila melanogaster B-II cell in vitro assay. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2038
Environment Canada (2008) Screening Assessment for the Challenge: Phenol, 4,40-(1-Methylethylidene) bis-bisphenol A. Chemical Abstracts Service Registry Number 80-05-7. Gatineau, Quebec. http://www.ec.gc.ca/ese-ees/default.asp. Accessed 20 Jan 2012
Flint S, Markle T, Thompson S, Wallace E (2012) Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: a wildlife perspective. J Environ Manage 104:19e34
Gehring U (1998) Steroid hormone receptors and heat shock proteins. Vitam Horm 54:167–205
Gkouvitsas T, Kontogiannatos D, Kourti A (2008) Differential expression of two small Hsps during diapause in the corn stalk borer Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef). J Insect Physiol 54:1503–1510
Hiroi H, Tsutsumi O, Momoeda M, Takai Y, Osuga Y, Taketani Y (1999) Differential interactions of bisphenol A and 17beta-estradiol with estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and ERbeta. J Endocr 46:773–778
Izumi N, Yanagibori R, Shigeno S, Sajiki J (2008) Effects of bisphenol A on the development, growth and sex ratio of the housefly Musca domestica. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1343
Koelle MR, Talbot WS, Segraves WA, Bender MT, Cherbas P, Hogness DS (1991) The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell 67:59–77
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceutical, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999e2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36:1202e1211
Kontogiannatos D, Michail X, Kourti A (2011) Molecular characterization of an ecdysteroid inducible carboxylesterase with GQSCG motif in the corn borer, Sesamia nonagrioides. J Insect Physiol. 57:1000–1009
Kontogiannatos D, Swevers L, Maenaka K, Park EY, Iatrou K, Kourti A (2013) Functional characterization of a juvenile hormone esterase related gene in the moth Sesamia nonagrioides through RNA interference. PLoS ONE 8(9):e73834
Kumar VS, Santhi M, Krishnan M (2000) RH-5992: an ecdysone agonist on model system of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Indian J Exp al Biol 38:137–144
Lahnsteiner F, Berger B, Kletz M, Weismann T (2005) Effect of bisphenol A on maturation and quality of semen and eggs in the brown trout, Salmo trutta. Aquat Toxicol 75:213e224
Marcial HS, Hagiwara A, Snell TW (2003) Estrogenic compounds affect development of harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(12):3025e3030
Michail X, Kontogiannatos D, Syriou B, Kourti A (2012) Bisphenol-A affects the developmental progression and expression of heat-shock protein genes in the moth Sesamia nonagrioides. Ecotoxicology 21:2244–2253
Mourad AK, Saad AS, Esawy MM, Hassan SM (2004) Influence of the nonsteroidal ecdysone agonist, tebufenozide, on certain biological and physiological parameters of the cotton leaf worm, Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) in Egypt. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 69:119–139
Mu X, Rider CV, Hwang GS, Hoy H, Leblanc GA (2005) Covert signal disruption: anti-ecdysteroidal activity of bisphenol a involves cross talk between signaling pathways. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:146–152
Nakagawa Y, Minakuchi C, Ueno T (2000) Inhibition of [(3)H] ponasterone a binding by ecdysone agonists in the intact Sf-9 cell line. Steroids 65:537–542
Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Bachmann J, Oetken M, Lutz I, Kloas W, Ternes TA (2006) Bisphenol A induces superfeminization in the ramshorn snail Marisa cornuarietis (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Health Perspect 114:127e133
Oro AE, McKeown M, Evans RM (1992) The Drosophila retanoid X receptor homolog ultraspiricle functions in both female reproduction and eye morphogenesis. Development 115:449–462
Palli SR, Ladd TR, Ricci AR, Sohi SS, Retnakaran A (1997) Cloning and developmental expression of Choristoneura hormone receptor 75: a homologue of the Drosophila E75A gene. Dev Genet 20:36–46
Pineda S, Smagghe G, Schneider MI, Del Estal P, Vinuela E, Martınez AM, Budia F (2006) Toxicity and pharmacokinetics of spinosad and methoxyfenozide to Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ Entomol 35:856–864
Planello R, Martinez-Guitarte JL, Morcillo G (2008) The endocrine disruptor bisphenol A increases the expression of HSP70 and ecdysone receptor genes in the aquatic larvae of Chironomus riparius. Chemosphere 71:1870–1876
Retnakaran A, Hiruma K, Palli SR, Riddiford LM (1995) Molecular analysis of the mode of action of RH-5992, a lepidopteran-specific, non-steroidal ecdysteroid agonist. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25:109
Retnakaran A, Smith LR, Tomkins WL, Primavera M, Palli SR, Payne N (1997) Effect of RH-5992, a non-steroidal ecdysone agonist, on the spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): laboratory, greenhouse and ground spray trials. Can Entomol 129:871
Retnakaran A, Gelbic I, Sundaram M, Tomkins W, Ladd T, Primavera M, Feng Q, Arif B, Palli R, Krell P (2001) Mode of action of the ecdysone agonist tebufenozide (RH-5992), and an exclusion mechanism to explain resistance to it. Pest Manag Sci 57:951–957
Richter CA, Taylor JA, Ruhlen RL, Welshons WV, Vom Saal FS (2007) Estradiol and bisphenol A stimulate a androgen receptor and estrogen receptor gene expression in fetal mouse prostate mesenchyme cells. Environ Health Perspect 115:902–908
Schneider MI, Smagghe G, Pineda S, Vinuela E (2008) Ecological impact of four IGR insecticides in adults of Hyposoter didymator (Hym., Ichneumonidae): pharmacokinetics approach. Ecotoxicology 17:181–188
Smagghe G, Dhadialla TS, Lezzi M (2002) Comparative toxicity and ecdysone receptor affinity of non-steroidal ecdysone agonists and 20-hydroxyecdysone in Chironomus tentas. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:187–192
Sohoni P, Tyler CR, Hurd K, Caunter J, Hetheridge M, Williams T, Woods C, Evans M, Toy R, Gargas M, Sumpter JP (2001) Reproductive effects of longterm exposure to bisphenol A in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ Sci Technol 35:2917e2925
Sundaram M, Palli SR, Krell PJ, Sohi SS, Dhadialla TS, Retnakaran A (1998) Basis for selective action of a synthetic molting hormone agonist, RH-5992 on lepidopteran insects. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28:693–704
Swevers L, Cherbas L, Cherbas P, Iatrou K (1996) Bombyx EcR (BmEcR) and Bombyx USP (BmCF1) combine to form a functional ecdysone receptor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 26:217–221
Swevers L, Kravariti L, Ciolfi S, Xenou-Kokoletsi M, Ragoussis N, Smagghe G, Nakagawa Y, Mazomenos B, Iatrou K (2003) A cell-based high-throughput screening system for detecting ecdysteroid agonists and antagonists in plant extracts and libraries of synthetic compounds. FASEB J Express Article. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0627fje
Thomas HE, Stunnenberg HG, Stewart AF (1993) Heterodimerization of the Drosophila ecdysone receptor with retinoid X receptor and ultraspiracle. Nature 362:471–475
Tsitsipis JA (1984) Rearing the corn borer Sesamia nonagrioides on artificial media in the laboratory. In Proceedings, XVII international congress of entomology, Hamburg, pp 16–26 August Abstracts, 316
Vandenberg LN, Maffini MV, Sonnenschein C, Rubin BS, Soto AM (2009) Bisphenol-A and the great divide: a review of controversies in the field of endocrine disruption. Endocr Rev 30:75–95
Walkiewicz MA, Stern M (2009) Increased insulin/insulin growth factor signaling advances the onset of metamorphosis in Drosophila. PLoS One 4:e5072. dx.plos.org
Watts MM, Pascoe D, Carroll K (2003) Exposure to 17a-ethinylestradiol and bisphenol A effects on larval moulting and mouthpart structure of Chironomus riparius. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:207e215
Welshons WV, Nagel SC, vom Saal FS (2006) Large effects from small exposures. III. Endocrine mechanisms mediating effects of Bisphenol A at levels of human exposure. Endocrinology 147:S56–S69
Wing KD, Slawecki RA, Carlson GR (1988) RH-5849, a nonsteroidal ecdysone agonist: effects on larval Lepidoptera. Science 241:470–472
Yanagi M, Tsukamoto Y, Watanabe T, Kawagishi A (2006) Development of a novel lepidopteran insect control agent, chromafenozide. J Pest Sci 31:163–164
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontogiannatos, D., Swevers, L., Zakasis, G. et al. The molecular and physiological impact of bisphenol A in Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ecotoxicology 24, 356–367 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1384-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1384-6