Abstract
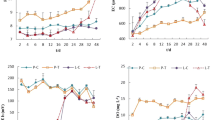
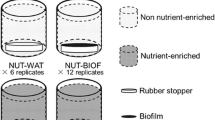
Biofilms are a key component in the nutrient removal from the water column. However, nutrient uptake by biofilms may be hampered by the occurrence of pollutants or other stressors. This study aimed: (i) to investigate the biofilm phosphorus (P) uptake capacity as a relevant process for the maintenance of fluvial water quality and (ii) to explore the sensitivity of this process to different chemical and environmental stressors. We conducted chamber experiments to test for the relevance of biofilm P uptake capacity (PUC) as a tool to detect effects of pollutants on river self-depuration. PUC was calculated by measuring P temporal decay after performing controlled P-spikes in chambers with biofilm-colonized tiles. Four different experiments were conducted to evaluate the response of PUC to: (a) several river waters from increasing polluted sites; (b) the effect of the bactericide triclosan (TCS); (c) the combined effect of TCS and grazers; and (d) the effect of TCS after a drought episode that affected the biofilms. These experiments showed that biofilms decreased their PUC along the pollution gradient. The biofilm PUC was significantly reduced after receiving high TCS concentrations, though lower TCS concentrations also affected the biofilm when this was submitted to grazing pressure. PUC decrease was induced by flow interruption which further enhanced the TCS negative effects. Overall, PUC was sensitive to the effects of pollutants like TCS as well as to the action of biological (grazing) and environmental (drought) factors. The study also showed that multiple stressors enhance the negative effects of pollutants on the PUC of biofilms. Our study values the use of biofilms’ PUC as a sensitive ecological-based tool to assess the effects of chemicals on freshwater communities and their derived functioning in river ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- PUC:
-
Phosphorus uptake capacity
- TCS:
-
Triclosan
References
Adey W, Luckett C, Jensen K (1993) Phosphorus removal from natural waters using controlled algal production. Restor Ecol 1:29–39. doi:10.1111/j.1526-100X.1993.tb00006.x
Alvarez M, Proia L, Ruggiero A et al. (2010) A comparison between pulse and constant rate additions as methods for the estimation of nutrient uptake efficiency in-streams. J Hydrol 388:273–279. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.05.006
Amalfitano S, Fazi S (2008) Recovery and quantification of bacterial cells associated with streambed sediments. J Micro Meth 75:237–243. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2008.06.004
American Public Health Association (1989) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed. APHA, Washington, DC
Barlocher F, Murdoch J H (1989) Hyporheic biofilms—a potential food source for interstitial animals. Hydrobiologia 184:61–67. doi:10.1007/BF00014302
Bothwell ML (1988) Growth rate responses of lotic periphytic diatoms to experimental phosphorus enrichment: the influence of temperature and light. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:261–270. doi:10.1139/f88-031
Bonnineau C, Guasch H, Proia L et al. (2010) Fluvial biofilms: A pertinent tool to assess β-blockers toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 96:225–233. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.10.024
Borchardt MA (1996) Nutrients. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds) Algal Ecology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 184–227
Burkholder JM, Wetzel RG, Klomparens KL (1990) Direct comparison of phosphate uptake by adnate and loosely attached microalgae within an intact biofilm matrix. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2882–2890
Cole JJ (1982) Interactions between bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 13:291–314. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.13.110182.001451
Dodds WK (2003) the role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. J Phycol 39:840–849. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.02081.x
Flemming H (1995) Sorption sites in biofilms. Water Sci Technol 32:27–33. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(96)00004-2
Ginebreda A, Muñoz I, de Alda ML et al. (2010) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in rivers: Relationships between hazard indexes and aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity indexes in the Llobregat River (NE Spain). Environ Int 36:153–162. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2009.10.003
Guasch H, Navarro E, Serra A, Sabater S (2004) Phosphate limitation influences the sensitivity to copper in periphytic algae. Freshw Biol 49:463–473. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01196.x
Guasch H, Ricart M, López-Doval J, et al. (2016) Influence of grazing on triclosan toxicity to stream periphyton. Freshw Biol. 10.1111/fwb.12797
Healey FP (1980) Slope of the monod equation as an indicator of advantage in nutrient competition. Microb Ecol 5:281–286. doi:10.2307/4250586
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Bio und Phy der Pfla 167:191–194
Kantiani L, Farré M, Asperger D, et al. (2008) Triclosan and methyl-triclosan monitoring study in the northeast of Spain using a magnetic particle enzyme immunoassay and confirmatory analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Hydrol 361:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.07.016
Köck-Schulmeyer M, Ginebreda A, González S, et al. (2012) Analysis of the occurrence and risk assessment of polar pesticides in the Llobregat River Basin (NE Spain). Chemosphere 86:8–16. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.08.034
Kuster M, López de Alda MJ, Hernando MD, et al. (2008) Analysis and occurrence of pharmaceuticals, estrogens, progestogens and polar pesticides in sewage treatment plant effluents, river water and drinking water in the Llobregat river basin (Barcelona, Spain). J Hydrol 358:112–123. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.05.030
Lawrence JR, Zhu B, Swerhone GDW, et al. (2009) Comparative microscale analysis of the effects of triclosan and triclocarban on the structure and function of river biofilm communities. Sci Total Environ 407:3307–3316. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.060
López-Doval JC, Ricart M, Guasch H, et al. (2010) Does grazing pressure modify diuron toxicity in a biofilm community?. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:955–962. doi:10.1007/s00244-009-9441-5
McAvoy DC, Schatowitz B, Jacob M, et al. (2002) Measurement of triclosan in wastewater treatment systems. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1323–1329. doi:10.1002/etc.5620210701
McMurry LM, Oethinger M, Levy SB (1998) Triclosan targets lipid synthesis. Nature 394:531–532. doi:10.1038/28970
Morin S, Proia L, Ricart M, et al. (2010) Effects of a bactericide on the structure and survival of benthic diatom communities. Vie Milieu 60:109–116
Muñoz I, Real M, Guasch H, et al. (2001) Effects of atrazine on periphyton under grazing pressure. Aquat Toxicol 55:239–249. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(01)00179-5
Osorio V, Pérez S, Ginebreda A, Barceló D (2012) Pharmaceuticals on a sewage impacted section of a Mediterranean River (Llobregat River, NE Spain) and their relationship with hydrological conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1013–1025. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0603-4
Osorio V, Proia L, Ricart M, et al. (2014) Hydrological variation modulates pharmaceutical levels and biofilm responses in a Mediterranean River. Sci Total Environ 472:1052–1061. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.069
Phan T-N, Marquis RE (2006) Triclosan inhibition of membrane enzymes and glycolysis of Streptococcus mutans in suspensions and biofilms. Can J Microbiol 52:977–983. doi:10.1139/w06-055
Pimentel D, Houser J, Preiss E, et al. (1997) Water resources: agriculture, the environment, and society. Bioscience 47:97–106. doi:10.2307/1313020. CR – Copyright © 1997 Oxford Universi
Porter KG, Feig YS (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948. doi:10.4319/lo.1980.25.5.0943
Proia L, Lupini G, Osorio V, et al. (2013a) Response of biofilm bacterial communities to antibiotic pollutants in a Mediterranean River. Chemosphere 92:1126–1135. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.063
Proia L, Morin S, Peipoch M, et al. (2011) Resistance and recovery of river biofilms receiving short pulses of Triclosan and Diuron. Sci Total Environ 409:3129–3137. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.013
Proia L, Cassió F, Pascoal C, et al. (2012) The Use of Attached Microbial Communities to Assess Ecological Risks of Pollutants in River Ecosystems: The Role of Heterotrophs. In: Guasch H, Ginebreda A, Geiszinger A (eds) Emerging and Priority Pollutants in Rivers: Bringing Science into River Management Plans. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 55–83. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-25722-3_3
Proia L, Osorio V (2013) The Effect of PhACs on Biological Communities in Rivers: Field Studies. In: Petrovic M, Barceló D, Perez S, (eds) Analysis, Removal, Effects and Risk of Pharmaceuticals in the Water Cycle Occurrence and Transformation in the Environment. Elsevier, pp 649–670. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62657-8.00018-5
Proia L, Osorio V, Soley S, et al. (2013b) Effects of pesticides and pharmaceuticals on biofilms in a highly impacted river. Environ Pollut 178:220–228. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.022
Proia L, Vilches C, Boninneau C, et al. (2013c) Drought episode modulates the response of river biofilms to triclosan. Aquat Toxicol 127:36–45. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.01.006
Pusch M, Fiebig I, Brettar H, et al. (1998) The role of micro-organisms in the ecological connectivity of running waters. Freshw Biol 40:453–495. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.1998.00372.x
Reiss R, Mackay N, Habig C, Griffin J (2002) An ecological risk assessment for triclosan in lotic systems following discharge from wastewater treatment plants in the United States. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:2483–2492. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2002)021<2483:AERAFT>2.0.CO;2
Ricart M, Barceló D, Geiszinger A, et al. (2009) Effects of low concentrations of the phenylurea herbicide diuron on biofilm algae and bacteria. Chemosphere 76:1392–1401. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.017
Ricart M, Guasch H, Barceló D, et al. (2010) Primary and complex stressors in polluted mediterranean rivers: pesticide effects on biological communities. J Hydrol 383:52–61. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.014
Rodriguez-Mozaz S, López de Alda MJ, Barceló D (2004) Monitoring of estrogens, pesticides and bisphenol A in natural waters and drinking water treatment plants by solid-phase extraction–liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1045:85–92. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.06.040
Romaní AM, Giorgi A, Acuña V, Sabater S (2004) The influence of substratum type and nutrient supply on biofilm organic matter utilization in streams. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1713–1721. doi:10.4319/lo.2004.49.5.1713
Sabaliunas D, Webb SF, Hauk A, et al. (2003) Environmental fate of Triclosan in the River Aire Basin, UK. Water Res 37:3145–3154. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00164-7
Sabater S, Guasch H, Ricart M, et al. (2007) Monitoring the effect of chemicals on biological communities. The biofilm as an interface. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1425–1434. doi:10.1007/s00216-006-1051-8
Sabater S, Guasch H, Roman A (2002) The effect of biological factors on the effciency of river bio lms in improving water quality. Hydrobiologia 149–156.
Serra A, Guasch H, Admiraal W, et al. (2010) Influence of phosphorus on copper sensitivity of fluvial periphyton: the role of chemical, physiological and community-related factors. Ecotoxicology 19:770–780. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0454-7
Stasinakis AS, Gatidou G, Mamais D, et al. (2008) Occurrence and fate of endocrine disrupters in Greek sewage treatment plants. Water Res 42:1796–1804. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.11.003
Stevenson RJ (1996) In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds.), Algal Ecology. Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Academic Press.
Steinman AD (1996) Effects of grazers on freshwater benthic algae. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds) Algal Ecology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 341–373
Stream Solute Workshop (1990) Concepts and Methods for Assessing Solute Dynamics in Stream Ecosystems. J-NABS 9:95–119. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1467445
Tilman D (1981) Tests of resource competition theory using four species of Lake Michigan algae. Ecology 62:802–815
Tixier C, Singer HP, Canonica S, Müller SR (2002) Phototransformation of triclosan in surface waters: a relevant elimination process for this widely used biocide—Laboratory studies, field measurements, and modeling. Environ Sci Technol 36:3482–3489. doi:10.1021/es025647t
Tlili A, Bérard A, Roulier J-L, et al. (2010) PO43—dependence of the tolerance of autotrophic and heterotrophic biofilm communities to copper and diuron. Aquat Toxicol 98:165–177. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.02.008
Villalaín J, Mateo CR, Aranda FJ, et al. (2001) Membranotropic effects of the antibacterial agent triclosan. Arch Biochem Biophys 390:128–136. doi:10.1006/abbi.2001.2356
Ylla I, Borrego C, Romanà AM, Sabater S (2009) Availability of glucose and light modulates the structure and function of a microbial biofilm. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:27–42. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00689.x
Acknowledgements
Lorenzo Proia was supported by the European Commission project KEYBIOEFFECTS (MRTN-CT-2006-035695). Additional funding was provided by the project SCARCE (CONSOLIDER-INGENIO CSD2009-00065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Present address: Lorenzo Proia, Ecology of Aquatic Systems, Université Libre de Bruxelles, 10 Boulevard du Triomphe. B-1050 Bruxelles
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proia, L., Romaní, A. & Sabater, S. Biofilm phosphorus uptake capacity as a tool for the assessment of pollutant effects in river ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 26, 271–282 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1761-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1761-z