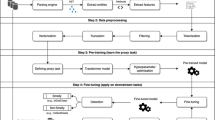
Abstract
Code clones are created when a developer duplicates a code fragment to reuse existing functionalities. Mitigating clones by refactoring them helps ease the long-term maintenance of large software systems. However, refactoring can introduce an additional cost. Prior work also suggest that refactoring all clones can be counterproductive since clones may live in a system for a short duration. Hence, it is beneficial to determine in advance whether a newly-introduced clone will be short-lived or long-lived to plan the most effective use of resources. In this work, we perform an empirical study on six open source Java systems to better understand the life expectancy of clones. We find that a large number of clones (i.e., 30% to 87%) lived in the systems for a short duration. Moreover, we find that although short-lived clones were changed more frequently than long-lived clones throughout their lifetime, short-lived clones were consistently changed with their siblings less often than long-lived clones. Furthermore, we build random forest classifiers in order to determine the life expectancy of a newly-introduced clone (i.e., whether a clone will be short-lived or long-lived). Our empirical results show that our random forest classifiers can determine the life expectancy of a newly-introduced clone with an average AUC of 0.63 to 0.92. We also find that the churn made to the methods containing a newly-introduced clone, the complexity and size of the methods containing the newly-introduced clone are highly influential in determining whether the newly-introduced clone will be short-lived. Furthermore, the size of a newly-introduced clone shares a positive relationship with the likelihood that the newly-introduced clone will be short-lived. Our results suggest that, to improve the efficiency of clone management efforts, practitioners can leverage our classifiers and insights in order to determine whether a newly-introduced clone will be short-lived or long-lived to plan the most effective use of their clone management resources in advance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Tomcat6.0, 7.0, and 8.0 are asynchronously developed in different repositories. We select Tomcat8.0 for this study since it is a long lived version.
The version control systems of the systems were accessed on April, 2017
A list of Git repositories of Apache projects is available at https://git.apache.org/
The most recent version of our studied systems are Ant v1.10.0, Camel v2.18.3, Jackrabbit v2.14.0, Maven v3.5.0, Pig v0.16.0, and Tomcat v8.0.43
The commit hash is a760df0b20425eef2820b2526baa617c81358ce4.
ln:appendix
References
Al-Ekram R, Kapser C, Holt R, Godfrey M (2005) Cloning by accident: an empirical study of source code cloning across software systems. In: Proceedings of the 4th international symposium on empirical software engineering (ISESE), pp 376–385
Baker BS (1995) On finding duplicatation and near-duplication in large software systems. In: Proceedings of the 2nd working conference on reverse engineering (WCRE), pp 86–95
Baker BS (1997) Parameterized duplication in strings: algorithms and an application to software maintenance. Journal of Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) 26(5):1343–1362
Barbour L, Khomh F, Zou Y (2011) Late propagation in software clones. In: Proceedings of the 27th international conference on software maintenance (ICSM), pp 273–282
Baxter ID, Yahin A, Moura L, Sant’Anna M, Bier L (1998) Clone detection using abstract syntax trees. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on software maintenance (ICSM), pp 368–377
Bettenburg N, Shang W, Ibrahim W, Adams B, Zou Y, Hassan AE (2009) An empirical study on inconsistent changes to code clones at release level. In: Proceedings of the 16th working conference on reverse engineering (WCRE), pp 85–94
Bettenburg N, Shang W, Ibrahim WM, Adams B, Zou Y, Hassan AE (2012) An empirical study on inconsistent changes to code clones at the release level. J Sci Comput Program 77(6):760–776
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Breiman L, Cutler A (2015) Breiman and cutler’s random forests for classification and regression. https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/
Caliński T, Harabasz J (1974) A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun Stat 3(1):1–27
Charrad M, Ghazzali N, Boiteau V, Niknafs A (2014) Nbclust : An R package for determining the relevant number of clusters in a data set. J Stat Softw 61(6):1–36
Cordy JR (2003) Comprehending reality - practical barriers to industrial adoption of software maintenance automation. In: Proceedings of the 11th international workshop on program comprehension, pp 196–205
Dang Y, Zhang D, Ge S, Chu C, Qiu Y, Xie T (2012) XIAO: tuning code clones at hands of engineers in practice. In: Proceedings of the 28th annual computer security applications conference (ACSAC), pp 369–378
Duala-Ekoko E, Robillard MP (2007) Tracking code clones in evolving software. In: Proceedings of the 29th international conference on software engineering (ICSE), pp 158–167
Ducasse S, Rieger M, Demeyer S (1999) A language independent approach for detecting duplicated code. In: Proceedings of the 15th international conference on software maintenance (ICSM), pp 109–118
Efron B (1983) Estimating the error rate of a prediction rule: Improvement on cross-validation. J Am Stat Assoc 78(382):316–331
Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1994) An introduction to the bootstrap. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fowler M, Beck K (1999) Refactoring: improving the design of existing code. Addison-Wesley Professional, Reading
Göde N (2010) Clone removal: fact or fiction?. In: Proceedings of the 4th international workshop on software clones (IWSC), pp 33–40
Göde N (2011) Clone evolution. PhD Thesis, The Universitat Bremen, Bremen
Göde N, Koschke R (2009) Incremental clone detection. In: Proceedings of the 13th conference on software maintenance and reengineering (CSMR), pp 219–228
Göde N, Koschke R (2011) Frequency and risks of changes to clones. In: Proceeding of the 33rd international conference on software engineering (ICSE), pp 311–320
Harrell FE Jr (2002) Regression modeling strategies: with application to linear models, logistic regression, and survival analysis, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Hassan AE (2008) Automated classification of change messages in open source projects. In: Proceedings of the 23rd symposium on applied computing (SAC), pp 837–841
Hata H, Mizuno O, Kikuno T (2011) Historage: fine-grained version control system for java. In: Proceedings of the 12th international workshop principles on software evolution and the 7th annual ERCIM workshop on software evolution (IWPSE-EVOL), pp 96–100
Hou D, Jablonski P, Jacob F (2009) CnP: towards an environment for the proactive management of copy-and-paste programming. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on program comprehension (ICPC), pp 238–242
Jiarpakdee J, Tantithamthavorn C, Hassan AE (2018) The impact of correlated metrics on defect models. arXiv:1801.10271
Johnson JH (1993) Identifying redundancy in source code using fingerprints. In: Proceedings of the conference of the centre for Advanced studies on collaborative research (CASCON), pp 171–183
Kamiya T, Kusumoto S, Inoue K (2002) CCFInder: a multilinguistic token-based code clone detection system for large scale source code. Trans Softw Eng (TSE) 28(28):654–670
Kapser C, Godfrey MW (2006) “Cloning considered harmful” considered harmful. In: Proceedings of the 13th working conference on reverse engineering (WCRE), pp 19–28
Kapser CJ, Godfrey MW (2008) “Cloning considered harmful” considered harmful: Patterns of cloning in software. Empir Softw Eng 13(6):645–692
Khanchouch I, Charrad M, Limam M (2015) An improved multi-SOM algorithm for determining the optimal number of clusters. J Future Comput Commun 4(3):198–202
Kim M, Bergman L, Lau T, Notkin D (2004) An ethnographic study of copy and paste programming practices in OOPL. In: Proceedings of the international symposium of empirical software engineering (ISESE), pp 83–92
Kim M, Sazawal V, Notkin D, Murphy G (2005) An empirical study of code clone genealogies. In: Proceedings of the 10th joint meeting of the European software engineering conference and the international symposium on the foundations of software engineering (ESEC/FSE), pp 187–196
Kim M, Zimmermann T, Nagappan N (2012) A field study of refactoring challenges and benefit. In: Proceedings of the 20th international symposium on the foundations of software engineering (FSE), p Article No. 50
Kim S, Whitehead J Jr, Zhang Y (2008) Classifying software changes: clean or buggy? Trans Softw Eng (TSE) 34(2):181–196
Koschke R, Bazrafshan S (2016) Software-clone rates in open-source programs written in C or C++. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on software analysis, evolution, and reengineering (SANER), pp 1–7
Krzanowski WJ, Lai YT (1988) A criterion for determining the number of groups in a data set using sum-of-squares clustering. J Biometrics 44(1):23–34
Lague B, Proulx D, Merlo EM, Mayrand J, Hudepohl J (1997) Assessing the benefits of incorporating function clone detection in a development process. In: Proceedings international conference on software maintenance (ICSM), pp 314–321
Li Z, Lu S, Myagmar S, Zhou Y (2006) CP- miner: finding copy-paste and related bugs in large-scale software code. Trans Softw Eng 32(3):176–192
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2(3):18–22
Lopes CV, Maj P, Martins P, Saini V, Yang D, Zitny J, Sajnani H, Vitek J (2017) DéjàVu: A map of code duplicates on GitHub. In: Proceedings of the object-oriented programming, systems, languages & applications (OOPSLA), pp 1–28
Macbeth G, Razumiejczyk E, Ledesma RD (2011) Cliff’s delta calculator: a non-parametric effect size program for two groups of observations. Universitas Psychologica 10:545–555
Marriott FHC (1971) Practical problems in a method of cluster analysis. Biometrics 27(3):501–514
Mockus A, Votta LG (2000) Identifying reasons for software changes using historic databases. In: Proceedings of the 16th international conference on software maintainance (ICSM), pp 120–130
Monden A, Nakae D, Kamiya T, Sato Si, Matsumoto Ki (2002) Software quality analysis by code clones in industrial legacy software. In: Proceeding of the 8th symposium on software metrics (METRICS), pp 87–94
Nicodemus KK, Malley JD, Strobl C, Ziegler A (2010) The behaviour of random forest permutation-based variable importance measures under predictor correlation. BMC Bioinforma 11(1):110–124
Ragkhitwetsagul C, Krinke J, Clark D (2017) A comparison of code similarity analysers. J Empir Softw Eng (EMSE) 23(4):2464–2519
Rattan D, Bhatia R, Singh M (2013) Software clone detection: a systematic review, vol 55
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, Müller M, Siegert S (2014) Display and Analyze ROC Curves
Romano J, Kromrey JD, Coraggio J, Skowronek J (2006) Appropriate statistics for ordinal level data: should we really be using t-test and Cohen’s d for evaluating group differences on the NSSE and other surveys?. In: The annual meeting of the Florida association of institutional research (FAIR), pp 1–33
Roy CK, Zibran MF, Koschke R (2014) The vision of software clone management: past, present, and future. In: Proceedings of the joint European conference on software maintenance and reengineering and the working conference on reverse engineering (CSMR-WCRE), pp 18–33
Saha RK, Asaduzzaman M, Zibran MF, Roy CK, Schneider KA (2010) Evaluating code clone genealogies at release level: an empirical study. In: Proceedings of the 10th source code analysis and manipulation (SCAM), pp 87–96
Saha RK, Roy CK, Schneider KA (2011) An automatic framework for extracting and classifying near-miss clone genealogies. In: Proceedings of the 27th international conference on software maintenance (ICSM), pp 293–302
Saini V, Sajnani H, Lopes C (2016) Comparing quality metrics for cloned and non cloned java methods : A large scale empirical study. In: Proceedings of the international conference on software maintenance and evolution (ICSME), pp 256–266
Scott AJ, Knott M (1974) A cluster analysis method for grouping means in the analysis of variance. Biometrics 30(3):507–512
Scott AJ, Symons MJ (1971) Clustering methods based on likelihood ratio criteria. Biometrics 27(2):387–397
Silva D, Tsantalis N, Valente MT (2016) Why we refactor? Confessions of github contributors. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGSOFT international symposium on foundations of software engineering, pp 858–870
Svajlenko J, Roy CK (2014) Evaluating modern clone detection tools. In: Proceedings of the 30th international conference on software maintenance and evolution (ICSME), pp 321–330
Tantithamthavorn C (2017) The Scott-Knott Effect Size Difference (ESD) Test version 2.0.2. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ScottKnottESD/ScottKnottESD.pdf
Tantithamthavorn C, Hassan AE (2018) An experience report on defect modelling in practice: Pitfalls and challenges. In: Proceedings of the international conference on software engineering: software engineering in practice track (ICSE-SEIP’18), p To Appear
Tantithamthavorn C, McIntosh S, Hassan AE, Ki Matsumoto (2017) An empirical comparison of model validation techniques for defect prediction models. Trans Softw Eng (TSE) 43(1):1–18
Tantithamthavorn C, Hassan AE, Matsumoto K (2018) The impact of class rebalancing techniques on the performance and interpretation of defect prediction models. arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1801.10269
Thongtanunam P, McIntosh S, Hassan AE, Iida H (2017) Review participation in modern code review. Empir Softw Eng (EMSE) 22(2):768–817
Thummalapenta S, Cerulo L, Aversano L, Penta MD (2010) An empirical study on the maintenance of source code clones. Empir Softw Eng (EMSE) 15(1):1–34
Tsantalis N, Mansouri M, M-Eshkevari L, Mazinanian D, Dig D (2018) Accurate and efficient refactoring detection in commit history. In: Proceedings of the 40th international conference on software engineering (ICSE), p to appear
Wagstaff K, Cardie C, Rogers S, Schroedl S (2001) Constrained K-means clustering with background knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on machine learning, pp 577–584
Wang W, Godfrey MW (2014) Recommending clones for refactoring using design, context, and history. In: Proceedings of the 30th international conference on software maintenance and evolution (ICSME), pp 331–340
WS S (1983) SAS technical report A-108, cubic clustering criterion. Tech. Rep. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Xie S, Khomh F, Zou Y, Keivanloo I (2014) An empirical study on the fault-proneness of clone migration in clone genealogies. In: Proceedings of the international conference on software maintenance, reengineering and reverse engineering (CSMR-WCRE), pp 94–103
Yun Lin, Xing Z, Xue Y, Liu Y, Peng X, Sun J, Zhao W (2014) Detecting differences across multiple instances of code clones. In: Proceedings of the 36th international conference on software engineering (ICSE), pp 164–174
Zhang G, Peng X, Xing Z, Zhao W (2012) Cloning practices: why developers clone and what can be changed. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on software maintenance (ICSM), pp 285–294
Zhang G, Peng X, Xing Z, Jiang S, Wang H, Zhao W (2013) Towards contextual and on-demand code clone management by continuous monitoring. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on automated software engineering (ASE), pp 497–507
Zibran MF, Saha RK, Roy CK, Schneider KA (2013) Genealogical insights into the facts and fictions of clone removal. SIGAPP Applied Computing Review 13(4):30–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Tim Menzies
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thongtanunam, P., Shang, W. & Hassan, A.E. Will this clone be short-lived? Towards a better understanding of the characteristics of short-lived clones. Empir Software Eng 24, 937–972 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-018-9645-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-018-9645-2