Abstract
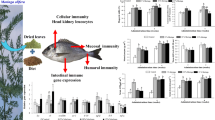
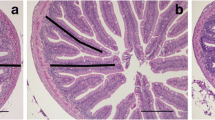
The effect of dietary grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extract (GSE) on growth performance and mucosal immune parameters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry was studied. Fish (1.3 g mean weight) were randomly distributed in nine tanks (15 fish per tank) and fed diets containing GSE at 0 (control), 100, and 200 mg kg−1for 60 days. The results showed that growth parameters were enhanced in both treatment groups compared to the control group. Histological examination of fish skin showed higher epidermis thickness, goblet cell density, and volume density in the GSE groups compared to the values of the control group. Furthermore, the villus height, goblet cell density, and intraepithelial lymphocytes were increased in the fish intestine in those fish fed GSE, with respect to control fish. Feeding fish with low dose of GSE (100 mg kg−1) up-regulated the expression of some immune-relevant genes, including complement component 3 (C3), lysozyme (Lys), omDB-3, interferon gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in different mucosal tissues. However, feeding fish the high dose of GSE (200 mg kg−1) mostly enhanced expression of these genes in the skin. Besides, skin mucus of fish fed GSE showed bactericidal activity against Yersinia ruckeri. It was concluded that GSE, especially at 100 mg kg−1, modulates the growth performance and mucosal immunity of rainbow trout.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarike ED, Kuebutornye FKA, Jian J, Tang J, Lu Y, Cai J (2018) Influences of immunostimulants on phagocytes in cultured fish: a mini review. Rev Aquac 11:1219–1227. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12288
Abelli L, Picchietti S, Romano NO, Mastrolia L, Scapigliati G (1997) Immunohistochemistry of gut associated lymphoid tissue of the sea bass Dicentrachus labrax (L.). Fish Shelfish Immunol 7:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1006/fsim.1996.0079
Amiot MJ, Riva C, Vinet A (2016) Effects of dietary polyphenols on metabolic syndrome features in humans: a systematic review. Obes Rev 17:573–586. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12409
Arciuli M, Fiocco D, Fontana S, Arena MP, Frassanito MA, Gallone A (2017) Administration of a polyphenol-enriched feed to farmed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): kidney melanomacrophages response. Fish Shelfish Immunol 68:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.07.043
Arslan G, Sönmez AY, Yanik T (2018) Effects of grape Vitis vinifera seed oil supplementation on growth, survival, fatty acid profiles, antioxidant contents and blood parameters in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquac Res 49:2256–2266. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13686
Banan Khoajasteh SM, Sheikhzadeh F, Mohammadnejad D, Azami A (2009) Histological, histochemical and ultrastructural study of the intestine of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). World Appl Sci J 6:1525–1531
Bibi S, Kang Y, Yang G, Zhu MJ (2016) Grape seed extract improves small intestinal health through suppressing inflammation and regulating alkaline phosphatase in IL-10-deficient mice. J Funct Foods 20:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2015.10.021
Biswas G, Korenaga H, Nagamine R, Takayama H, Kawahara S, Takeda S, Kikuchi Y, Dashnyam B, Kono T, Sakai M (2013) Cytokine responses in the Japanese pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) head kidney cells induced with heat-killed probiotics isolated from the Mongolian dairy products. Fish Shelfish Immunol 34:1170–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.01.024
Boshra H, Li J, Sunyer JO (2006) Recent advances on the complement system of teleost fish. Fish Shelfish Immunol 20:239–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.04.004
Bruce TJ, Brown ML (2017) A review of immune system components, cytokines, and immunostimulants in cultured finfish species. Open J Anim Sci 7:267–288. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojas.2017.73021
Caipang CMA, Lazado CC (2015) Nutritional impacts on fish mucosa: immunostimulants, pre- and probiotics. Mucosal health in aquaculture by Beck BH, Peatman E. Academic Press, United States. 211-272.
Casadei E, Bird S, González Vecino JL, Wadsworth S, Secombes CJ (2013) The effect of peptidoglycan enriched diets on antimicrobial peptide gene expression in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shelfish Immunol 34:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.11.027
Cerezuela R, Fumanal M, Tapia-Paniagua ST, Meseguer J, Morinigo MA, Esteban MA (2012) Histological alterations and microbial ecology of the intestine in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata. L.) fed dietary probioticsand microalgae. Cell Tissue Res 350:477–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-012-1495-4
Chen RN, Su YQ, Wang J, Liu M, Qiao Y, Mao Y, Ke QZ, Han KH, Zheng WQ, Zhang JS, Wu CW (2015) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of interferon-gamma in the large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Fish Shelfish Immunol 46:596–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.07.008
Cruz TMP, Moretti DB, Nordi WM, Cyrino JEP, Machado-Neto R (2017) Dietary lyophilized colostrum alters distribution of goblet cells and the intestinal epithelium of Piaractus mesopotamicus. Aquaculture 468:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.10.03
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Esteban MA (2018) Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Rev Aquac 10:950–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12209
Duong DN, Qin JG, Harris JO, Hoang TH, Bansemer MS, Currie KL, Phan-Thien KY, Dowell A, Stone DAJ (2016) Effects of dietary grape seed extract, green tea extract, peanut extract and vitamin C supplementation on metabolism and survival of greenlip abalone (Haliotis laevigata Donovan) cultured at high temperature. Aquaculture 464:364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.07.011
Enes P, Pérez-Jiménez A, Peres H, Couto A, Pousão-Ferreira P, Oliva-Teles A (2012) Oxidative status and gut morphology of white sea bream, Diplodus sargus fed soluble non-starch polysaccharide supplemented diets. Aquaculture 358-359:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.06.020
Estensoro I, Redondo MJ, Salesa B, Kausik S, Pérez-Sánchez J, Sitjà-Bobadilla A (2012) Effect of nutrition and Enteromyxum leei infection on gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata intestinal carbohydrate distribution. Dis Aquat Org 100:29–42. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02486
Evenhuis JP, Cleveland BM (2012) Modulation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) intestinal immune gene expression following bacterial challenge. Vet. Immunol Immunopathol 146:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2012.01.008
Galino-Villegas J, Mulero I, García-Alcazar A, Muñoz I, Peñalver-Mellado M, Streitenberger S, Scapigliati G, Meseguer J, Mulero V (2013) Recombinant TNFα as oral vaccine adjuvant protects European sea bass against vibriosis: insights into the role of the CCL25/CCR9 axis. Fish Shelfish Immunol 35:1260–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.07.046
Gomez D, Sunyer JO, Salinas I (2013) The mucosal immune system of fish: the evolution of tolerating commensals while fighting pathogens. Fish Shelfish Immunol 35:1729–1739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.09.032
Guerra RR, Santos NP, Cecarelli P, Mangetti AJ, Silva JRMC, Hernandez-Blazquez FJ (2006) Stratum adiposum, a special structure of the African catfish skin (Clarias gariepinus, Burchell 1822). Anat Histol Embryol 35:144–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0264.2005.00614.x
Hamidian G, Zirak K, Sheikhzadeh N, Khani Oushani A, Shabanzadeh S, Divband B (2018) Intestinal histology and stereology in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) administrated with nanochitosan/zeolite and chitosan/zeolite composites. Aquac Res 49:1803–1815. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13634
Han M, Song P, Huang C, Rezaei A, Farrar S, Brown MA, Ma X (2016) Dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins (GSPs) improve weaned intestinal microbiota and mucosal barrier using a piglet model. Oncotarget 7:80313–80326. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13450
Hasan MT, Jang WJ, Lee JM, Lee BJ, Hur SW, Lim SG, Kim KW, Han HS, Kong IS (2019) Effects of immunostimulants, prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, and potentially immunoreactive feed additives on olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus): A review. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 27:417–437. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2019.1622510
Heidarieh M, Mirvaghefi AR, Sepah A, Sheikhzadeh N, Shahbazfar AA, Akbari M (2013) Effects of dietary aloe vera on growth performance, skin and gastrointestine morphology in Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 13:367–373. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v13_2_20
Heidarieh M, Diallo A, Moodi S, Taghinejad V, Akbari M, Monfaredan A (2015) Gene expression analysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skin: immunological responses to radiovaccine against Ichthyophthirius multifliis. Rev Med Vet 166:233–242. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.4019.8889
Jaafar RM, Skov J, Kania PW, Buchmann K (2011) Dose dependent effects of dietary immunostimulants on rainbow trout immune parameters and susceptibility to the parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. J Aquac Res Dev S3:001. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.S3-001
Ji L, Sun G, Li J, Wang Y, Du Y, Li X, Liu Y (2017) Effect of dietary b-glucan on growth, survival and regulation of immune processes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) infected by Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish Shelfish Immunol 64:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.03.015
Kato K, Yamamoto M, Peerapon K, Fukada H, Biswas A, Yamamoto S, Takii K, Miyashita S (2014) Effects of dietary taurine levels on epidermal thickness and scale loss in red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquac Res 45:1818–1824. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12130
Kesbiç OS, Yigit M (2019) Structural and chemical changes of grape seed extract after thermal processing and its use in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets as an organic feed supplement. Aquaculture 503:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.01.021
Koshio S (2016) Immunotherapies targeting fish mucosal immunity – current knowledge and future perspectives. Front Immunol 6:643. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00643
Kumar G, Hummel K, Razzazi-Fazeli E, El-Matbouli M (2019) Modulation of posterior intestinal mucosal proteome in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after Yersinia ruckeri infection. Vet Res 50(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2016.03.014
Lazado CC, Marlowe C, Caipang A (2014) Mucosal immunity and probiotics in fish. Fish Shelfish Immunol 39:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.04.015
Liu YZ, Cao YG, Ye JQ, Wang WG, Song KJ, Wang XL, Wang CH, Li RT, Deng XM (2010) Immunomodulatory effects of proanthocyanidin A-1 derived in vitro from Rhododendron spiciferum. Fitoterapia 81:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2009.08.005
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆Ct method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Machado-Neto R, Pontin MCF, Nordi WM, Lima AL, Moretti DB (2013) Goblet cell mucin distribution in the small intestine of newborn goat kids fed lyophilized bovine colostrum. Livest Sci 157:125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2013.06.033
Makela V, Korhonen LK, Lilius G (1971) Carbohydrate-rich compounds in the colonic mucosa of man. Histochemical characteristics of normal and adenomatous colonic mucosa. Cancer 27:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(197101)27:1<120
Martin SA, Dehler CE, Król E (2016) Transcriptomic responses in the fish intestine. Dev Comp Immunol 64:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2016.03.014
Menaa F, Menaa A, Treton J (2014) Polyphenols against skin aging. In: Preedy RR, Zibadi VR, Watson S (eds) Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease. Academic Press, Elsevier, San Diego, pp 819–830
Mousavi S, Sheikhzadeh N, Tayefi-Nasrabadi H, Alizadeh Salteh S, Khani Oushani A, Firouzamandi M, Mardani K (2020) Administration of Grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extract to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) modulates growth performance, some biochemical parameters, and antioxidant-relevant gene expression. Fish Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00716-4
Nassiri-Asl N, Hosseinzadeh H (2016) Review of the pharmacological effects of Vitis vinifera (Grape) and its bioactive constituents: an update. Phytother Res 30:1392–1403. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2761
Nawad A, Javaid AB, Irshad S, Hoseinifar SH, Xiong H The functionality of prebiotics as immunostimulant: evidences from trials on terrestrial and aquatic animals. Fish Shelfish Immunol 76:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.03.004
Ngamkala S, Futami K, Endo M, Maita M, Katagiri T (2010) Immunological effects of glucan and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, a probiotic bacterium, on Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus intestine with oral Aeromonas challenges. Fish Sci 76:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-010-0280-0
Nichols JA, Katiyar SK (2010) Skin photoprotection by natural polyphenols: anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and dna repair mechanisms. Arch Dermatol Res 302:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-009-1001-3
Nowshehri JA, Bhat Z, Shah MY (2015) Blessings in disguise: bio-functional benefits of grape seed extracts. Food Res Int 77:333–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.08.026
Oteiza PI, Fraga CG, Mills DA, Taft DH (2018) Flavonoids and the gastrointestinal tract: local and systemic effects. Mol Asp Med 61:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2018.01.001
Panigrahi A, Viswanath K, Satoh S (2011) Real-time quantification of immune gene expression in rainbow trout fed different forms of probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Aquac Res 1042:906–917. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02633.x
Peng S, Chen L, Qin JG, Hou J, Yu N, Long Z, Li E, Ye J (2009) Effects of dietary vitamin E supplementation on growth performance, lipid peroxidation and tissue fatty acid composition of black sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegeli) fed oxidized fish oil. Aquac Nutr 15:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00657.x
Rajanbabu V, Chen JY (2011) Applications of antimicrobial peptides from fish and perspectives for the future. Peptides 32:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.11.005
Ringø E, Olsen RE, Mayhew TM, Myklebust R (2003) Electron microscopy of the intestinal microflora of fish. Aquaculture 227:395–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2003.05.001
Ringø E, Olsen RE, Vecino JLG, Wadsworth S, Song SK (2012) Use of immunostimulants and nucleotides in aquaculture: a review. J Marine Sci Res Dev 1:104. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9910.1000104
Safari R, Hoseinifar SH, Kavandi M (2016) Modulation of antioxidant defense and immune response in zebra fish (Danio rerio) using dietary sodium propionate. Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1733–1739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0253-z
Salinas I, Parra D (2015) Fish mucosal immunity: intestine. In: Beck B, Peatman E (eds) Mucosal health in aquaculture. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 135–170
Shabir U, Ali S, Magray AR, Ganai BA, Firdous P, Hassan T, Nazir R (2018) Fish antimicrobial peptides (AMP's) as essential and promising molecular therapeutic agents: a review. Microb Pathog 114:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.11.039
Sheikhzadeh N, Karimi Pashaki A, Nofouzi K, Heidarieh M, Tayefi-Nasrabadi H (2012) Effects of dietary ergosan on cutaneous mucosal immune response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shelfish Immunol 32:407–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2011.11.028
Sheikhzadeh N, Mousavi S, Hamidian G, Firouzamandi M, Khani Oushani A, Mardani (2019) Role of dietary Spirulina platensis in improving mucosal immune responses and disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 510:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.05.009
Sitjà-bobadilla A, Peña-Llopis S, Gómez-Requeni P, Médale F, Kaushik S, Pérez-Sánchez J (2005) Effect of fish meal replacement by plant protein sources on non-specific defence mechanisms and oxidative stress in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 249:387–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.03.031
Song SK, Bo RB, Kim D, Park J, Jungjoon K, Hyun DK, Ringø E (2014) Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Fish Shelfish Immunol 40:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.06.016
Standen BT, Rawling MD, Davies SJ, Castex M, Foey A, Gioacchini G, Carnevali O, Merrifield DL (2013) Probiotic P. acidilactici modulates both localised intestinal-and peripheral-immunity in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shelfish Immunol 35:1097–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.07.018
Talbot AT, Pottinger TG, Smith TJ, Cairns MT (2009) Acute phase gene expression in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after exposure to a confinement stressor: a comparison of pooled and individual data. Fish Shelfish Immunol 27:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.05.016
Tong H, Song X, Sun X, Sun G, Du F (2011) Immunomodulatory and antitumor activities of grape seed proanthocyanidins. J Agric Food Chem 59:11543–11547. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf203170k
Torrecillas S, Makol A, Caballero MJ, Montero D, Ginés R, Sweetman J, Izquierdo MS (2011) Improved feed utilization, intestinal mucus production and immune parameters in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed mannan oligosaccharides (MOS). Aquac Nutr 17:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00730.x
Viveros A, Chamorro S, Pizarro M, Arija I, Centeno C, Brenes A (2011) Effects of dietary polyphenol-rich grape products on intestinal microflora and gut morphology in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 90:566–578. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2010-00889
Wang JX, Peng KM (2008) Developmental morphology of the small intestine of African ostrich chicks. Poult Sci 87:2629–2635. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2008-00163
Xia EQ, Deng GF, Guo YJ, Li HB (2010) Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int J Mol Sci 11:622–646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11020622
Xu DH, Moreira GSA, Shoemaker CA, Zhang D, Beck BH (2017) Expression of immune genes in systemic and mucosal immune tissues of channel catfish vaccinated with live theronts of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shelfish Immunol 66:540–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.051
Yamakoshi J, Tokutake S, Kikuchi M, Kubota Y, Konishi H, Mitsuoka T (2001) Effect of proanthocyanidin-rich extract from grape seeds on human fecal flora and fecal odor. Microb Ecol Health Dis 13:25–31. https://doi.org/10.3402/mehd.v13i1.7996
Yang G, Wang H, Kang Y, Zhu MJ (2014) Grape seed extract improves epithelial structure and suppresses inflammation in ileum of IL-10-deficient mice. Food Funct 5:2558–2563. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4fo00451e
Zhai SW, Lu JJ, Chen XH (2014) Effects of dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins on growth performance, some serum biochemical parameters and body composition of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. Ital J Anim Sci 13:536–540. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2014.3357
Zhang JX, Guo LY, Feng L, Jiang WD, Kuang SY, Liu Y, Hu K, Jiang J, Li SH, Tang L, Zhou XQ (2013) Soybean b-Conglycinin induces inflammation and oxidation and causes dysfunction of intestinal digestion and absorption in fish. PLoS One 8:e58115. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058115
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Funding
The authors are thankful to the Research affairs of the University of Tabriz for funding this project. This work was partly supported by the Fundación Seneca de la Región de Murcia (Grupo de Excelencia grant no. 19883/GERM/15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiment: SM, NS, MAE. Carried out the feeding trial and sampling: AKO, PS. Performed the molecular experiment: MF, SM, NS. Carried out the histological studies: GH. Analyzed all the data: KM. Wrote and revised the manuscript: NS, MAE, SM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experiments in this study were carried out according to the guidelines for the care of experimental animals that are approved by the ethical committee of the University of Tabriz.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Dietary grape seed extract (GSE) could improve the growth performance in rainbow trout.
• GSE could alter histological structure in rainbow trout mucosal tissues.
• Up-regulated the expression of some immune-relevant genes in different mucosal tissues were shown.
• Skin mucus in treatment groups showed antibacterial activity against Yersinia ruckeri.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 618 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, S., Sheikhzadeh, N., Hamidian, G. et al. Changes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) growth and mucosal immune parameters after dietary administration of grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extract. Fish Physiol Biochem 47, 547–563 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-00930-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-00930-z