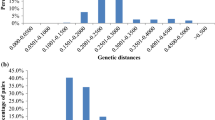
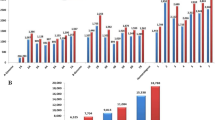
Abstract
Despite a large number of Aegilops L. species and their diversity in Azerbaijan, a majority of this genetic material has not been characterized at molecular levels. The current study has implemented DArTseq technology to evaluate genetic diversity among 150 accessions of different Aegilops species from Azerbaijan. A total of 61,574 SilicoDArTseq and 30,433 SNP markers were used to assess genetic diversity in Aegilops species. Genetic diversity was measured using Shannon’s genetic diversity index, which was equal to 0.852. Dendrograms were built to establish the relationship among Aegilops species. Both the DArTseq and SNP markers could completely segregate the U genome species from those with D genome with high confidence and allowed assigning most species to separate subclusters. The pattern of clustering within the Aegilops tauschii Coss. to certain extent was related to their geographical regions. Genetic structure among the 150 Aegilops accessions was similar with the cluster analysis. Two groups were identified in the studied population, which were exactly corresponded to two clusters in the dendrogram. Principal coordinate analysis confirmed sub-grouping obtained by cluster analysis. The first two principal coordinates explained 82.34% of the total variation. The study reported a sufficient level of genetic diversity of Aegilops from different eco-geographical regions of Azerbaijan, which can be very useful for their conservation and management, as well as for profitable diversifying the gene pool of hexaploid wheat.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alnaddaf LM, Moualla MY, Haider N (2012) The genetic relationships among Aegilops L. and Triticum L. species. Asian J Agr Sci 4(5):352–367
Aminov N, Aliyeva A (2012) The genetic interactions between Aegilops L. and Triticum L. genera. Elm, Baku
Amri A, Nawar M, Shehadeh A, Piggin J, Maxted N, Gill B (2016) Ex situ and in situ conservation efforts for Aegilops and wild Triticum species. In: Bonjean AP, Angus WJ (eds) The world wheat book: a history of wheat breeding, vol 3. Lavoisier, Paris, pp 1–48
Badaeva ED, Amosova AV, Muravenko OV, Samatadze TE, Chikida NN, Zelenin AV, Friebe B, Gill BS (2002) Genome differentiation in Aegilops. 3. Evolution of the D-genome cluster. Plant Syst Evol 231:163–190
Baloch FS, Alsaleh A, Shahid MQ, Çiftçi V, de Miera LES, Aasim M, Nadeem MA, Aktaş H, Özkan H, Hatipoğlu R (2017) A whole genome DArTseq and SNP analysis for genetic diversity assessment in durum wheat from central fertile crescent. PLoS ONE 12(1):e0167821
Baum BR, Edwards T, Johnson DA (2009) Phylogenetic relationships among diploid Aegilops species inferred from 5S rDNA units. Mol Phylogenet Evol 53(1):34–44
Bordbar F, Rahiminejad MR, Saeidi H, Blattner FR (2011) Phylogeny and genetic diversity of D-genome species of Aegilops and Triticum (Triticeae, Poaceae) from Iran based on microsatellites, ITS, and trnL-F. Plant Syst Evol 291(1–2):117–131
Caldwell K, Dvorak J, Lagudah ES, Akhunov E, Luo M-C, Wolters P, Powell W (2004) Sequence polymorphism in polyploid wheat and their D genome diploid ancestor. Genetics 167:941–947
Castillo A, Ramírez MC, Martín AC, Kilian A, Martín A, Atienza SG (2013) High-throughput genotyping of wheat-barley amphiploids utilizing diversity array technology (DArT). BMC Plant Biol 13(1):87–97
Chhuneja P, Dhaliwal HS, Bains NS, Singh K (2006) Aegilops kotschyi and Aegilops tauschii as sources for higher levels of grain iron and zinc. Plant Breed 125(5):529–531
Cui F, Fan X, Zhao C, Zhang W, Chen M, Ji J, Li J (2014) A novel genetic map of wheat: utility for mapping QTL for yield under different nitrogen treatments. BMC Genet 15(1):57
Dvorak J, Luo MC, Yang ZL (1998) Genetic evidence on the origin of Triticum aestivum L. In: Damania AB, Valkoun J, Willcox G, Qualset CO (eds) The origins of agriculture and crop domestication, proceedings of Harlan symposium. ICARDA, Aleppo, pp 235–251
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2014) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Farooq S, Farooq EA (2001) Co-existence of salt and drought tolerance in Triticeae. Hereditas 135:205–210
Fu YB, Somers DJ (2009) Genome-wide reduction of genetic diversity in wheat breeding. Crop Sci 49(1):161–168
Gandhi HT, Vales MI, Watson CJ, Mallory-Smith CA, Mori N, Rehman M, Zemetra RS, Riera-Lizarazu O (2005) Chloroplast and nuclear microsatellite analysis of Aegilops cylindrica. Theor Appl Genet 111(3):561–572
Gill BS, Friebe B, Raupp WJ, Wilson DL, Cox TS, Sears RG, Brown-Guedira GL, Fritz AK (2006) Wheat genetics resource center: the first 25 years. Adv Agron 89:73–136
Gong HY, Liu AH, Wang JB (2006) Genomic evolutionary changes in Aegilops allopolyploids revealed by ISSR markers. Acta Phytotax Sin 44:286–295
Goryunova SV, Kochieva EZ, Chikida NN, Pukhalskyi VA (2004) Phylogenetic relationships and intraspecific variation of D-Genome Aegilops L. as revealed by RAPD analysis. Russ J Genet 40:515–523
Grzebelus D, Iorizzo M, Senalik D, Ellison S, Cavagnaro P, Macko-Podgorni A, Heller-Uszynska K, Kilian A, Nothnagel T, Allender C, Simon PW (2014) Diversity, genetic mapping, and signatures of domestication in the carrot (Daucus carota L) genome, as revealed by Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) markers. Mol Breed 33(3):625–637
Hammer K (1980) Vorarbeiten zur monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzensortimenten: Aegilops L. Kulturpflanze 28:33–180
Hammer K, Laghetti G (2005) Genetic erosion-examples from Italy 1, 2. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52(5):629–634
Huang S, Sirikhachornkit A, Su X, Faris J, Gill B, Haselkorn R, Gornicki P (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Nat Acad Sci 99(12):8133–8138
Jaccoud D, Peng K, Feinstein D, Kilian A (2001) Diversity arrays: a solid state technology for sequence information independent genotyping. Nucleic Acids Res 29(4):E25
Kilian B, Özkan H, Deusch O, Effgen S, Brandolini A, Kohl J, Martin W, Salamini F (2006) Independent wheat B and G genome origins in outcrossing Aegilops progenitor haplotypes. Mol Biol Evol 24(1):217–227
Kilian B, Mammen K, Millet E, Sharma R, Graner A, Salamini F, Hammer K, Özkan H (2011) Aegilops. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources: cereals. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–76
Lelley T, Stachel M, Grausgruber H, Vollmann J (2000) Analysis of relationships between Aegilops tauschii and the D-genome of wheat utilizing microsatellites. Genome 43:661–668
Luikart G, England PR, Tallmon D, Jordan S, Taberlet P (2003) The power and promise of population genomics: from genotyping to genome typing. Nat Rev Genet 4(12):981
Naghavi MR, Aghaei MJ, Taleei AR, Omidi M, Hassani ME (2008) Genetic diversity of hexaploid wheat and three Aegilops species using microsatellite markers. https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/bitstream/2123/3231/1/P028.pdf
Okuno K, Ebana K, Noov B, Yoshida H (1998) Genetic diversity of Central Asian and north Caucasian Aegilops species as revealed by RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 45(4):389–394
Pacheco A, Alvarado G, Rodriguez F, Burgueno J (2016) BIO-R (Biodiversity analysis with R for Windows) Version 1.0.1, hdl:11529/10820, CIMMYT Research Data and Software Repository Network, V6
Pester TA, Ward SM, Fenwick AL, Westra P, Nissen SJ (2003) Genetic diversity of jointed goatgrass (Aegilops cylindrica) determined with RAPD and AFLP markers. Weed Sci 51:287–293
Pestsova E, Korzun V, Goncharov NP, Hammer K, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2000) Microsatellite analysis of Aegilops tauschii germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 101(1):100–106
Petersen G, Seberg O, Yde M, Berthelsen K (2006) Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum and Aegilops and evidence for the origin of the A, B, and D genomes of common wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39(1):70–82
Pour-Aboughadareh A, Ahmadi J, Mehrabi AA, Etminan A, Moghaddam M (2018) Insight into the genetic variability analysis and relationships among some Aegilops and Triticum species, as genome progenitors of bread wheat, using SCoT markers. Plant Biosyst 152:694–703
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genet 155(2):945–959
Queen RA, Gribbon BM, James C, Jack P, Flavell AJ (2004) Retrotransposon-based molecular markers for linkage and genetic diversity analysis in wheat. Mol Gen Genom 271:91–97
Raman H, Dalton-Morgan J, Diffey S, Raman R, Alamery S, Edwards D, Batley J (2014) SNP markers-based map construction and genome-wide linkage analysis in Brassica napus. Plant Biotechnol J 12(7):851–860
Ren J, Sun D, Chen L, You FM, Wang J, Peng Y, Nevo E, Sun D, Luo MC, Peng J (2013) Genetic diversity revealed by single nucleotide polymorphism markers in a worldwide germplasm collection of durum wheat. Int J Mol Sci 14(4):7061–7088
Sansaloni C, Petroli C, Jaccoud D, Carling J, Detering F, Grattapaglia D, Kilian A (2011) Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) and next-generation sequencing combined: genome-wide, high throughput, highly informative genotyping for molecular breeding of Eucalyptus. BMC Proc 5(Suppl 7):P54
Sears ER (1956) The transfer of leaf rust resistance from Aegilops umbellulata to wheat. Brookhaven Symp Biol 9:1–22
Sharma M, Nagavardhini A, Thudi M, Ghosh R, Pande S, Varshney RK (2014) Development of DArT markers and assessment of diversity in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceris, wilt pathogen of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). BMC Genom 15(1):454
Singh RP, Hodson DP, Jin Y, Huerta-Espino J, Kinyua MG, Wanyera R, Njau P, Ward RW (2006) Current status, likely migration and strategies to mitigate the threat to wheat production from race Ug99 (TTKS) of stem rust pathogen. CAB Rev Perspect Agric Vet Sci Nutr Nat Resour 1(54):1–3
Sliai AM, Amer SA (2013) Molecular relationships among different Serbian Aegilops species (Poaceae). Nat Resour 4(01):76–81
Sohail Q, Shehzad T, Kilian A, Eltayeb AE, Tanaka H, Tsujimoto H (2012) Development of diversity array technology (DArT) markers for assessment of population structure and diversity in Aegilops tauschii. Breed Sci 62(1):38–45
Trethowan RM, van Ginkel M (2009) Synthetic wheat—an emerging genetic resource. Wheat Sci Trade 29:369–385
Vikram P, Franco J, Burgueño-Ferreira J, Li H, Sehgal D, Saint Pierre C, Ortiz C, Sneller C, Tattaris M, Guzman C, Sansaloni CP (2016) Unlocking the genetic diversity of Creole wheats. Sci Rep 6:23092
Wang J, Luo MC, Chen Z, You FM, Wei Y, Zheng Y, Dvorak J (2013) Aegilops tauschii single nucleotide polymorphisms shed light on the origins of wheat D-genome genetic diversity and pinpoint the geographic origin of hexaploid wheat. New Phytol 198(3):925–937
Watanabe N, Mastui K, Furuta Y (1994) Uniformity of the alpha-amylase isozymes of Aegilops cylindrica introduced into North America. In: Wang RRC, Jensen KB, Jaussi C (eds) Comparison with ancestral Eurasian accessions. Second Int Wheat Symp, Logan, pp 215–218
Wright S (1978) Evolution and the genetics of populations, volume 3: experimental results and evolutionary deductions. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Yamane K, Kawahara T (2005) Intra-and interspecific phylogenetic relationships among diploid Triticum–Aegilops species (Poaceae) based on base-pair substitutions, indels, and microsatellites in chloroplast noncoding sequences. Am J Bot 92(11):1887–1898
Yu H, Deng Z, Xiang C, Tian J (2014) Analysis of diversity and linkage disequilibrium mapping of agronomic traits on B-genome of wheat. J Genom 2:20–30
Ziems LA, Hickey LT, Hunt CH, Mace ES, Platz GJ, Franckowiak JD, Jordan DR (2014) Association mapping of resistance to Puccinia hordei in Australian barley breeding germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 127(5):1199–1212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasov, M., Sansaloni, C.P., Burgueño, J. et al. Genetic diversity analysis using DArTseq and SNP markers in populations of Aegilops species from Azerbaijan. Genet Resour Crop Evol 67, 281–291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-019-00866-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-019-00866-7