Abstract
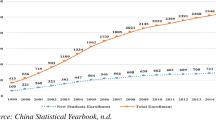
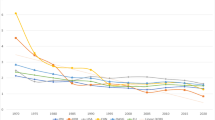
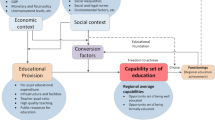
Within the context of broad literature on cross-border flows for higher education, this article examines the distinctive case of mainland Chinese students in Hong Kong and Macau. These territories are a sort of bridge between the fully domestic and the fully international. Hong Kong and Macau higher education plays a dual role, as a destination in itself for higher education and as a stepping-stone for students’ further international development. Patterns in Hong Kong are slightly different from those in Macau, and the territories may thus be usefully compared with each other as well as taken as a pair for comparison with other parts of the world. The paper begins by noting the literature on the ways that push and pull factors influence student mobility, and then turns to motivations in pursuit of academic and professional growth, economic benefit, individual internationalisation, and enhanced social status. The paper shows that flows of mainland Chinese students are driven by both excess and differentiated demand. Analysis of the distinctive features of this pair of territories adds to wider conceptual understanding of the nature of cross-border flows for higher education.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.G. Altbach (1998) Comparative Higher Education: Knowledge, the University, and Development Comparative Education Research Centre, The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong
P.G. Altbach (2004) ArticleTitle‘Higher education crosses borders’ Change 36 IssueID2 18–24
M. Bray R. Koo (Eds) (2004) Education and Society in Hong Kong and Macao: Comparative Perspectives on Continuity and Change EditionNumber2 Kluwer Academic Publishers Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre, The University of Hong Kong, and Boston
M. Bray O. Kwo (2003) ArticleTitle‘Higher education in small territories: Political transition and development in Macau’ Higher Education Policy 16 IssueID4 413–432 Occurrence Handle10.1057/palgrave.hep.8300031
L.K.C. Chan P. Cunich (Eds) (2002) An Impossible Dream: Hong Kong University from Foundation to Re-establishment, 1910–1950 Oxford University Press Hong Kong
C.G. Chen (1996) The External Flow and Return of Talent Hubei Education Press Wuhan
C.G. Chen C.M. Liu (2003) Talents’ Return and Utilization Guangdong People’s Press Guangzhou
D.Y. Chen (2004) ArticleTitle‘China’s mass higher education: Problem, analysis, and solutions’ Asia Pacific Education Review 5 IssueID1 23–33
InstitutionalAuthorNameChina, People’s Republic of (1997) Educational Statistics Yearbook of China People’s Education Press Beijing
InstitutionalAuthorNameChina, People’s Republic of (2000) Memorandum of Foreign Affairs Conference on National Education. Document No.9 National Education Bureau Beijing
InstitutionalAuthorNameChina, People’s Republic of (2001) Educational Statistics Yearbook of China 2001 People’s Education Press Beijing
InstitutionalAuthorNameChina, People’s Republic of (2003a) China Statistical Yearbook 2003 China Statistics Press Beijing
InstitutionalAuthorNameChina, People’s Republic of (2003b) Education Statistics Report 2003 China Education Development and Planning Bureau Beijing
T. Davis (1995) ArticleTitle‘Flows of international students: Trends and issues’ International Higher Education 1 2–4
Deng, Z. (1990). Brain Drain and the Chinese Education Movement: Causes, Implications, and Policy Options. Ph.D. dissertation, The Pennsylvania State University
J. Drago (2003) ArticleTitle‘New aims in higher education’ Macau Quarterly 15 68–84
D. Held A. McGrew D. Goldblatt J. Perraton (1999) Global Transformations: Politics, Economics and Culture Polity Press Cambridge
InstitutionalAuthorNameHong Kong, Information Services Department (2003) Hong Kong 2002 Information Services Department Hong Kong
D.M. Lampton J.A. Mandancy K.M. Williams (1986) A Relationship Restored: Trends in U.S.-China Educational Exchange, 1978–1984 National Academy Press Washington, DC
K.H. Lee J.P. Tan (1984) ArticleTitle‘The international flow of third level less developed country students to developed countries: Determinants and implications’ Higher Education 13 IssueID6 687–707 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00137020
InstitutionalAuthorNameMacao, Government Information Bureau (2004) Macao Yearbook 2004 Government Information Bureau Macao
T. Mazzarol G.N. Soutar (2001) The Global Market for Higher Education: Sustainable Competitive Strategies for the New Millennium Edward Elgar Cheltenham
M.E. McMahon (1992) ArticleTitle‘Higher education in a world market: A historical look at the global context to international study’ Higher Education 24 IssueID4 465–482 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00137243
P. Ninnes M. Hellstén (Eds) (2005) Internationalizing Higher Education: Critical Explorations of Pedagogy and Policy Springer Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre, The University of Hong Kong, and Dordrecht
L. Orleans (1988) Chinese Students in America: Polices, Issues and Numbers National Academy Press Washington, DC
G.A. Postiglione (1998) ArticleTitle‘Maintaining global engagement in the face of national integration in Hong Kong’ Comparative Education Review 42 IssueID1 30–45 Occurrence Handle10.1086/447477
G.A. Postiglione (2005) ArticleTitle‘China’s Global Bridging: The Transformation of University Mobility between Hong Kong and the United States’ Journal of Studies in International Education 9 IssueID1 5–25 Occurrence Handle10.1177/1028315304271481
L. Reisberg (2004) ArticleTitle‘Where Did All the International Students Go?’ International Higher Education 37 11–13
G. Shive (2004) Hong Kong higher education as international export Paper presented at the annual conference of the Federation of Continuing Education City University of Hong Kong
N.P. Stromquist K. Monkman (Eds) (2000) Globalization and Education: Integration and Contestation Across Cultures Rowman and Littlefield Lanham, Maryland
A.E. Sweeting (1995) Hong Kong P. Morris A.E. Sweeting (Eds) Education and Development in East Asia Garland New York 41–77
University Grants Committee (2005). ‘Student Numbers: Headcount’. http://www.ugc. edu.hk/eng/ugc/stat/ student_head.htm accessed 11 May 2005
H.S. Yee M. Kou (2001) ArticleTitle‘Government intervention in higher education in Macau’ Higher Education Management 13 IssueID1 75–91
A.M.S. Yung (2004) Higher education M. Bray R. Koo (Eds) Education and Society in Hong Kong and Macao: Comparative Perspectives on Continuity and Change EditionNumber2 Kluwer Academic Publishers Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre, The University of Hong Kong, and Boston 61–72
X.H. Zheng (2003) An Analysis on Study Abroad of Graduates of Undergraduate in Tsinghua University L. Tian (Eds) Research on China’s Foreign Cultural Exchange in Higher Education Minzu Press Beijing 199–237
D. Zweig (2002) Internationalizing China: Domestic Interests and Global Linkages Cornell University New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Bray, M. Cross-border flows of students for higher education: Push–pull factors and motivations of mainland Chinese students in Hong Kong and Macau. High Educ 53, 791–818 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-005-5423-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-005-5423-3