Abstract
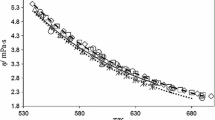
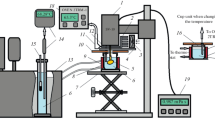
A new apparatus was developed for measuring the viscosity, density, and bubble-point pressure of CO2 and organic liquid mixtures. The apparatus is based on the rolling-ball principle and consists of a computer-controlled stepper motor that rotates a high-pressure cell that is equipped with a sapphire window, a movable piston, and a position-sensing device. Design of the high-pressure cell was made such that compositions could be determined by mass. The viscosity was determined by sensing the speed of a rolling ball, and the density was determined by sensing the position of the piston with a linear-variable differential transformer. Bubble-point pressures were measured with the synthetic method. The viscosity and density of octane and decane were measured, and the average deviations of these properties compared with reliable literature values were 1.1 % and 0.15 %, respectively. The viscosity and density of CO2 + tetrahydrofuran system were measured at a temperature of 60 °C, a pressure of 10.2 MPa, and CO2 mole fractions up to 0.3. Bubble-point pressures for the CO2 + tetrahydrofuran system were in good agreement with literature data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsumura Y., Sasaki M., Okuda K., Takami S., Ohara S., Umetsu M., Adschiri T.: Combust. Sci. Technol. 178, 509 (2006)
Hernandez-Galvan M.A., Garcia-Sanchez F., Macias-Salinas R.: Fluid Phase Equilib. 262, 51 (2007)
Briscoe B.J., Luckham P.F., Ren S.R.: Colloids Surf. 62, 153 (1992)
Tomida D., Kumagai A., Qiao K., Yokoyama C.: J. Chem. Eng. Data 52, 1638 (2007)
Tomida D., Kumagai A., Yokoyama C.: Int. J. Thermophys. 28, 133 (2007)
Stanley E.M., Batten R.C.: Anal. Chem. 40, 1751 (1968)
Izuchi M., Nishibata K.: Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 25, 1091 (1986)
Nishibata K., Izuchi M.: Physica B & C 139, 903 (1936)
Dindar C., Kiran E.: Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 3664 (2002)
Assael M.J., Dalaouti N.K., Polimatidou S.: Int. J. Thermophys. 20, 1367 (1999)
Oliveira C.M.B.P., Wakeham W.A.: Int. J. Thermophys. 13, 773 (1992)
Huber M.L., Laesecke A., Xiang H.W.: Fluid Phase Equilib. 224, 263 (2004)
Fenghour A., Wakeham W.A., Vesovic V.: J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 27, 31 (1998)
Lazzaroni M.J., Bush D., Brown J.S., Eckert C.A.: J. Chem. Eng. Data 50, 60 (2005)
Zhang W., Kiran E.: J. Chem. Thermodyn. 35, 605 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, Y., Yoshioka, H., Aikawa, S. et al. A Digital Variable-Angle Rolling-Ball Viscometer for Measurement of Viscosity, Density, and Bubble-Point Pressure of CO2 and Organic Liquid Mixtures. Int J Thermophys 31, 1896–1903 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-008-0542-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-008-0542-6