Abstract
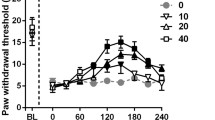
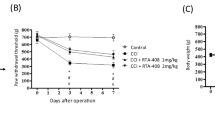
Neuropathic pain is still considered as incurable disease as current therapies are not ideal in terms of efficacy and tolerability. It is imperative to search for novel drugs to obtain better treatments. Sulforaphane (SFN), a derivative of glucoraphanin present in cruciferous vegetables, exhibits therapeutic effects on inflammation-related diseases. Since inflammation plays an important role in regulating chronic pain, in the present study, we investigated anti-nociceptive effects of SFN and its underlying mechanisms in a neuropathic pain mouse model, sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury (CCI). SFN (0.1–100 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally for 7 days when pain behaviors, including mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia, reached to the maximum in CCI mice. We observed that SFN dose-dependently attenuated CCI-induced pain behavioral hypersensitivity, accompanied by reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and upregulation of an anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10). Moreover, SFN counteracted CCI enhancement of COX2 and iNOS in injured nerves, two key enzymes implicated in inflammation and neuropathic pain. Furthermore, pretreatment of naloxone, an antagonist of opioid receptors, significantly blocked SFN attenuation of behavioral hypersensitivity without affecting SFN modulation of inflammatory cytokines in CCI mice. Interestingly, CCI-induced increase in µ-opioid receptors in injured sciatic nerves was further increased by SFN treatment. Taken together, SFN has both anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory actions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altier N, Dion D, Boulanger A, Choiniere M (2005) Management of chronic neuropathic pain with methadone: a review of 13 cases. Clin J Pain 21:364–369
Banafshe HR, Hamidi GA, Noureddini M, Mirhashemi SM, Mokhtari R, Shoferpour M (2014) Effect of curcumin on diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: possible involvement of opioid system. Eur J Pharmacol 723:202–206. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.11.033
Baron R (2006) Mechanisms of disease: neuropathic pain–a clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:95–106. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0113
Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G (2010) Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol 9:807–819. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70143-5
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Bidlack JM, Khimich M, Parkhill AL, Sumagin S, Sun B, Tipton CM (2006) Opioid receptors and signaling on cells from the immune system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1:260–269. doi:10.1007/s11481-006-9026-2
Davidson RK et al (2013) Sulforaphane represses matrix-degrading proteases and protects cartilage from destruction in vitro and in vivo. Arthritis Rheum 65:3130–3140. doi:10.1002/art.38133
Donnelly RP, Dickensheets H, Finbloom DS (1999) The interleukin-10 signal transduction pathway and regulation of gene expression in mononuclear phagocytes. J Interferon Cytokine Res 19:563–573. doi:10.1089/107999099313695
El-Sobky A, Dostrovsky JO, Wall PD (1976) Lack of effect of naloxone on pain perception in humans. Nature 263:783–784
Finnerup NB, Otto M, McQuay HJ, Jensen TS, Sindrup SH (2005) Algorithm for neuropathic pain treatment: an evidence based proposal. Pain 118:289–305. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2005.08.013
Finnerup NB et al (2015) Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 14:162–173. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70251-0
Franchi S et al (2012) Intravenous neural stem cells abolish nociceptive hypersensitivity and trigger nerve regeneration in experimental neuropathy. Pain 153:850–861. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2012.01.008
Guerrero-Beltran CE, Calderon-Oliver M, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Chirino YI (2012) Protective effect of sulforaphane against oxidative stress: recent advances. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:503–508. doi:10.1016/j.etp.2010.11.005
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Herr I, Buchler MW (2010) Dietary constituents of broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables: implications for prevention and therapy of cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 36:377–383. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.01.002
Hughes JP et al (2012) Understanding chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1255:30–44. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06561.x
Jaggi AS, Jain V, Singh N (2011) Animal models of neuropathic pain. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 25:1–28. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00801.x
Kensler TW et al (2013) Keap1-nrf2 signaling: a target for cancer prevention by sulforaphane. Top Curr Chem 329:163–177. doi:10.1007/128_2012_339
Labuz D, Schmidt Y, Schreiter A, Rittner HL, Mousa SA, Machelska H (2009) Immune cell-derived opioids protect against neuropathic pain in mice. J Clin Invest 119:278–286. doi:10.1172/JCI36246
Lees JG, Duffy SS, Moalem-Taylor G (2013) Immunotherapy targeting cytokines in neuropathic pain. Front Pharmacol 4:142. doi:10.3389/fphar.2013.00142
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marchand F, Perretti M, McMahon SB (2005) Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:521–532. doi:10.1038/nrn1700
Milligan ED, Penzkover KR, Soderquist RG, Mahoney MJ (2012) Spinal interleukin-10 therapy to treat peripheral neuropathic pain. Neuromodulation 15:520–526. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1403.2012.00462.x (discussion 526)
Moalem G, Tracey DJ (2006) Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res Rev 51:240–264. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2005.11.004
Nallasamy P et al (2014) Sulforaphane reduces vascular inflammation in mice and prevents TNF-alpha-induced monocyte adhesion to primary endothelial cells through interfering with the NF-kappaB pathway. J Nutr Biochem 25:824–833. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.03.011
Negi G, Kumar A, Sharma SS (2011) Nrf2 and NF-kappaB modulation by sulforaphane counteracts multiple manifestations of diabetic neuropathy in rats and high glucose-induced changes. Curr Neurovasc Res 8:294–304
O’Connor AB, Dworkin RH (2009) Treatment of neuropathic pain: an overview of recent guidelines. Am J Med 122:S22–S32. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.04.007
Plunkett JA, Yu CG, Easton JM, Bethea JR, Yezierski RP (2001) Effects of interleukin-10 (IL-10) on pain behavior and gene expression following excitotoxic spinal cord injury in the rat. Exp Neurol 168:144–154. doi:10.1006/exnr.2000.7604
Przewlocki R, Przewlocka B (2001) Opioids in chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:79–91
Sacerdote P (2006) Opioids and the immune system. Palliat Med 20(Suppl 1):s9–s15
Singh K, Zimmerman AW (2016) Sulforaphane treatment of young men with autism spectrum disorder. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 15:597–601
Singh K, Connors SL, Macklin EA, Smith KD, Fahey JW, Talalay P, Zimmerman AW (2014) Sulforaphane treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:15550–15555. doi:10.1073/pnas.1416940111
Sloane EM, Soderquist RG, Maier SF, Mahoney MJ, Watkins LR, Milligan ED (2009) Long-term control of neuropathic pain in a non-viral gene therapy paradigm. Gene Ther 16:470–475. doi:10.1038/gt.2009.21
Sun CC et al (2015) Sulforaphane attenuates muscle inflammation in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 290:17784–17795. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.655019
Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107:7–11. doi:10.1172/JCI11830
Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ (1999) Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet 353:1959–1964. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)01307-0
Zhang JM, An J (2007) Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin 45:27–37. doi:10.1097/AIA.0b013e318034194e
Zhang Y, Kensler TW, Cho CG, Posner GH, Talalay P (1994) Anticarcinogenic activities of sulforaphane and structurally related synthetic norbornyl isothiocyanates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3147–3150
Zhu C et al (2016) Effects of ginkgo biloba extract EGb-761 on neuropathic pain in mice: involvement of opioid system. Phytother Res 30:1809–1816. doi:10.1002/ptr.5685
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving animals
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Wang, C. Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory actions of sulforaphane in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain mice. Inflammopharmacol 25, 99–106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-016-0307-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-016-0307-y