Abstract
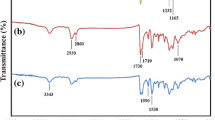
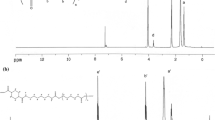
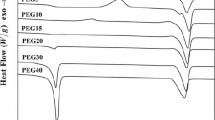
Three series of shape memory poly(ester–urethane) with varying hard-segment contents were synthesized. The materials were designed to display a three-phase structure consisting of a disperse phase formed by crystallites and hard domains embedded in an amorphous matrix. The initial undeformed morphology was investigated using techniques such as modulated differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and wide angle X-ray scattering. These techniques were used to determine the phase separation, hydrogen-bonding structure, and crystalline fraction of the specimens prior to thermo-mechanical treatments. The obtained information was correlated with small angle X-ray scattering investigations of morphological changes that occurred during shape memory cycling. The deformation cycle led to the formation of an oriented nanostructure derived from chain alignment. The nanostructure recovered was observed to be triggered by the melting of the crystallites and bulk incompatibility. A relationship between the ability of the studied poly(ester–urethane) specimens to recover their original shape and their original nanostructure was determined.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szycher M (1999) Szycher’s handbook of polyurethanes, chap 1.1–1.6. CRC Press, London
Oertel G (1994) Polyurethane handbook, 2nd edn. Hanser Publisher, New York, pp 11–45
Pan H, Chen D (2007) Eur Polym J 43:3766
Chen G, Ma Y, Zheng X et al (2007) J Polym Sci B 45(6):654
Lendlein A, Langer R (2002) Science 296(5573):1673
Wilson TS, Small W, Benett WJ et al (2005) In: Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng, 60070R-1-8
Miaudet P, Derre A, Maugey M et al (2007) Science 318:1294
Gall K, Dunn ML, Liu YP, Stefanic G, Balzar (2004) Appl Polym Sci 85(2):290
Gall K, Kreiner P, Turner D, Hulse M (2004) J Micro Sys 13(3):472
Van Krevelen DW (1990) Properties of polymers, 3rd edn. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, p 121
Oliveira W, Glasser WG (1994) Macromolecules 27:5
Bao H, Zhang Z, Ying S (1996) Polymer 37(13):2751
Seymour RW, Cooper RL (1973) Macromolecules 6:48
Gunes IS, Jana SC (2008) J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8(4):1616
Gorna K, Gogolewski S (2002) Polym Degrad Stab 75(1):113
Yeganeh H, Lakouraj MM, Jamshidi S (2005) Eur Polym J 41(10):2370
Jiang X, Li JH, Ding MM et al (2007) Eur Polym J 43(5):1838
Ayres E, Oréfice RL, Yoshida MI (2007) Eur Polym J 43(8):3510
Coates JP (2000) In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry. Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp 10815–10837
Marcos-Fernández A, Abraham GA, Valentín JL, San Román J (2006) Polymer 47(3):785
Chattopadhyay DK, Sreedhar B, Raju KVSN (2006) Polymer 47(11):3814
Cho JW, Lee SH (2004) Eur Polym J 40(7):1343
Huang SL, Lai JY (1997) Eur Polym J 33(10–12):1563
Liu Y, Pan C (1998) Eur Polym J 34(5–6):621
Nakamae K, Nishino T, Asaoka S et al (1999) Int J Adhes Adhes 19(5):345
Pompe G, Pohlers A, Pötschke P, Pionteck J (1998) Polymer 39(21):5147
Lin JR, Chen LW (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 69(8):1563
Li YJ, Gao T, Liu J et al (1992) Macromolecules 25(26):7365
Pretsch T, Jakob I, Werner M (2009) Polym Degrad Stab 94:61
Tien YI, Wei KH (2001) Polymer 42(7):3213
Jia QM, Zheng M, Zhu YC et al (2007) Eur Polym J 43(1):35
Kim BK, Lee SY, Xu M (1996) Polymer 37(26):5781
Xu J, Shi W, Pang W (2006) Polymer 47(1):457
Charnetskaya AG, Polizos G, Shtompel VI et al (2003) Eur Polym J 39(11):2167
Wang ZG, Hsiao BS, Fu BX et al (2000) Polymer 41(5):1791
Wang SH, Zhang Y, Ren WT et al (2005) Polym Test 24(6):766
Jiang ZY, Tang YJ, Men YF et al (2007) Macromolecules 40(20):7263
Chang SL, Yu TL, Huang CC, Chen WC, Linliu K, Lin TL (1998) Polymer 39(15):3479
Li YJ, Kang WX, Stoffer JO et al (1994) Macromolecules 27(2):612
Tang YJ, Jiang ZY, Men YF et al (2007) Polymer 48(17):5125
Lee BS, Chun BC, Chung YC et al (2001) Macromolecules 34(18):6431
Yang JH, Chun BC, Chung YC, Cho JH (2003) Polymer 44(11):3
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the following institutions: the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), a foundation linked to the Ministry of Science and Technology (MCT) of the Brazilian Government; the State of Minas Gerais Research Foundation (FAPEMIG); and the National Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS-Brazil) for the use of the SAXS beamline facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, I.M., Oréfice, R.L. The morphology and phase mixing studies on poly(ester–urethane) during shape memory cycle. J Mater Sci 45, 511–522 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3969-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3969-7