Abstract
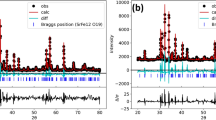
In this paper, an experimental study was performed on the effect induced by different strontium precursors in the growth processes and optical properties of strontium tungstate (SrWO4) microcrystals synthesized by the co-precipitation method. The structural behavior was analyzed by means of X-ray diffractions, Rietveld refinements, Fourier transform (FT)-Raman, and FT-infrared spectroscopies. X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectra performed at the W-L1 and L3 edges revealed the first coordination shell around the tungsten atoms is composed of four oxygens, i.e., existence of tetrahedral [WO4] clusters inside the SrWO4 structure. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images showed the presence of pitch and longleaf pine cone-like SrWO4 microcrystals for most of the strontium precursors employed in the synthesis. Based on these FE-SEM images, a hypothetical crystal growth mechanism was proposed to explain the origin of these microcrystals. The optical properties were investigated by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) measurements at room temperature. The different optical band gap values found for this material, depending on the type of strontium precursor, were correlated with the existence of intermediary energy levels within the forbidden region. Finally, PL profiles were associated to the degree of distortions in tetrahedral [WO4] clusters.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan L, Fan YX, Duan YH, Wang Q, Wang HT, Jia GH, Tu CY (2009) Continuous-wave intracavity Raman laser at 1179.5 nm with SrWO4 Raman crystal in diode-end-pumped Nd:YVO4 laser. Appl Phys B 94:553–557
Wang A, Wang C, Jia G (2009) Recent advances in strontium tungstate scheelite material. Front Chem China 5:61–70
Liao J, Qiu B, Wen H, Chen J, You W, Liu L (2009) Synthesis process and luminescence properties of Tm3+ in AWO4 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba) blue phosphors. J Alloys Compd 487:758–762
Shan Z, Wang Y, Ding H, Huang F (2009) Structure-dependent photocatalytic activities of MWO4 (M = Ca, Sr, Ba). J Mol Catal A 302:54–58
Cavalcante LS, Sczancoski JC, Batista NC, Longo E, Varela JA, Orlandi MO (2013) Growth mechanism and photocatalytic properties of SrWO4 microcrystals synthesized by injection of ions into a hot aqueous solution. Adv Powder Technol 24:344–353
Lou Z, Cocivera M (2002) Cathodoluminescence of CaWO4 and SrWO4 thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater Res Bull 37:1573–1582
Fan JD, Zhang HJ, Wang JY, Jiang MH, Boughton RI, Ran DG, Sun SQ, Xia HR (2006) Growth and thermal properties of SrWO4 single crystal. J Appl Phys 100:063513–063518
Fan YX, Liu Y, Duan Y, Wang Q, Fan L, Wang HT, Jia GH, Tu CY (2008) High-efficiency eye-safe intracavity Raman laser at 1531 nm with SrWO4 crystal. Appl Phys B 93:327–330
Porto SL, Longo E, Pizani PS, Boschi TM, Simões LGP, Lima SJG, Ferreira JM, Soledade LEB, Espinosa JWM, Cássia-Santos MR, Maurera MAMA, Paskocimas CA, Santos IMG, Souza AG (2008) Photoluminescence in the Ca x Sr1−x WO4 system at room temperature. J Solid State Chem 181:1876–1881
Tian G, Sun S (2011) Additive induced morphology changes of nano-crystalline SrWO4. Cryst Res Technol 46:389–392
Dong FJ, Hu ZA, Zheng WP, Wen GW, Ji WY (2006) Synthesis of polycrystalline materials of SrWO4 and growth of its single crystal. Front Chem China 1:264–267
Yang S, Sun J (2004) Synthesis and properties of Tb3+-doped Ca x Sr1−x WO4. J Rare Earths 22:331–333
Caprez A, Meyer P, Mikhail P, Hulliger J (1997) New host-lattices for hyperfine optical hole burning: materials of low nuclear spin moment. Mater Res Bull 32:1045–1054
Errandonea D, Pellicer-Porres J, Manjón FJ, Segura A, Ferrer-Roca C, Kumar RS, Tschauner O, Rodrıguez-Hernandez P, Lopez-Solano J, Radescu S, Mujica A, Munoz A, Aquilanti G (2005) High-pressure structural study of the scheelite tungstates CaWO4 and SrWO4. Phys Rev B 72:174106–174119
Patel AR, Arora SK (1974) Crystal growth of BaWO4 and SrWO4 by flux evaporation. J Cryst Growth 23:95–100
Chen L, Gao Y (2009) Electro-deposition of luminescent molybdate and tungstate thin films via a cell route. Mater Chem Phys 116:242–246
Jiang X, Ma J, Yao Y, Sun Y, Liu Z, Ren Y, Liu J, Lin B (2009) Low-temperature synthesis of SrWO4 nano-particles by a molten salt method. Ceram Int 35:3525–3528
Thongtem T, Phuruangrat A, Thongtem S (2008) Characterization of MeWO4 (Me = Ba, Sr and Ca) nanocrystallines prepared by sonochemical method. Appl Surf Sci 254:7581–7585
Rangappa D, Fujiwara T, Watanabe T, Yoshimura M (2008) Preparation of Ba1−x Sr x WO4 and Ba1−x Ca x WO4 films on tungsten plate by mechanically assisted solution reaction at room temperature. Mater Chem Phys 109:217–223
Maurera MAMA, Souza AG, Soledade LEB, Pontes FM, Longo E, Leite ER, Varela JA (2004) Microstructural and optical characterization of CaWO4 and SrWO4 thin films prepared by a chemical solution method. Mater Lett 58:727–732
Huang JY, Jia QX (2003) Structural properties of SrWO4 films synthesized by pulsed-laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 444:95–98
Chen Z, Gong Q, Zhu J, Yuan YP, Qian LW, Qian XF (2009) Controllable synthesis of hierarchical nanostructures of CaWO4 and SrWO4 via a facile low temperature route. Mater Res Bull 44:45–50
Sun L, Guo Q, Wu X, Luo S, Pan W, Huang K, Lu J, Ren L, Cao M, Hu C (2007) Synthesis and photoluminescent properties of strontium tungstate nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 111:532–537
Ciminelli VST, Dias A (2000) Theoretical predictions and experimental results of the hydrothermal processing of strontium tungstates. Ferroelectrics 241:271–278
Thongtem T, Phuruangrat A, Thongtem S (2010) Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of SrMoO4 and SrWO4 nanocrystals. J Nanopart Res 12:2287–2294
Sczancoski JC, Cavalcante LS, Joya MR, Espinosa JWM, Pizani PS, Varela JA, Longo E (2009) Synthesis, growth process and photoluminescence properties of SrWO4 powders. J Colloid Interface Sci 330:227–236
Ryu EK, Huh YD (2008) Morphology-controlled synthesis of SrWO4 crystals. Mater Lett 62:3081–3083
Thongtem T, Phuruangrat A, Thongtem S (2008) Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline SrWO4 using cyclic microwave radiation. Curr Appl Phys 8:189–197
Pereira PFS, Nogueira IC, Longo E, Nassar EJ, Rosa ILV, Cavalcante LS (2015) Rietveld refinement and optical properties of SrWO4:Eu3+ powders prepared by the non-hydrolytic sol-gel method. J Rare Earths 33:113–128
Zhang L, Bai Q, Wang L, Zhang A, Zhang Y, Xing Y (2014) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of SrWO4/graphene composite as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Funct Mater Lett 7:1450010–1450013
Sharma JC, Vijay A, Bhardwaj S (2013) Photocatalytic activity of a novel compound SrWO4: removal of toxic metal lead (II) from water. World Appl Sci J 23:208–212
Gouveia AF, Sczancoski JC, Ferrer MM, Lima AS, Santos MRMC, Li MS, Santos RS, Longo E, Cavalcante LS (2014) Experimental and theoretical investigations of electronic structure and photoluminescence properties of β-Ag2MoO4 microcrystals. Inorg Chem 53:5589–5599
Rodriguez-Hernandez P, Lopez-Solano J, Radescu S, Mujica A, Munoz A, Errandonea D, Pellicer-Porres J, Segura A, Ferrer-Roca C, Manjón FJ, Kumar RS, Tschauner O, Aquilanti G (2006) Theoretical and experimental study of CaWO4 and SrWO4 under pressure. J Phys Chem Solids 67:2164–2171
Rietveld HM (1969) A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J Appl Cryst 2:65–71
Larson AC, Von Dreele RB (1994) General structure analysis system (GSAS), Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR. 86:748–768
Chebyshev PL (1854) Théorie des mécanismes connus sous le nom de parallélogrammes. Mémoires des Savants trangers prsents—Acadmie de Saint-Ptersbourg. 7:539–586
Thompson P, Cox DE, Hastings JB (1987) Rietveld refinement of Debye-Scherrer synchrotron X-ray data from Al2O3. J Appl Cryst 20:79–83
Finger LW, Cox DE, Jephcoat AP (1994) A correction for powder diffraction peak asymmetry due to axial divergence. J Appl Cryst 27:892–900
Stephens PW (1999) Phenomenological model of anisotropic peak broadening in powder diffraction. J Appl Crystallogr 32:281–289
Hallaoui A, Taoufyq A, Arab M, Bakiz B, Benlhachemi A, Bazzi L, Villain S, Valmalettea JC, Guinnetona F, Gavarri JR (2015) Influence of chemical substitution on the photoluminescence of Sr(1–x)Pb x WO4 solid solution. J Solid State Chem 227:186–195
Pereira PFS, de Moura AP, Nogueira IC, Lima MVS, Longo E, de Sousa Filho PC, Serra OA, Nassar EJ, Rosa ILV (2012) Study of the annealing temperature effect on the structural and luminescent properties of SrWO4: Eu phosphors prepared by a non-hydrolytic sol-gel process. J Alloys Compd 526:11–21
Li Q, Jia C (2014) Synthesis and characteristics of SrWO4:Sm3+ nanofiber phosphors by electrospinning method. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 6:1014–1017
Chen Y, Wu QS, Ding YP (2007) Oil/water interface synthesis and optical property of strontium tungstate nanorods. Nano 2:195–199
Jia G, Wang C, Xu S (2010) Local site symmetry determination of scheelite-type structures by Eu3+ spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 114:17905–17913
Krayzman V, Levin I, Woicik JC, Yoder D, Fischer DA (2006) Effects of local atomic order on the pre-edge structure in the Ti-K X-ray absorption spectra of perovskite CaTi1−x Zr x O3. Phys Rev B 74:224104–224110
Gracia L, Longo VM, Cavalcante LS, Beltran A, Avansi W, Li MS, Mastelaro VR, Varela JA, Longo E, Andres J (2011) Presence of excited electronic state in CaWO4 crystals provoked by a tetrahedral distortion: an experimental and theoretical investigation. J Appl Phys 110:043501–043511
Cavalcante LS, Almeida MAP, Avansi W Jr, Tranquilin RL, Longo E, Batista NC, Mastelaro VR, Li MS (2013) Cluster coordination and photoluminescence properties of α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals. Inorg Chem 51:10675–10687
Basu S, Naidu BS, Viswanadh B, Sudarsan V, Jha SN, Bhattacharyya D, Vatsa RK (2014) Nature of WO4 tetrahedra in blue light emitting CaWO4 probed through the EXAFS technique. RSC Adv 4:15606–15612
Kuzmin A, Purans J (2001) Local atomic and electronic structure of tungsten ions in AWO4 crystals of scheelite and wolframite types. Radiat Meas 33:583–586
Poirier GL, Cassanjes FC, Messaddeq Y, Ribeiro SJL, Michalowicz A, Poulain M (2005) Local order around tungsten atoms in tungstate fluorophosphates glasses by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J Non-Cryst Solids 351:3644–3648
Montanari B, Barbosa AJ, Ribeiro SJL, Messaddeq Y, Poirier G, Li MS (2008) Structural study of thin films prepared from tungstate glass matrix by Raman and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl Surf Sci 254:5552–5556
Daviero-Minaud S, Rolle A, Kongmark C, Vannier RN (2009) Local environment in Ba2In2−x W x O5+3x/2 oxide ion conductors. J Solid State Chem 182:289–294
Ko JYP, Hu Y, Armelao L, Sham TK (1990) XANES and XEOL studies of Eudoped calcium tungstate in silica synthesized by sol-gel method. J Phys 190:012078–012081
Gonçalves RF, Cavalcante LS, Nogueira IC, Longo E, Godinho MJ, Sczancoski JC, Mastelaro VR, Pinatti IM, Rosa ILV, Marques APA (2015) Rietveld refinement, cluster modelling, growth mechanism and photoluminescence properties of CaWO4:Eu3+ microcrystals. CrystEngComm 17:1654–1666
Porto SP, Scott JF (1967) Raman spectra of CaWO4, SrWO4, CaMoO4, and SrMoO4. Phys Rev 157:716–719
Wannapop S, Thongtem T, Thongtem S (2011) Characterization of SrWO4-PVAand SrWO4 spiders’ webs synthesized by electrospinning. Ceram Inter 37:3499–3507
Degreniers S, Jandl S, Carlone C (1984) Temperature dependence of the Raman active phonons in CaWO4, SrWO4 and BaWO4. J Phys Chem Solids 45:1105–1109
Golubović A, Gajić R, Dohčević-Mitrović Z, Nikolić S (2006) Nd induced changes in IR spectra of CaWO4 single crystals. J Alloys Compd 415:16–22
Gong Q, Qian X, Ma X, Zhu Z (2006) Large-scale fabrication of novel hierarchical 3D CaMoO4 and SrMoO4 mesocrystals via a microemulsion-mediated route. Cryst Growth Des 6:1821–1825
Yin Y, Yang F, Yang Y, Gan Z, Qin Z, Gao S, Zhou B, Li X (2011) Controlled synthesis of BaWO4 hierarchical nanostructures by exploiting oriented attachment in the solution of H2O and C2H5OH. Superlatt Microstruct 49:599–607
Tian Y, Chen B, Yu H, Hua R, Li X, Sun J, Cheng L, Zhong H, Zhang J, Zheng Y, Yu T, Huang L (2011) Controllable synthesis and luminescent properties of three-dimensional nanostructured CaWO4:Tb3+ microspheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 360:586–592
Kubelka P, Munk F (1931) Ein Beitrag zur optik der farbanstriche. Zeit Für Tech Physik 12:593–601
Morales AE, Mora ES (2007) Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. U Pal Rev Mex Fis S 53:18–22
Smith RA (1978) Semiconductors, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, London
Zhang Y, Holzwarth NAW, Williams RT (1998) Electronic band structures of the scheelite materials CaMoO4, CaWO4, PbMoO4, and PbWO4. Phys Rev B 57:12738–12750
Lacomba-Perales R, Ruiz-Fuertes J, Errandonea D, Martínez-García D, Segura A (2008) Optical absorption of divalent metal tungstates: correlation between the band-gap energy and the cation ionic radius. Eur Phys Lett 83:37002–37006
Longo VM, Orhan E, Cavalcante LS, Porto SL, Espinosa JWM, Varela JA, Longo E (2007) Understanding the origin of photoluminescence in disordered Ca0.60Sr0.40WO4: an experimental and first-principles study. Chem Phys 334:180–188
Tian G, Sheng N, Qiu X (2014) Structure and photoluminescence properties of SrWO4 3D microspheres synthesized by the surfactant-assisted hydrothermal method. Cryst Res Technol 49:360–365
Ling CS (2014) Cyclic Microwave-assisted metathetic synthesis and spectroscopic properties of SPION/SrWO4:Er3+, Yb3+ composites. Asian J Chem 26:1848–1852
Sun X, Sun X, Li X, He J, Wang B (2014) Molten salt synthesis, characterization, and luminescence of SrWO4, SrWO4:Tb3+ and SrWO4:Eu3+ powders. J Mater Sci 25:2320–2324
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the following Brazilian research funding institutions: the FAPESP (2012/14004-5; 2013/07296-2), CNPq (304531/2013-8; 479644/2012-8), National Laboratory of Synchrotron Light (D04B-XAFS1-11883), and CAPES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sczancoski, J.C., Avansi, W., Costa, M.G.S. et al. Effect of different strontium precursors on the growth process and optical properties of SrWO4 microcrystals. J Mater Sci 50, 8089–8103 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9377-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9377-2