Abstract
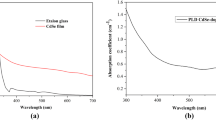
In the present work, optical, structural and morphological properties of CdS-doped phosphate films obtained by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) method were investigated. In the deposition process, a target based on a mixture composed of Li2O-Al2O3-BaO-La2O3-ZnO-P2O5 glass and CdS powder as dopant was used. The phosphate glass target was obtained by non-conventional wet route of raw reagents processing followed by melt-quenching technique. The complex oxide composition of the glass as well as the final PLD target consisting in a mixture of glass and CdS powder followed by pressing and heat treatment represents the novelty of the work. CdS dopant particles were highlighted by X-ray diffraction analysis as well as by Raman spectroscopy. Thus, cubic CdS particles having less than 10 nm size corroborated with specific LO (longitudinal optical phonons) and 2LO CdS Raman peaks from 300 and 600 cm−1, respectively, certified the presence of the dopant in the deposited films. Specific vibration modes for the vitreous phosphate matrix were revealed by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and spherulitic units characteristic to PLD technique were found by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy analyses. A relative large luminescence band located around 430 nm was provided by UV excitation, representative for CdS nanoparticles having about 9–10 nm size.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, To CY, Ng DHL (2006) Controlled synthesis of CdS nanobelts and the study of their cathodoluminescence. Mater Lett 60:1151
Romano R, Alves OL (2006) Semiconductor/porous glass nanocomposites via the single-source precursor approach. Mater Res Bull 41:376
Morales-Acevedo A (2006) Can we improve the record efficiency of CdS/CdTe solar cells? Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 90:2213
Acharya KP, Skuza JR, Lukaszew RA, Liyanage C, Ullrich B (2007) CdS thin films formed on flexible plastic substrates by pulsed-laser deposition. J Phys: Condens Matter 19(19):196221
Hernandez-Como N, Martinez-Landeros V, Mejia I, Aguirre-Tostado FS, Nascimento CD, de Azevedo GM, Krug C, Quevedo-Lopez MA (2014) Defect control in room temperature deposited cadmium sulfide thin films by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 550:665
Cheng Z, Su F, Pan L, Cao M, Sun Z (2010) CdS quantum dot-embedded silica film as luminescent down-shifting layer for crystalline Si solar cells. J Alloys Comp 494(1–2):L7–L10
Feraru I, Iordanescu R, Elisa M, Vasiliu C, Volceanov A, Stoleriu S, Peretz A, Filipescu M (2013) CdSe-doped phosphate glassy films obtained by PLD on silicon substrate. Chalcogenide Lett. 10:509
Elisa M, Vasiliu IC, Feraru ID, Iordanescu R, Rusu MI, Trusca R, Vasile E, Peretz S (2015) CdSe/ZnS-doped silicophosphate films prepared by sol-gel method. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 73:660
Bakshi MS (2016) How surfactants control crystal growth of nanomaterials. Cryst Growth Des 16:1104–1133
Rao MC (2013) Growth of metal oxide thin films by Pulsed laser deposition perspectives of pulsed laser ablation mechanism. J Chem Biol Phy Sci 3(2):1412–1424
Kumar P, Saxena N, Chandra R, Gupta V, Agarwal A, Kanjilal D (2012) Nanotwinning and structural phase transition in CdS quantum dots. Nanoscale Res Lett 7(1):584
Kumar P, Saxena N, Singh F, Agarwal A (2012) Nanotwinning in CdS quantum dots. Phys B 407(17):3347–3351
Perna G, Capozzi V, Pagliara S, Ambrico M (2000) Absorption and photoluminescence analysis of CdS ablated films grown on quartz substrate. Appl Surf Sci 154–155:238–243
Wang H, Zhu Y, Ong PP (2002) Effect of substrate temperature on the formation of CdO composite in CdS-doped SiO2 films as deposited by PLD. J Cryst Growth 241(1–2):183–188
Scherrer P (1918) Determination of the size and internal structure of colloidal particles using X-rays. Nachr Ges Wiss Gőttingen Math-Phys Kl 2:98
Schreder B, Dem C, Schmitt M, Materny A, Kiefer W, Winkler U, Umbach E (2003) Raman spectroscopy of II–VI semiconductor nanostructures: CdS quantum dots. J Raman Spectrosc 34:100–103
Prabhu RR, Khadar MA (2008) Study of optical phonon modes of CdS nanoparticles using Raman spectroscopy. Bull Mater Sci 31(3):511–515
Thambiduraia M, Murugan N, Muthukumarasamy N, Vedanta S, Balasundaraprabhu R, Agilana S (2009) Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline CdS thin films. Chalcogenide Lett 6(4):171–179
Saunders E, Popov I, Banin U (2006) Synthesis of hybrid CdS-Au colloidal nanostructures. J Phys Chem B 110(50):25421–25429
Pinna N, Weiss K, Urban J, Pileni M (2001) Triangular CdS nanocrystals: structural and optical studies. Adv Mater 13(4):261 (Weinhen, Ger.)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to UEFISCDI (Executive Unity for Financing of Higher Education, Research and Innovation) for the financial support in the frame of the projects 51/2011 Ideas-Program, and SEM analyses on samples were possible due to EU-funding Grant POSCCE-A2-O2.2.1-2013-1/Priority direction 2, Project No.638/12.c03.2014, cod SMIS-CSrNR 48652.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elisa, M., Iordanescu, C.R., Vasiliu, I.C. et al. Synthesis and characterization of PLD glass phosphate films doped with CdS. J Mater Sci 52, 2895–2901 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0583-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0583-3