Abstract
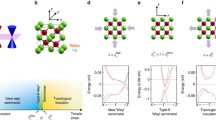
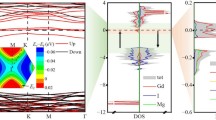
Topological quantum phases in two-dimensional materials have been a fascinating research topic since the discovery of graphene. Particularly, the topological quantum phases could appear in two-dimensional magnetic systems. However, identifying concrete materials that host topological quantum phases is still a challenge, especially the magnetic ones. In this work, we propose a novel hybrid Weyl semimetal in two dimensions, the monolayer AgCrS2. We show that this material has a stable ferromagnetic ground state with an in-plane magnetic moment. Particularly, it hosts a hybrid of two Weyl nodes close to the Fermi level: one is a double Weyl point, and the other one is type-II linear Weyl point. The features of their band structure could be inferred from the effective models for them. When the spin-orbital coupling is included, the double Weyl point is gapped. In comparison, the type-II linear Weyl nodes on high-symmetry path can be tuned by controlling the orientation of the magnetization direction. To be specific, the magnetization could change locations of type-II linear Weyl nodes and control its stability. Therefore, our results offer a platform to study novel hybrid of Weyl nodes in two-dimensional ferromagnetic system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ezawa M (2012) Valley-polarized metals and quantum anomalous Hall effect in silicene. Phys Rev Lett 109:055502. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.055502
Ezawa M (2013) Spin valleytronics in silicene: quantum spin Hall–quantum anomalous Hall insulators and single-valley semimetals. Phys Rev B 87:155415. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.87.155415
Zhang L, Bampoulis P, Rudenko AN, Yao Q, van Houselt A, Poelsema B, Katsnelson MI, Zandvliet HJW (2016) Structural and electronic properties of germanene on MoS2. Phys Rev Lett 116:256804. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.256804
Amlaki T, Bokdam M, Kelly PJ (2016) Z2 invariance of Germanene on MoS2 from first principles. Phys Rev Lett 116:256805. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.256805
Tang P, Chen P, Cao W, Huang H, Cahangirov S, Xian L, Xu Y, Zhang SC, Duan W, Rubio A (2014) Stable two-dimensional dumbbell stanene: a quantum spin Hall insulator. Phys Rev B 90:121408. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.90.121408
De Martino A, Dell’Anna L, Egger R (2007) Magnetic confinement of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Phys Rev Lett 98:066802. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.066802
Park CH, Yang L, Son YW, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2008) New generation of massless Dirac fermions in graphene under external periodic potentials. Phys Rev Lett 101:126804. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.126804
Zhou XF, Dong X, Oganov AR, Zhu Q, Tian Y, Wang HT (2014) Semi-metallic two-dimensional boron allotrope with massless Dirac fermions. Phys Rev Lett 112:085502. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.085502
Nomura K, MacDonald AH (2007) Quantum transport of massless Dirac fermions. Phys Rev Lett 98:076602. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.076602
Castro Neto AH, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2009) The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys 81:109. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.109
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Zhang DJ, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306:666–669. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
Zhou SY, Gweon GH, Graf J, Fedorov AV, Spataru CD, Diehl RD, Kopelevich Y, Leel DH, Steven G, Lanzara A (2006) First direct observation of Dirac fermions in graphite. Nature Phys 2:595–599. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys393
Young SM, Kane CL (2015) Dirac semimetals in two dimensions. Phys Rev Lett 115:126803. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.126803
Fashandi H, Ivády V, Eklund P, Spetz AL, Katsnelson MI, Abrikosov IA (2015) Dirac points with giant spin-orbit splitting in the electronic structure of two-dimensional transition-metal carbides. Phys Rev B 92:155142. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.92.155142
Wu H, Qian Y, Du Z, Zhu R, Kan E, Deng K (2017) Prediction of another semi-metallic silicene allotrope with Dirac fermions. Phys Lett A 381:3754–3759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2017.09.049
Meng W, Zhang X, Yu W, Liu Y, Tian L, Dai X, Liu G (2021) Multiple Weyl fermions and tunable quantum anomalous Hall effect in 2D half-metal with huge spin-related energy gap. Appl Surf Sci 551:149390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149390
Zhu L, Wang SS, Guan S, Liu Y, Zhang T, Chen G, Yang SA (2016) Blue phosphorene oxide: strain-tunable quantum phase transitions and novel 2D emergent fermions. Nano Lett 16:6548–6554. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03208
Guan S, Liu Y, Yu ZM, Wang SS, Yao Y, Yang SA (2017) Two-dimensional spin-orbit Dirac point in monolayer HfGeTe. Phys Rev Mater 1:054003. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.1.054003
Jin YJ, Wang R, Zhao JZ, Du YP, Zheng CD, Gan LY, Liu JF, Xu H, Tong S (2017) The prediction of a family group of two-dimensional node-line semimetals. Nanoscale 9:13112–13118. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR03520A
Li S, Liu Y, Wang SS, Yu ZM, Guan S, Sheng XL, Yao Y, Yang SA (2018) Nonsymmorphic-symmetry-protected hourglass Dirac loop, nodal line, and Dirac point in bulk and monolayer X3SiTe6 (X= Ta, Nb). Phys Rev B 97:045131. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.045131
Feng B, Fu B, Kasamatsu S, Ito S, Cheng P, Liu CC, Feng Y, Wu S, Mahatha SK, Sheverdyaeva P, Moras P, Arita M, Sugino O, Chiang TC, Shimada K, Miyamoto K, Okuda T, Wu K, Chen L, Yao Y, Matsuda I (2017) Experimental realization of two-dimensional Dirac nodal line fermions in monolayer Cu2Si. Nat Comm 8:1007. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01108-z
Yang LM, Bacic V, Popov IA, Boldyrev AI, Heine T, Frauenheim T, Ganz E (2015) Two-dimensional Cu2Si monolayer with planar hexacoordinate copper and silicon bonding. J Am Chem Soc 137:2757–2762. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja513209c
Zhang X, Jin L, Dai X, Liu G (2017) Topological type-II nodal line semimetal and Dirac semimetal state in stable kagome compound Mg3Bi2. J Phys Chem Lett 8:4814–4819. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b02129
Sharma G, Goswami P, Tewari S (2017) Chiral anomaly and longitudinal magnetotransport in type-II Weyl semimetals. Phys Rev B 96:045112. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.96.045112
He T, Zhang X, Wang L, Liu Y, Dai X, Wang L, Liu G (2021) Ideal fully spin-polarized type-II nodal line state in half-metals X2YZ4 (X= K, Cs, Rb, Y=Cr, Cu, Z= Cl, F). Mater Today Phys 17:100360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100360
Meng W, Zhang X, Liu Y, Dai X, Liu G (2021) Antiferromagnetism caused by excess electrons and multiple topological electronic states in the electride Ba4Al5·e−. Phys Rev B 104:195145. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.104.195145
Meng W, Zhang X, He T, Jin L, Dai X, Liu Y, Liu G (2020) Ternary compound HfCuP: an excellent Weyl semimetal with the coexistence of type-I and type-II Weyl nodes. J Adv Res 24:523–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.05.026
Soluyanov AA, Gresch D, Wang Z, Wu Q, Troyer M, Dai X, Bernevig BA (2015) Type-ii Weyl semimetals. Nature 527:495–498. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15768
Wang Z, Gresch D, Soluyanov AA, Xie W, Kushwaha S, Dai X, Troyer M, Cava RJ, Bernevig BA (2016) MoTe2: a type-II Weyl topological metal. Phys Rev Lett 117:056805. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.056805
Koepernik K, Kasinathan D, Efremov DV, Khim S, Borisenko S, Büchner B, van den Brink J (2016) TaIrTe4: a ternary type-II Weyl semimetal. Phys Rev B 93:201101(R). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.93.201101
Chang G, Xu SY, Sanchez DS, Huang SM, Lee CC, Chang TR, Bian G, Zheng H, Belopllski I, Alidoust N, Jeng HT, Bansil A, Lin H, Hasan MZ (2016) A strongly robust type II Weyl fermion semimetal state in Ta3S2. Sci adv 2:e1600295. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1600295
Meng W, Zhang X, Liu Y, Wang L, Dai X, Liu G (2021) Two-dimensional Weyl semimetal with coexisting fully spin-polarized type-I and type-II Weyl points. Appl Surf Sci 540:148318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148318
Peng J, Liu Y, Lv H, Li Y, Lin Y, Su Y, Wu J, Liu H, Guo Y, Zhuo Z, Wu X, Wu C, Xie Y (2021) Stoichiometric two-dimensional non-van der Waals AgCrS2 with superionic behavior at room temperature. Nat Chem 13:1235–1240. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-021-00800-4
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 59:1758. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758
Blochl PE (1994) Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B 50:17953. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.50.17953
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865
Grimme S (2006) Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J Comput Chem 27:1787–1799. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20495
Anisimov VI, Zaanen J, Andersen OK (1991) Band theory and Mott insulators: Hubbard U instead of Stoner I. Phys Rev B 44:943. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.44.943
Wu QS, Zhang SN, Song HF, Troyer M, Soluyanov AA (2018) WannierTools: an open-source software package for novel topological materials. Comput Phys Commun 224:405–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2017.09.033
Xu W, Ali S, Jin Y, Wu X, Xu H (2020) Intrinsic ferromagnetic semiconductors in two-dimensional alkali-based chromium chalcogenides. ACS Appl Electron Mater 2:3853–3858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.0c00686
Wang W, Dai S, Li X, Yang J, Srolovitz DJ, Zheng Q (2015) Measurement of the cleavage energy of graphite. Nat Commun 6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8853
Jing Y, Ma Y, Li Y, Heine T (2017) GeP3: a small indirect band gap 2D crystal with high carrier mobility and strong interlayer quantum confinement. Nano Lett 17:1833–1838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05143
Miao N, Xu B, Bristowe NC, Zhou J, Sun Z (2017) Tunable magnetism and extraordinary sunlight absorbance in indium triphosphide monolayer. J Am Chem Soc 139:11125–11131. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.256804
Zhao S, Li Z, Yang J (2014) Obtaining two-dimensional electron gas in free space without resorting to electron doping: an electride based design. J Am Chem Soc 136:13313–13318. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja5065125
Wang H, Liu E, Wang Y, Wan B, Ho CH, Miao F, Wan XG (2017) Cleavage tendency of anisotropic two-dimensional materials: ReX2 (X= S, Se) and WTe2. Phys Rev B 96:165418. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.96.165418
Ushakov AV, Kukusta DA, Yaresko AN, Khomskii DI (2013) Magnetism of layered chromium sulfides MCrS2 (M= Li, Na, K, Ag, and Au): a first-principles study. Phys Rev B 87:014418. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.87.014418
Damay F, Martin C, Hardy V, Andre G, Petit S, Maignan A (2011) Magnetoelastic coupling and unconventional magnetic ordering in the multiferroic triangular lattice AgCrS2. Phys Rev B 83:184413. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.83.184413
Evans RF, Fan WJ, Chureemart P, Ostler TA, Ellis MO, Chantrell RW (2014) Atomistic spin model simulations of magnetic nanomaterials. J Phys Condens Matter 26:103202. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/26/10/103202
Zhu Y, Xu S, Chen T, Cheng X, Fang L, Hu S, Hu T, Jia F, Gao H, Ren W (2022) Prediction of 2D ferromagnetic metal VNI monolayer with tunable topological properties. J Appl Phys 132:183913. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0107680
Yu WW, Liu Y, Meng W, Liu H, Gao J, Zhang X, Liu G (2022) Phononic higher-order nodal point in two dimensions. Phys Rev B 105:035429. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.105.035429
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 11904074). The work is funded by the Science and Technology Project of the Hebei Education Department, the Nature Science Foundation of Hebei Province, the S&T Program of Hebei (No. A2021202012), the Overseas Scientists Sponsorship Program by Hebei Province (C20210330), and the fund from the State Key Laboratory of Reliability and Intelligence of Electrical Equipment of Hebei University of Technology (No. EERI_PI2020009). One of the authors (X.M.Z.) acknowledges financial support from the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by Tianjin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Kevin Jones.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Liu, Y., Dai, X. et al. A ferromagnetic hybrid Weyl semimetal in two dimensions: the monolayer AgCrS2. J Mater Sci 58, 281–290 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08043-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08043-5