Abstract
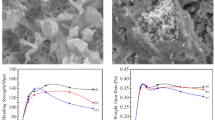
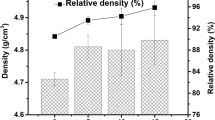
The composite ceramics (NiMn2O4)0.50(La1−x Ca x MnO3)0.50 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.3) consisting of spinel-structured NiMn2O4 and perovskite-structured CaO-doped LaMnO3 were prepared by classical solid state reaction. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns have shown that the major phases presented in the sintered samples are NiMn2O4 compounds with a spinel structure, La1−x Ca x MnO3 with a perovskite structure. The Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) pictures have exhibited that the grain size of the composite ceramics decreases from ca. 6.5 to 2.0 μm as the mole fraction of CaO increases from 0 to 0.3. The ρ 25 °C and B 25/50 constants of the composite samples are in the range of 0.234–8.61 Ω cm and 2,600–2,962 K, respectively. In particular, CaO-doped leads to a decrease in the resistance drift of the (NiMn2O4)0.50(La1−x Ca x MnO3)0.50 composite NTC (negative temperature coefficient) ceramics after aging test. This indicates that the CaO-doped (NiMn2O4)0.50(La1−x Ca x MnO3)0.50 NTC ceramics display high electrical stability in comparison with the Ca-free (NiMn2O4)0.50(LaMnO3)0.50 ceramics. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis verifies that the valence states of the manganese ions have a highly mixed state of Mn2+, Mn3+ and Mn4+ at B site. And the electrical conduction of the composite ceramics can be elaborated by the ions migration mechanism.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Feteira, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 967 (2009)
M.M. Vakiv, O.I. Shpotyuk, V.O. Balitska, B. Butkiewicz, L.I. Shpotyuk, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1243 (2004)
T. Yokoyama, T. Meguro, Y. Shimada, J. Tatami, K. Komeya, Y. Abe, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 5860 (2007)
T. Yokoyama, T. Meguro, Y. Shimada, J. Tatami, K. Komeya, Y. Abe, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 5860 (2007)
R.N. Jadhav, V. Puri, J. Alloy Compd. 507, 151 (2010)
Z.B. Wang, C.H. Zhao, C.S. Chen, A.J.A. Winnubst, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2833 (2006)
K. Park, J.K. Lee, S.J. Kim, W.S. Seo, W.S. Cho, C.W. Lee, S. Nahm, J. Alloy Compd. 467, 310 (2009)
C.H. Zhao, Z.B. Wang, S.M. Wang, P.H. Yang, C.S. Chen, J. Electroceram. 20, 113 (2008)
W. Luo, H.M. Yao, P.H. Yang, C.S. Chen, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 2682 (2009)
M.L. Singla, S. Awasthi, A. Srivastava, D.V.S. Jain, Sens. Actuators A 136, 604 (2007)
I. Maurin, P. Barboux, Y. Lassailly, J.P. Boilot, J. Solid State Chem. 160, 123 (2001)
Z. Branković, K. Ðuriš, A. Radojković, S. Bernik, Z. Jaglićić, M. Jagodić, K. Vojisavljevic, J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 55, 311 (2010)
S. Guillemet-Fritsch, J.L. Baudour, C. Chanel, F. Bouree, A. Rousset, Solid State Ion. 132, 63 (2000)
R.D. Shannon, Acta Cryst. A 32, 751 (1976)
K. Park, I.H. Han, J. Electroceram. 17, 1079 (2006)
P.N. Lisboa-Filho, M. Bahout, P. Barahona, C. Moure, O. Pena, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66, 1206 (2005)
Y. Boudeville, F. Fiqueras, M. Forissier, J.L. Portefaix, J.C. Vedrine, J. Catal. 58, 52 (1979)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50902148) and the “Western Light Joint Scholar Foundation” Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. RCPY200901) for providing the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, F., Zhang, H., Chang, A. et al. Effect of CaO-doped in NiMn2O4–LaMnO3 composite ceramics on microstructure and electrical properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 1728–1733 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0654-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-0654-4