Abstract
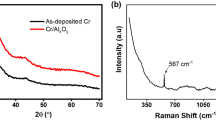
This work investigated the effect of thermal treatment of as-deposited chromium (Cr) thin films in a vacuum and argon/oxygen ambient for effective deposition of spectral selective solar absorber multilayer films. The DC sputtered Cr thin films were thermally exposed at different temperatures in a controlled argon/oxygen environment. Both as-deposited films and those thermally treated in vacuum and in oxygen–argon ambient revealed a weak XRD diffraction peak at 2θ≈44.3° corresponding to (110) plane of BCC structure of Cr metal. Raman analysis revealed one peak at 846 cm−1 corresponding to Cr–O vibration bonds for films thermally treated at 300 °C in a vacuum and 150 °C and 300 °C in argon–oxygen ambient. As determined by AFM and FE-SEM, surface roughness decreased with temperature increase for films thermally treated in a vacuum. Besides, a mixed trend in the evolution of surface roughness was observed for films thermally treated in argon/oxygen ambient. The average spectral transmittance for samples thermally treated in a vacuum decreased with an increase in temperature; however, the samples thermally treated in an argon–oxygen environment exhibited an increasing trend in average spectral transmittance with the increase in temperature. The results clearly show that post-deposition processing at elevated temperatures, particularly in argon–oxygen ambient, influences the structural and optical properties of prior-deposited Cr thin films. This should be considered when designing and depositing multi-layered dielectric/Cr spectral selective solar absorber films.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
R.T. Kivaisi, L. Stensland, Appl. Phys. A (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619084
G. Katumba, J. Lu, L. Olumekor, G. Westin, E. Wäckelgård, J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-005-4793-4
T.K. Tsai, S.J. Hsueh, J.H. Lee, J.S. Fang, J. Electron. Mater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-011-1746-2
Y. Li, C. Lin, D. Zhou, Y. An, D. Li, C. Chi, H. Huang, S. Yang, C.Y. Tso, C.Y. Chao, B. Huang, Nano Energy (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.103947
K. Xu, M. Du, L. Hao, J. Mi, Q. Yu, S. Li, J. Materiom. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2019.12.012
A. Foroughi-Abari, C. Xu, K.C. Cadien, Thin Solid Films (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2011.08.063
A. Rauf, K. Ahmed, F. Nasim, A.N. Khan, A. Gul, I.O.P. Conf, Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/146/1/012013
J. Peralta, J. Esteve, A. Lousa, Thin Solid Films (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2019.137676
Z.Y. Nuru, M. Msimanga, T.F.G. Muller, C.J. Arendse, C. Mtshali, M. Maaza, Sol. Energy (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2014.11
A.B. Khelifa, S. Khamlich, Z.Y. Nuru, L. Kotsedi, A. Mebrahtu, M. Balgouthi, A.A. Guizani, W. Dimassi, M. Maaza, J. Alloys Compds. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.036
Z. Zeng, L. Wang, L. Chen, J. Zhang, Surf. Coat. Technol. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.03.038
X.Z. Wang, H.Q. Fan, T. Muneshwar, K. Cadien, J.L. Luo, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.06.012
H. Barshilia, N. Selvakumar, K. Rajam, A. Biswas, J. Appl. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2831364
S.F. Wang, H.C. Lin, H.Y. Bor, Y.L. Tsai, C.N. Wei, J. Alloys Compds. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.08.052
J.J. Tibaijuka, M.E. Samiji, M. Diale, N.R. Mlyuka, Tanz. J. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.4314/tjs.v48i3.13
F. Maury, A. Douard, S. Delclos, D. Samelor, C. Tendero, Surf. Coat. Technol. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.04.020
M. Muralidhar Singh, G. Vijaya, M.S. Krupashankara, B.K. Sridhara, T.N. Shridhar, Mater. Today: Proc. 5, 2696 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.01.050
N.R. Mlyuka, PhD Thesis, University of Dar es Salaam (2010)
E.R. Ollotu, N.R. Mlyuka, M.E. Samiji, Tanz. J. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.4314/tjs.v47i2
N.R. Moody, D.P. Adams, A.A. Volinsky, M.D. Kriese, W.W. Gerberich, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-586-195
R.T. Kivaisi, Sol. Energy Mater. (1981). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1633(81)90023-X
R.A. Miller, E. Carl, Lowell (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6090(82)90019-0
C.T. Rueden, J. Schindelin, M.C. Hiner, B.E. DeZonia, A.E. Walter, E.T. Arena, K.W. Eliceiri, BMC Bioinform. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1934-z
I. Horcas, R. Fernández, J.M. Gómez-Rodríguez, J. Colchero, J. Gómez-Herrero, A.M. Baro, Rev. Sci. Instrum. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2432410h
F.D. Hardcastle, I.E. Wachs, J. Mol. Catal. (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-5102(88)85092-2
A.K. Yadav, P. Singh, RSC Adv. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0xx00000x
A. Kumar, D. Pednekar, S. Mukherjee, R.K. Choubey, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04263-0
B. Hymavathi, B. Rajesh Kumar, T. Subba Rao, J. Electron. Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5799-8
J.J. Tibaijuka, M.E. Samiji, N.R. Mlyuka, Tanz. J. Sci. 48, 660 (2018)
D. Naveena, T. Logu, K. Sethuraman, A. Chandra Bose, J. Alloys Compds. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04
S. Baturay, A. Tombak, D. Kaya, Y.S. Ocak, M. Tokus, M. Aydemir, T. Kilicoglu, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3953-4
A. Kumar, M. Kumar, V. Bhatt, S. Mukherjee, S. Kumar, H. Sharma, M.K. Yadav, S. Tomar, J. Yun, R.K. Choubey, Sens. Actuator A Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112988
M. Hezam, N. Tabet, A. Mekki, Thin Solid Films (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2010.03.091
G.P. Daniel, V.B. Justinvictor, P.B. Nair, K. Joy, P. Koshy, P.V. Thomas, Phys. B Condens. Matter. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.01.039
P. Eaton, P. West, Atomic Force Microscopy, 1st edn. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2010), pp.104–121
O. Malik, F.J. De la Hidalga-Wade, J. Mater. Res. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.159
E.R. Ollotu, J.S. Nyarige, N.R. Mlyuka, M.E. Samiji, M. Diale, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04192-y
K.H. Choi, J.Y. Kim, Y.S. Lee, H.J. Kim, Thin Solid Films (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(98)01556-9
Acknowledgements
J.T gratefully thanks the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology of Tanzania (MoEST) for a scholarship. The authors thank the University of Dar es Salaam -Tanzania, University of Pretoria—South Africa, Materials Science and Solar Energy Network for Eastern and Southern Africa (MSSEESA), SARCHI UID No.115463 and the International Science Programme (ISP)—Uppsala University, Sweeden for research facilities and materials, as well as logistical and financial support during J.T. laboratory stay in the University of Pretoria.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology of Tanzania (MoEST) for a scholarship. In addition, The University of Dar es Salaam—Tanzania, University of Pretoria – South Africa, Materials Science and Solar Energy network for Eastern and Southern Africa (MSSEESA), SARCHI UID No.115463 and the International Science Programme (ISP)—Uppsala University, Sweeden supported the research facilities and materials, as well as logistical and financial support during JJ Tibaijuka laboratory stay in the University of Pretoria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conceptualization. Sample preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by JJT. JSN was involved in SEM, Raman and XRD characterization. NRM, MD and MES were involved in financial acquisition and supervision of work. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JJT and all authors reviewed and edited on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tibaijuka, J.J., Nyarige, J.S., Diale, M. et al. The effects of thermal treatment under argon–oxygen ambient on the microstructure and optical properties of DC sputtered Cr thin films for selective solar absorbers applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 173 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09571-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09571-1