Abstract
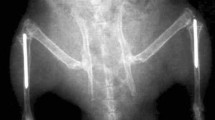
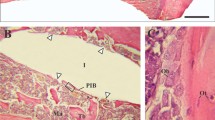
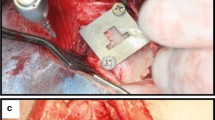
Permanent metal implants are widely used in human medical treatments and orthopedics, for example as hip joint replacements. They are commonly made of titanium alloys and beyond the optimization of this established material, it is also essential to explore alternative implant materials in view of improved osseointegration. The aim of our study was to characterize the implant performance of zirconium in comparison to titanium implants. Zirconium implants have been characterized in a previous study concerning material properties and surface characteristics in vitro, such as oxide layer thickness and surface roughness. In the present study, we compare bone material quality around zirconium and titanium implants in terms of osseointegration and therefore characterized bone material properties in a rat model using a multi-method approach. We used light and electron microscopy, micro Raman spectroscopy, micro X-ray fluorescence and X-ray scattering techniques to investigate the osseointegration in terms of compositional and structural properties of the newly formed bone. Regarding the mineralization level, the mineral composition, and the alignment and order of the mineral particles, our results show that the maturity of the newly formed bone after 8 weeks of implantation is already very high. In conclusion, the bone material quality obtained for zirconium implants is at least as good as for titanium. It seems that the zirconium implants can be a good candidate for using as permanent metal prosthesis for orthopedic treatments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Navarro M, Michiardi A, Castaño O, Planell JA. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J R Soc Interface. 2008;5(27):1137–58. doi:10.1098/rsif 2008.0151.
Messaddeq SH, Pulcinelli SH, Santilli CV, Guastaldi AC, Messaddeq Y. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of inorganic-organic (ZrO2-PMMA) hybrid coating on stainless steel. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1999;247:164–70. doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(99)00058-7.
Neumann HG, Beck U, Drawe M, Steinbach J. Multilayer systems for corrosion protection of stainless steel implants. Surf Coat Tech. 1998;98(1–3):1157–61. doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(97)00236-3.
Chou TP, Chandrasekaran C, Limmer SJ, Seraji S, Wu Y, Forbess MJ, et al. Organic–inorganic hybrid coatings for corrosion protection. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2001;290(2–3):153–62. doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(01)00818-3.
Fathi MH, Moosavi S, Mortazavi V. Novel materials for endodontic implant, in vitro and in vivo tests. Dent Res J. 2003;1(1):36–46.
Mehdikhani-Nahrkhalaji M, Fathi MH, Mortazavi V, Mousavi SB, Hashemi-Beni B, Razavi SM. Novel nanocomposite coating for dental implant applications in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(2):485–95.
Krupa D, Baszkiewicz J, Sobczak JW, Biliński A, Barcz A. Modifying the properties of titanium surface with the aim of improving its bioactivity and corrosion resistance. J Mater Process Tech. 2003;143:158–63. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00398-4.
Rodríguez HH, Vargas G, Cortés DA. Electrophoretic deposition of bioactive wollastonite and porcelain-wollastonite coatings on 316L stainless steel. Ceram Int. 2008;34(5):1303–7. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.03.002.
Yang BC, Uchida M, Kim HM, Zhang XD, Kokubo T. Preparation of bioactive titanium metal via anodic oxidation treatment. Biomaterials. 2004;25(6):1003–10. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00626-4.
Cabrini RL, Guglielmotti MB, Almagro JC. Histomorphometry of initial bone healing around zirconium implants in rats. Implant Dent. 1993;2(4):264–7.
Saldaña L, Méndez-Vilas A, Jiang L, Multigner M, González-Carrasco JL, Pérez-Prado MT, et al. In vitro biocompatibility of an ultrafine grained zirconium. Biomaterials. 2007;28(30):4343–54. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.06.015.
Wang K. The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA. Mat Sci Eng A. 1996;213(1–2):134–7. doi:10.1016/0921-5093(96)10243-4.
Scarano A, Piattelli M, Caputi S, Favero GA, Piattelli A. Bacterial adhesion on commercially pure titanium and zirconium oxide disks: an in vivo human study. J Periodontol. 2004;75(2):292–6. doi:10.1902/jop.2004.75.2.292.
Gomez Sanchez A, Schreiner W, Duffó G, Ceré S. Surface modification of titanium by anodic oxidation in phosphoric acid at low potentials. Part 1. Structure, electronic properties and thickness of the anodic films. Surf Interface Anal. 2013;45(6):1037–46. doi:10.1002/sia.5210.
Gomez Sanchez A, Ballarre J, Orellano JC, Duffó G, Ceré S. Surface modification of zirconium by anodisation as material for permanent implants: in vitro and in vivo study. J Mater Sci. 2012;. doi:10.1007/s10856-012-4770-8.
Gomez Sanchez A, Schreiner W, Duffó G, Ceré S. Surface characterization of anodized zirconium for biomedical applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;257(15):6397–405. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.02.005.
Ballarre J, Seltzer R, Mendoza E, Orellano JC, Mai YW, Garcia C, et al. Morphologic and nanomechanical characterization of bone tissue growth around bioactive sol-gel coatings containing wollastonite particles applied on stainless steel implants. Mat Sci Eng C. 2011;31(3):545–52. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2010.11.030.
Sul YT, Johansson CB, Jeong Y, Albrektsson T. The electrochemical oxide growth behaviour on titanium in acid and alkaline electrolytes. Med Eng Phys. 2001;23(5):329–46. doi:10.1016/S1350-4533(01)00050-9.
Ballarre J, Manjubala I, Schreiner WH, Orellano JC, Fratzl P, Cere S. Improving the osteointegration and bone-implant interface by incorporation of bioactive particles in sol-gel coatings of stainless steel implants. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1601–9. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2009.10.015.
Perez CA, Radtke M, Sanchez HJ, Tolentino H, Neuenshwander RT, Barg W, et al. Synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence at the LNLS: beamline instrumentation and experiments. X-Ray Spectrom. 1999;28(5):320–6. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4539(199909/10)28:5<320:AID-XRS359>3.0.CO;2-1.
Sole VA, Papillon E, Cotte M, Walter P, Susini J. A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim Acta B. 2007;62(1):63–8. doi:10.1016/j.sab.2006.12.002.
Rinnerthaler S, Roschger P, Jakob HF, Nader A, Klaushofer K, Fratzl P. Scanning small angle X-ray scattering analysis of human bone sections. Calcif Tissue Int. 1999;64(5):422–9. doi:10.1007/Pl00005824.
Roschger P, Gupta HS, Berzanovich A, Ittner G, Dempster DW, Fratzl P, et al. Constant mineralization density distribution in cancellous human bone. Bone. 2003;32(3):316–23. doi:10.1016/S8756-3282(02)00973-0.
Gamsjaeger S, Masic A, Roschger P, Kazanci M, Dunlop JWC, Klaushofer K, et al. Cortical bone composition and orientation as a function of animal and tissue age in mice by Raman spectroscopy. Bone. 2010;47(2):392–9. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.04.608.
Yerramshetty JS, Akkus O. The associations between mineral crystallinity and the mechanical properties of human cortical bone. Bone. 2008;42(3):476–82. doi:10.1016/j.bon.2007.12.001.
Penel G, Leroy G, Rey C, Bres E. MicroRaman spectral study of the PO4 and CO3 vibrational modes in synthetic and biological apatites. Calcif Tissue Int. 1998;63(6):475–81. doi:10.1007/s002239900561.
Donnelly E, Boskey AL, Baker SP, van der Meulen MCH. Effects of tissue age on bone tissue material composition and nanomechanical properties in the rat cortex. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92A(3):1048–56. doi:10.1002/Jbm.A.32442.
Mendonça G, Mendonça DBS, Aragão FJL, Cooper LF. Advancing dental implant surface technology: from micron- to nanotopography. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28):3822–35. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.05.012.
Sul YT, Kang BS, Johansson C, Um HS, Park CJ, Albrektsson T. The roles of surface chemistry and topography in the strength and rate of osseointegration of titanium implants in bone. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;89A(4):942–50. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32041.
Sul YT. The significance of the surface properties of oxidized titanium to the bone response: special emphasis on potential biochemical bonding of oxidized titanium implant. Biomaterials. 2003;24(22):3893–907. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00261-8.
Hanawa T. In vivo metallic biomaterials and surface modification. Mat Sci Eng A. 1999;267(2):260–6. doi:10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00101-X.
Cipriano CA, Issack PS, Beksac B, Della Valle AG, Sculco TP, Salvati EA. Metallosis after metal-on-polyethylene total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop. 2008;37(2):E18–25.
Kerschnitzki M, Wagermaier W, Liu YF, Roschger P, Duda GN, Fratzl P. Poorly ordered bone as an endogenous scaffold for the deposition of highly oriented lamellar tissue in rapidly growing ovine bone. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194(2–4):119–23. doi:10.1159/000324467.
Liu YF, Manjubala I, Schell H, Epari DR, Roschger P, Duda GN, et al. Size and habit of mineral particles in bone and mineralized callus during bone healing in sheep. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(9):2029–38. doi:10.1002/Jbmr.84.
Guglielmotti MB, Guerrero C, Cabrini RL. Chronodynamic evaluation of the stages of osseointegration in zirconium laminar implants. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 1997;10(1):11–23.
Cipitria A, Lange C, Schell H, Wagermaier W, Reichert JC, Hutmacher DW, et al. Porous scaffold architecture guides tissue formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(6):1275–88.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank C. Li, S. Siegel, I. Zenke, and B. Schonert for technical support, the Max Planck Gesellschaft (MPG), the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD), and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for funding. Contributions were made possible by DFG funding through the Berlin-Brandenburg School for Regenerative Therapies. As well, we would like to thank A. Cisilino, B. Valcarce, M. Valdes (INTEMA, UNMdP), and C. Perez (LNLS), for the grateful help in different areas of this study and the Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS). We also want to thank the National Research Council of Argentina (CONICET), the National Agency for Science and Technology Promotion (ANPCyT - PICT 00550 and 0917), and the National University of Mar del Plata (UNMdP - 15/G331) for financial support. We especially want to thank the PROALAR exchange program (DAAD funding together with MINCyT, Argentina) for enabling the exchanges between our institutes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Results for the SAXS measurements performed with the same samples as in Fig. 5 but within the epiphysis (TIFF 2709 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoerth, R.M., Katunar, M.R., Gomez Sanchez, A. et al. A comparative study of zirconium and titanium implants in rat: osseointegration and bone material quality. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 411–422 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-5074-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-5074-3