Abstract
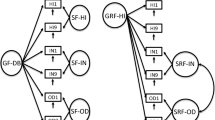
This study examined the test-retest measurement invariance of ratings of the ADHD symptoms. Mothers of a group of 217 clinic-referred children (boys = 169, girls = 49; age range = 7 to 17 years) completed ratings of the ADHD symptoms presented in a modified version of the Strengths and Weaknesses of ADHD-Symptoms and Normal Behavior Scale (SWAN-M) twice, 12 months apart. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) of their ratings at both time points provided more support for the bifactor model of ADHD [orthogonal general and specific factors for inattention (IA) and hyperactivity/impulsivity (HI) symptoms] over the 2-factor oblique model (factors for inattention IA and HI symptoms). For the bifactor model, measurement invariance testing using multiple-group CFA indicated support for configural and full scalar test-retest invariance when the chi-square difference test was applied. For metric invariance, all but one symptom showed invariance. When the differences in approximate fit indices were applied, there was support for full measurement invariance (configural, metric and scalar). The findings indicate that observed scores (based on maternal ratings of the SWAM-M), twelve months apart, are comparable as they have the same measurement properties. Several practical, theoretical, research and clinical implications of the findings are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Achenbach T. M., Rescorla L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth and Families
Aman, M. G., & Pearson, D. A. (1999). Monitoring, measuring drug effects. II. Behavioral, emotional, and cognitive effects. In J. S. Werry & M. G. Aman (Eds.), Practitioner's guide to psychoactive drugs for children and adolescents. 2 nd (pp. 99–164). New York: Plenum Press.
American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, National Council on Measurement in Education, Joint Committee on Standards for Educational, & Psychological Testing (US). (2014). Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington: American Educational Research Association.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders DSM-IV TR (text revision). Washington: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington: Author.
Arias, V. B., Ponce, F. P., Martínez-Molina, A., Arias, B., & Núñez, D. (2016a). General and specific attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder factors of children 4 to 6 years of age: An exploratory structural equation modeling approach to assessing symptom multidimensionality. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 125, 125–137.
Arias, V. B., Ponce, F. P, Nunez, D. E (2016b) Bifactor models of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): An evaluation of three necessary but underused psychometric indexes. Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191116679260.
Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. (2006). Robust chi square difference testing with mean and variance adjusted test statistics. Mplus web notes: No. 10. May 26, 2006.
Australian Bureau of Statistics. (2002). 2002 year book Australia. Canberra: ABS.
Biederman, J., Mick, E., & Faraone, S. V. (2000). Age-dependent decline of symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Impact of remission definition and symptom type. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157, 816–818.
Bonifay, W. E., Reise, S. P., Scheines, R., & Meijer, R. R. (2015). When are multidimensional data unidimensional enough for structural equation modeling? An evaluation of the DETECT multidimensionality index. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 22(4), 504–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2014.938596.
Brown, T. A. (2006). Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research. New York: Guilford Press.
Brunner, M., Nagy, G., & Wilhelm, O. (2012). A tutorial on hierarchically structured constructs. Journal of Personality, 80, 796–846. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.2011.00749.x.
Burns, G. L., Walsh, J. A., Servera, M., Lorenzo-Seva, U., Cardo, E., & Rodríguez-Fornells, A. (2013). Construct validity of ADHD/ODD rating scales: Recommendations for the evaluation of forthcoming DSM-V ADHD/ODD scales. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 41, 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9660-5.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling, 14, 464–504.
Cheung, G. W. (2008). Testing equivalency in the structure, means, and variances of higher-order constructs with structural equation modelling. Organizational Research Methods, 11, 593–613.
Conners, C. K. (2008). Conners (3rd ed.). North Tonawanda: Multi-Health Systems.
Daley, D. (2006). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A review of the essential facts. Child: Care, Health and Development, 32, 193–204.
Drasgow, F., & Kanfer, R. (1985). Equivalence of psychological measurement in heterogeneous populations. Journal of Applied Psychology, 70, 662–680.
DuPaul, G. J., Power, T. P., Anastopoulos, A. D., & Reid, R. (1998). ADHD rating scale-IV. New York: Guilford Press.
DuPaul, G. J., Power, T. P., Anastopoulos, A. D., & Reid, R. (2016). ADHD rating Scale-5. New York: Guilford Press.
Eich, D., Angst, J., Frei, A., Ajdacic-Gross, V., Rossler, W., & Gamma, A. (2012). A new rating scale for adult ADHD based on the symptom checklist 90 (SCL-90-R). European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 262, 519–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0288-1.
Gau, S. S. F., Lin, Y. J., Cheng, A. T. A., Chiu, Y. N., Tsai, W. C., & Soong, W. T. (2010). Psychopathology and symptom remission at adolescence among children with attention deficit–hyperactivity disorder. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 44, 323–332.
Gaub, M., & Carlson, C. L. (1997). Behavioral characteristics of DSM-IV ADHD subtypes in a school-based population. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25, 103–111.
Gomez, R., Harvey, J., Quick, C., Scharer, I., & Harris, G. (1999). DSM-IV AD/HD: Confirmatory factor models, prevalence, and gender and age differences based on parent and teacher ratings of Australian primary school children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 40, 265–274.
Gomez, R., Burns, G. L., Walsh, J. A., & Moura, M. A. (2003). Trait, source and error variance in ADHD symptoms: A multitrait-multisource analysis with Australian and Brazilian children. Psychological Assessment, 15, 3–16.
Gomez, R., Vance, A., & Gomez, R. M. (2013). Validity of the ADHD bifactor model in general community samples of adolescents and adults, and a clinic-referred sample of children and adolescents. Journal of Attention Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054713480034.
Grills, A. E., & Ollendick, T. H. (2003). Multiple informant agreement and the anxiety disorders interview schedule for parents and children. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 42, 30–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200301000-00008.
Hart, E. L., Lahey, B. B., Loeber, R., Applegate, B., & Frick, P. J. (1995). Developmental change in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in boys: A four-year longitudinal study. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 23, 729–749.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1998). Fit indices in covariance structure modeling: Sensitivity to underparameterized model misspecification. Psychological Methods, 3, 424–453.
Jarrett, M. A., Wolff, J. C., & Ollendick, T. H. (2007). Concurrent validity and informant agreement of the ADHD module of the anxiety disorders interview schedule for DSM-IV. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 29, 159–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-006-9041-x.
Jensen, P. S., Rubio-Stipec, M., Canino, G., Bird, H. R., Dulcan, M. K., Schwab-Stone, M. E., & Lahey, B. B. (1999). Parent and child contributions to diagnosis of mental disorder: Are both informants always necessary? Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 38, 1569–1579. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199912000-00019.
Jones, C. (2010). Archival data: Advantages and disadvantages for research in psychology. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 4(11), 1008–1017. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2010.00317.x
Kuntsi, J., Rijsdijk, F., Ronald, A., Asherson, P., & Plomin, R. (2005). Genetic influences on the stability of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms from early to middlechildhood. Biological Psychiatry, 57, 647–654.
Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., Loney, J., Kipp, H., Ehrhardt, A., Lee, S. S., et al. (2004). Three-year predictive validity of DSM-iv attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children diagnosed at 4-6 years of age. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 161, 2014–2020.
Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., Loney, J., Lee, S. S., & Willcutt, E. (2005). Instability of the DSM-IV subtypes of ADHD from preschool through elementary school. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 896–902.
Magnússon, P., Smári, J., Sigurðardóttir, D., Baldursson, G., Sigmundsson, J., et al. (2006). Validity of self-report and informant rating scales of adult ADHD symptoms in comparison with a semistructured diagnostic interview. Journal of Attention Disorders, 9, 494–503.
Martel, M. M., von Eye, A., & Nigg, J. (2012). Developmental differences in structure of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) between childhood and adulthood. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 36, 279–292. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025412444077.
Meredith, W. (1993). Measurement invariance, factor analysis, and factorial invariance. Psychometrika, 58, 525–542.
Mitsis, E. M., McKay, K. E., Schulz, K. P., Newcorn, J. H., & Halperin, J. M. (2000). Parent–teacher concordance for DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a clinic-referred sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(3), 308–313. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200003000-00012
Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (2010). Mplus user’s guide (6th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthen & Muthen.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2012). Mplus user’s guide (Seventh ed.). Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Normand, S., Flora, D. B., Toplak, M. E., & Tannock, R. (2012). Evidence for a general ADHD factor from a longitudinal general school population study. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40, 555–567.
Power, T. J., Doherty, B. J., Panichelli-Mindel, S. M., Karustis, J. L., Eiraldi, R. B., Anastopoulos, A. D., & DuPaul, G. J. (1998). The predictive validity of parent and teacher reports of ADHD symptoms. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 20, 57–81.
Reise, S. P. (2012). The rediscovery of bifactor measurement models. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 47, 667–696. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273171.2012.715555.
Reise, S. P., Bonifay, W. E., & Haviland, M. G. (2013). Scoring and modeling psychological measures in the presence of multidimensionality. Journal of Personality Assessment, 95, 129–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2012.725437.
Silverman, W. K., & Albano, A. M. (1996). The anxiety disorders interview schedule for DSM-IV: Child interview schedule. San Antonio: Psychological Corporation.
Silverman, W. K., Saavedra, L. M., & Pina, A. A. (2001). Test-retest reliability of anxiety symptoms and diagnoses with anxiety disorders interview schedule for DSM-IV : Child and parent versions. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 937–944.
Sprafkin, J., Gadow, K. D., Salisbury, H., Schneider, J., & Loney, J. (2002). Further evidence of reliability and validity of the child symptom Inventory-4: Parent checklist in clinically referred boys. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 31, 513–524.
Swanson, J. M. (2008). Parent and teacher SNAP-IV ratings of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms: psychometric properties and normative ratings from a school district sample. Assessment, 15, 317–328. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191107313888.
Swanson, J., Schuck, S., Mann, M., Carlson, C., Hartman, K., Sergeant, J., Clevenger, W., Wasdell, M., & McCleary, R. (2006). Categorical and dimensional definitions and evaluations of symptoms of ADHD: The SNAP and SWAN rating scales. Irvine: University of California.
Taylor, E., Chadwick, O., Heptinstall, E., & Danckaerts, M. (1996). Hyperactivity and conduct problems as risk factors for adolescent development. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 1213–1226.
Teegarden, L. A., & Burns, G. L. (1999). 12-month stability of ADHD, opposition defiant disorder, and conduct disorder symptoms in kindergarten through fifth grade children based on a single information source: Usefulness of teacher ratings for the creation and study of the ADHD subtypes. Child and Family Behavior Therapy, 21, 53–70.
Watkins, M. W. (2013). Omega [computer software]. Phoenix: Ed & Psych Associates.
Widaman, K. E., Ferrer, E., & Conger, R. D. (2010). Factorial invariance within longitudinal structural equation models: Measuring the same construct across time. Child Development Perspectives, 4, 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-8606.2009.00110.x.
Willcutt, E. G., & Carlson, C. L. (2005). The diagnostic validity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Neuroscience Research, 5, 219–232.
Willcutt, E. G., Hartung, C. M., Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., & Loney, J. (1999). Utility of behavior ratings made by examiners during assessments of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 27, 463–472.
Willoughby, M. T., Pek, J., Greenberg, M. T., & the Family Life Project Investigators. (2012). Parent-reported attention deficit/hyperactivity symptomatology in preschool-aged children: Factor structure, developmental change, and early risk factors. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40, 1301–1312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9641-8.
Wolraich, M. L., Lambert, W., Doffing, M. A., Bickman, L., Simmons, T., & Worley, K. (2003). Psychometric properties of the Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic parent rating scale in a referred population. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 28, 559–567.
Wu, A. D., Liu, Y., Gadermann, A. M., & Zumbo, B. D. (2010). Multiple-indicator multilevel growth model: A solution to multiple methodological challenges in longitudinal studies. Social Indicators Research, 97, 123–142.
Zinbarg, R. E., Revelle, W., Yovel, I., & Li, W. (2005). Cronbach’s α, Revelle’s β, and McDonald’s ωH: Their relations with each other and two alternative conceptualizations of reliability. Psychometrika, 70, 123–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11336-003-0974-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of Interest
Rapson Gomez, Alasdair Vance, and Vasileios Stavropoulos declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Experiment Participants
This article does not contain any experiments with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez, R., Vance, A. & Stavropoulos, V. Test-Retest Measurement Invariance of Clinic Referred Children’s ADHD Symptoms. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 40, 194–205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-017-9636-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-017-9636-4