Abstract
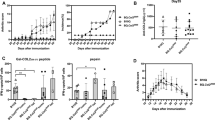
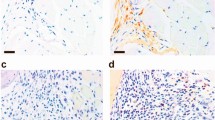
Studies of PECAM-1−/− mice have identified that PECAM-1 functions as an inhibitory co-receptor to modulate immunological responsiveness. In this study, we describe the in vivo consequences of PECAM-1 deficiency in mouse models of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and K/BxN passive transfer model that resembles many of the features of human rheumatoid arthritis. Immunization of PECAM-1−/− C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice with chicken collagen type II induced CIA with an incidence of 82% by day 49, while 33%; of wild-type and 100% of DBA/1 mice developed arthritis in a similar time frame. The mean onset of disease for PECAM-1−/− C57BL/6 mice was day 32 compared to day 51 for wild-type C57BL/6 mice and day 18 for DBA/1 mice (H-2q susceptible). In terms of disease severity, the mean maximal arthritic index for PECAM-1−/− C57BL/6 mice was comparable to DBA/1 mice (8.91 ± 0.91 vs 11.67 ± 0.82). This mean maximal index in PECAM-1−/− C57BL/6 mice was significantly higher than wild-type C57BL/6 mice (5.00 ± 0.73). IgG1 and IgG2b antibody responses against CII were elevated in arthritic PECAM-1−/− C57BL/6 mice compared to wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Histological examination of arthritic paws of PECAM-1−/− C57BL/6 mice revealed inflammatory infiltrates of lymphocytic/monocytic cells and cartilage/bone destruction similar to CIA-induced DBA/1 arthritic paws. In the K/BxN model, the arthritis was not augmented in PECAM-1−/− mice compared to wild-type mice. In contrast, in active CIA, PECAM-1−/− mice developed severe disease comparable to susceptible DBA/1 mice and profoundly more severe than C57BL/6 mice, where only one third developed a mild/moderate disease. Together these observations suggest that PECAM-1 plays a crucial role in the suppression of development of autoimmune arthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van den Berg WB: Lessons from animal models of arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 4(3):232–239, 2002
Myers LK Rosloniec EF, Cremer MA, Kang AH: Collagen-induced arthritis, an animal model of autoimmunity. Life Sci 61(19):1861–1878, 1997
Cremer MA, Rosloniec EF, Kang AH: The cartilage collagens: A review of their structure, organization, and role in the pathogenesis of experimental arthritis in animals and in human rheumatic disease. J Mol Med 76:275–288, 1998
Lindqvist AKB, Bockermann R, Johansson ACM, Nandakumar KS, Johannesson M, Holmdahl R: Mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis. Trends Genet. 18:S7–S13, 2002
Zvaifler NJ, Firestein GS: Pannus and pannocytes. Alternative models of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 37(6):783–789, 1994
Ji H, Pettit A, Ohmura K, Ortiz-Lopez A, Duchatelle V, Degott C, Gravallese E, et al.: Critical roles for Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor α in antibody-induced arthritis. J Exp Med 196(1):77–85, 2002
Maccioni M, Zeder-Lutz G, Huang H, Ebel C, Gerber P, Hergueux J, et al.: Arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies from K/BxN mice. J Exp Med 195(8):1071–1077, 2002
Kaplan CD, O’Neill SK, Koreny T, Czipri M, Finnegan A: Development of inflammation in proteoglycan-induced arthritis is dependent on Fcγ R regulation of the cytokine/chemokine environment. J Immunol 169:5851–5859, 2002
Matsumoto I, Lee DM, Goldbach-Mansky R, Sumida T, Hitchon CA, Schur PH, Anderson RJ, et al.: Low prevalence of antibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a spectrum of other chronic autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Rheum 48(4):944–954, 2003
Cook AD, Rowley MJ, Mackay IR, Gough A, Emery P: Antibodies to type II collagen in early rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with disease progression. Arthritis Rheum 39(10):1720–1727, 1996
Kleinau S, Martinsson P, Heyman B: Induction and suppression of collagen-induced arthritis is dependent on distinct Fcγ receptors. J Exp Med 191(9):1611–1616, 2000
Diaz de Stahl T, Andren M, Martinsson P, Verbeek JS, Kleinau S: Expression of Fcγ RIII is required for development of collageninduced arthritis. Eur J Immunol 32:2915–2922, 2002
Ji H, Ohmura K, Mahmood U, Lee DM, Hofhuis FM, Boackle SA, et al.: Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity 16: 157--168, 2002
Corr M, Crain B: The role of Fcγ R signalling in the K/BxN serum transfer model of arthritis. J Immunol 169:6604–6609, 2002
Takai T, Ono M, Hikida M, Ohmori H, Ravetch JV: Augmented humoral and anaphylactic responses in Fcγ RII-deficient mice. Nature 379:346–349, 1996
Yuasa T, Kubo S, Yoshino T, Ujike A, Matsumura K, Ono M, et al.: Deletion of Fcγ receptor IIb renders H-2b mice susceptible to collagen-induced arthritis. J Exp Med 189(1):187–194, 1999
Jackson DE: The unfolding tale of PECAM-FEBS Lett 540:7–14, 2003
Wilkinson R, Lyons AB, Roberts D, Wong MX, Bartley PA, Jackson DE: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31) acts as a regulator of B-cell development, B-cell antigen receptor (BCR)-mediated activation, and autoimmune disease. Blood 100(1):184–193, 2002
Scekanecs Z, Haines GK, Harlow LA, Shah MR, Fong TW, Fu R, et al.: Increased synovial expression of the adhesion molecules CD66a, CD66b, and CD31 in rheumatoid and osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 76:180–186, 1995
Volin MV, Szekanecz Z, Halloran MM, Woods JM, Magua J, Damergis JA, et al.: PECAM-1 and Leukosialin (CD43) expression correlate with heightened inflammation in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Exp Mol Pathol 66(3):211–219, 1999
Decking J, Mayer A, Petrow P, Seiffge D, Karbowski A: Antibodies to PECAM-1 and glucocorticoids reduce leukocyte adhesion in adjuvant arthritis of the rat knee synovium in vivo. Inflamm Res 50(12):609–615, 2001
Ishikaw J, Okada Y, Bird IN, Jasani B, Spragg JH, Yamada T: Use of anti-platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 antibody in the control of disease progression in established collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 88:332–340, 2002
Duncan GS, Andrew DP, Takimoto H, Kaufman SA, Yoshida H, Spellberg J, et al.: Genetic evidence for functional redundancy of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1): CD31 deficient mice reveal PECAM-1-dependent and PECAM-1-independent functions. J Immunol 162(5):3022–3030, 1999
Kouskoff V, Korganow AS, Duchatelle V, Degott C, Benoist C, Mathis D: Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell 87:811–822, 1996
Campbell IK, Hamilton JA, Wicks IP: Collagen-induced arthritis in C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice: New insights into an important disease model of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 30:1568–1575, 2000
Wooley PH, Luthra HS, Stuart JM, David SC: Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I-region) linkage and antibody correlates. J Exp Med 154:688–700, 1981
Wooley PH, Luthra HS, Griffiths MM, Stuart JM, Huse A, David SC: Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. IV. Variations in immunogenetic regulation provide evidence for multiple arthritogenic epitopes on the collagen molecule. J Immunol 135:2443–2451, 1985
Courtenay JS, Dallman MJ, Dayan AD, Martin A, Mosedale B: Immunization against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature 283:666–668, 1980
Seki N, Sudo Y, Yoshioka T, Sugihara S, Fujitsu T, Sakuma S, et al.: Type II collagen-induced murine arthritis. Induction and perpetuation of arthritis require synergy between humoral and cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol 140:1477–1484, 1988
Ravetch JV, Lanier LL: Immune inhibitory receptors. Science 290(5489):84–89, 2000
Benoist C, Mathis D: A revival of the B cell paradigm for rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis? Arthritis Res 2:90–94, 2000
Hirano T: Revival of the autoantibody model in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Immunol 3(4):342–344, 2002
Galloway TS, Ray K, Malhotra R: Regulation of B lymphocytes in health and disease. Meeting review. Mol Immunol 39:649–653, 2003
Hogarth PM: Fc receptors are major mediators of antibody based inflammation in autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol 14(6):798–802, 2002
Muller WA, Weigl SA, Deng X, Phillips DM: PECAM-1 is required for transendothelial migration of leukocytes. J Exp Med 178:449–460, 1993
Vaporciyan AA, DeLisser HM, Yan HC, Mendiguren II, Thom SR, Jones ML, et al.: Involvement of Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 in neutrophil recruitment in vivo. Science 262:1580–1582, 1993
Bogen S, Pak J, Garifallou M, Deng X, Muller WA: Monoclonal antibody to murine PECAM-1 blocks acute inflammation in vivo. J Exp Med 79:1059–1064, 1994
Ohto H, Maeda H, Shibata Y, Chen RF, Ozaki Y, Higashihara M, et al.: A novel leukocyte differentiation antigen: Two monoclonal antibodies TM2 and TM3 define a 120-kd molecule present on neutrophils, monocytes, platelets, and activated lymphoblasts. Blood 66(4):873–881, 1985
Laio F, Ali J, Greene T, Muller WA: Soluble domain 1 of platelet-endothelial cell–adhesion molecule (PECAM) is sufficient to block transendothelial migration in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 185(7):1349–1357, 1997
Laio F, Schenkel AR, Muller WA: Transgenic mice expressing different levels of soluble platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-IgG display distinct inflammatory phenotypes. J Immunol 163(10):5640–5648, 1999
Nakada MT, Amin K, Christofidou-Solomidou M, O’Brien CD, Sun J, Gurubhagavatula I, et al.: Antibodies against the first Ig-like domain of human platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) that inhibit PECAM-1-dependent homophilic adhesion block in vivo neutrophil recruitment. J Immunol 164(1):452–462, 2000
Graesser D, Solowiej A, Bruckner M, Osterweil E, Juedes A, Davis S, et al.: Altered vascular permeability and early onset of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in PECAM-1-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 109(3):383–392, 2002
Solowiej A, Biswas P, Graesser D, Madri JA: Lack of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 attenuates foreign body inflammation because of decreased angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 162(3):953–962, 2003
Jones KL, Hughan SC, Dopheide SM, Farndale RW, Jackson SP, Jackson DE: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 is a negative regulator of platelet–collagen interactions. Blood 98:1456–1463, 2001
Patil S, Newman DK, Newman PJ: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 serves as an inhibitory receptor that modulates platelet responses to collagen. Blood 97:1727–1732, 2001
Thai LM, Ashman LK, Harbour SN, Hogarth PM, Jackson DE: Physical proximity and functional interplay of PECAM-1 with the Fc receptor Fcγ RIIa on the platelet plasma membrane. Blood 102:3637–3745, 2003
Ji H, Gauguier D, Ohmura K, Gonzalez A, Duchatelle V, Danoy P, et al.: Genetic influences on the end-stage effector phase of arthritis. J Exp Med 194:321–330, 2001
Tada Y, Koarada S, Morito F, Ushiyama O, Haruta Y, Kanegae F, et al.: Acceleration of the onset of collagen-induced arthritis by a deficiency of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1. Arthritis Rheum 48(11):3280–3290, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WONG, MX., Hayball, J.D., Hogarth, P.M. et al. The Inhibitory Co-Receptor, PECAM-1 Provides a Protective Effect in Suppression of Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J Clin Immunol 25, 19–28 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-0354-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-0354-7