Abstract
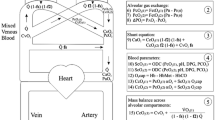
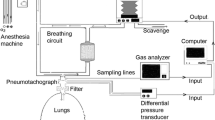
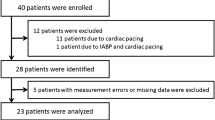
Techniques for the measurement of cardiac output from soluble gas uptake by the lungs include the rebreathing method using nitrous oxide. The accuracy of this␣technique is well accepted, but its repeatability of measurement (precision) has not been well documented. We assessed the repeatability of measurements of pulmonary blood flow by the Innocor, a device employing the nitrous oxide rebreathing method. Successive paired measurements of pulmonary blood flow were made separated by a 5 min interval by the nitrous oxide rebreathing method, in 8 patients pre- or post cardiac surgery, and in 8 healthy volunteers. The standard deviation of the difference between first and second measurements was 0.84 l/min in the cardiac surgery group, and 1.25 l/min in the healthy volunteers. There was no significant bias in successive paired measurements of pulmonary blood flow in either the cardiac surgery patients (mean [95%CI] = −0.02 l/min [−0.62 to 0.57] or the healthy volunteers (0.00 l/min [−0.88 to 0.88]). Intra-class correlation coefficients for the␣healthy and cardiac patients were 0.77 and 0.64 respectively. Multiple measurements should be made and averaged when using the inert gas rebreathing technique for pulmonary blood flow determination. When comparing agreement with other methods for cardiac output measurement, the internal consistency of both methods should be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cander L, Forster RE. Determination of pulmonary parenchymal tissue volume and pulmonary capillary blood flow in man. J Appl Physiol. 1959;14(4):541–51.
Elkayam U, Wilson AF, Morrison J, Meltzer P, Davis J, Klosterman P, et al. Non-invasive measurement of cardiac output by a single breath constant expiratory technique. Thorax. 1984;39:107–13.
Becklake MR, Varvis CJ, Pengelly LD, Kenning S, McGregor M, Bates DV. Measurement of pulmonary blood flow during exercise using nitrous oxide. J Appl Physiol. 1962;17(4):579–86.
Ayotte B, Seymour J, McIlroy MB. A new method for measurement of cardiac output with nitrous oxide. J Appl Physiol. 1970;28(6):863–6.
Sackner MA, Greentelch D, Heiman MS, Epstein S, Atkins N. Diffusing capacity, membrane diffusing capacity, capillary blood volume, pulmonary tissue volume, and cardiac output measured by a rebreathing technique. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975;3:157–65.
Petrini MF, Peterson BT, Hyde RW. Lung tissue volume and blood flow by rebreathing: theory. J Appl Physiol. 1978;44(5):795–802.
Hook C, Meyer M. Pulmonary blood flow, diffusing capacity and tissue volume by rebreathing: theory. Respir Physiol. 1982;48:255–79.
Burma G, Saidel G. Pulmonary and tissue volume: model analysis of rebreathing estimation methods. J Appl Physiol. 1983;55(1):205–11.
Triebwasser JH, Johnson RL Jr, Burpo RP, Campbell JC, Reardon WC, Blomqvist CG. Noninvasive determination of cardiac output by a modified acetylene rebreathing procedure utilizing mass spectrometer measurements. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1977;48(3):203–9.
Stokke T, Burchardi H, Angerer H, Hensel I. Measurement of pulmonary capillary blood flow by a nitrous oxide rebreathing technique. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1986;30:496–501.
Pierce RJ, McDonald CF, Thuys CA, Rochford PD, Barter CE. Measurement of effective pulmonary blood flow by soluble gas uptake in patients with chronic airflow obstruction. Thorax. 1987;42:604–14.
Kallay MC, Hyde RW, Smith RJ, Rothbard RL, Schreiner BF. Cardiac output by rebreathing in patients with cardiopulmonary diseases. J Appl Physiol. 1987;63(1):201–10.
Durkin RJ, Evans TW, Winter SM. Noninvasive estimation of pulmonary vascular resistance by stroke index measurement with an inert gas rebreathing technique. Chest. 1994;106:59–66.
Christensen P, Clemensen P, Andersen PK, Henneberg SW. Thermodilution versus inert gas rebreathing for estimation of effective pulmonary blood flow. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(1):51–6.
Gabrielsen A, Videbaek R, Schou M, Damgaard M, Kastrup J, Norsk P. Non-invasive measurement of cardiac output in heart failure patients using a new foreign gas rebreathing technique. Clin Sci. 2002;102:247–52.
Peyton P, Thompson B. Agreement of an inert gas rebreathing device with thermodilution and the direct oxygen Fick method in measurement of pulmonary blood flow. J Clin Monit. 2005;18:373–8.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res. 1999;8:135–60.
Neilsen OW, Hansen S, Christensen P, Gronlund J. Repeatability of the acetylene rebreathing method in measuring cardiac output: influence of acetylene concentration. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1990;34:354–7.
Neilsen OW, Hansen S, Gronlund J. Precision and accuracy of a non-invasive inert gas washin method for determination of cardiac output in men. J Appl Physiol. 1994;76(4):1560–1565.
Kennedy RR, Baker AB. Solubility characteristics of the ideal agent for measurement of cardiac output by soluble gas uptake methods. Br J Anaesth. 1993;71:398–402.
Kennedy RR, Baker AB. Analysis of uncertainty in theoretical methods of cardiac output measurement using the “Monte Carlo” technique. Br J Anaesth. 1993;71:403–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peyton PJ, Bailey M, Thompson BR. Reproducibility of cardiac output measurement by the nitrous oxide rebreathing technique.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peyton, P.J., Bailey, M. & Thompson, B.R. Reproducibility of cardiac output measurement by the nitrous oxide rebreathing technique. J Clin Monit Comput 23, 233–236 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-009-9187-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-009-9187-7