Abstract
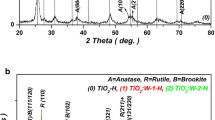
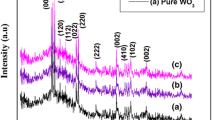
Abstract Tungsten oxide (WO3) nanoparticles doped with different amounts of manganese ions (W1−x Mn x O3, where x = 0.011, 0.022 and 0.044) were synthesised by hydraulic acid-assisted precipitation, followed by thermal calcinations. The powders were characterised by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and magnetic measurements. The monoclinic structure at room temperature (∼293 K) found for un-doped WO3 was preserved even with Mn doping. However, doping with Mn ions caused decease in unit-cell volume and slight increase in crystallite size (CS) of host WO3. The hydrogenation was observed to corrode the crystallites without changing in crystalline structure. Controllable room-temperature ferromagnetic (RT-FM) properties were obviously observed with hydrogenated WO3 doped with Mn. In addition, there existed an optimum doping concentration of Mn in WO3 to obtain superior FM properties. Therefore, Mn-doped WO3 nanopowders, owning to these amazingly tunable magnetic properties, could be considered a potential candidate for many applications partially required FM properties such as optical phosphors and catalysts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, P.: Syntheses, structures and characterizations of novel arsenotungstates. Ph.D dissertation University of Bremen-Germany (2015)
El-Nouby, M.S.: Structure control and characterization of tungsten oxide nanoparticles by aqueous solution methods. Doctoral dissertation, Osaka University, OUKA (2014)
Yan, H., Zhang, X., Zhou, S., Xie, X., Luo, Y., Yu, Y.: Synthesis of WO3 nanoparticles for photocatalytic O2 evolution by thermal decomposition of ammonium tungstate loading on g-C3 N 4. J. Alloy. Compds. 509, L232–L235 (2011)
Lee, K., Seo, W.S., Park, J.T.: Synthesis and optical properties of colloidal tungsten oxide nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 3408–3409 (2003)
Lee, S., Deshpande, R., Parilla, P.A., Jones, K.M., To, B., Mahan, A.H., Dillon, A.C.: Crystalline WO3 nanoparticles for highly improved electrochromic applications. Adv. Mater. 18, 763–766 (2006)
Lassner, E., Schubert, W.: Tungsten properties, chemistry, technology of the element alloys and chemical compounds. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York (1999)
Yamamoto, S., Takano, K., Inouye, A., Yoshikawa, M.: Effects of composition and structure on gasochromic coloration of tungsten oxide films investigated with XRD and RBS. Nucl. Instr. and Meth. Phys. Res. B 262, 29–32 (2007)
Yaacob, M.H., Breedon, M., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Wlodarski, W.: Absorption spectral response of nanotextured WO3 thin films with Pt catalyst towards H2. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 137, 115–120 (2009)
Reyes, L.F., Hoel, A., Saukko, S., Hessler, P., Lantto, V., Granqvist, C.G.: Gas sensor response of pure and activated WO3 nanoparticle films made by advanced reactive gas deposition. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 117, 128–134 (2006)
Kim, T.S., Kim, Y.B., Yoo, K.S., Sung, G.S., Jung, H.J.: Sensing characteristics of dc reactive sputtered WO3 thin films as an NO x gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 62, 102–108 (2000)
Khatko, V., Vallejos, S., Calderer, J., Gracia, I., Cane, C., Llobet, E., Correig, X.: Micro-machined WO3-based sensors with improved characteristics. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 140, 356–362 (2009)
Castro-Hurtadoa, I., Tavera, T., Yurrita, P., Perez, N., Rodriguez, A., Mandayo, G.G., Castano, E.: Structural and optical properties of WO3 sputtered thin films nano-structured by laser interference lithography. Appl. Surf. Sci. 276, 229–236 (2013)
Therese, H.A., Li, J., Kolb, U., Tremel, W.: Facile large scale synthesis of WS2 nanotubes from WO3 nanorods prepared by a hydrothermal route. Solid State Sci. 7, 67–72 (2005)
Djaoued, Y., Priya, S., Balaji, S.: Low temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline WO3 films by sol–gel process. J. Non Cryst. Solids 354, 673–679 (2008)
Kida, T., Nishiyama, A., Yuasa, M., Shimanoe, K., Yamazoe, N.: Highly sensitive NO2 sensors using lamellar-structured WO3 particles prepared by an acidification method. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 135, 568–574 (2009)
Wang, G., Ji, Y., Huang, X., Yang, X., Gouma, P., Dudley, M.: Fabrication and characterization of polycrystalline WO3 nanofibers and their application for ammonia sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 23777–23782 (2006)
Yang, B., Li, H., Blackford, M., Luca, V.: Novel low-density mesoporous WO3 films prepared by electrodeposition. Curr. Appl. Phys. 6, 436–439 (2006)
Hariharan, V., Aroulmoji, V., Prabakaran, K., Gnanavel, B., Parthibavarman, M., Sathyapriya, R., Kanagaraj, M.: Magnetic and electrochemical behaviour of cobalt doped tungsten oxide (WO3) nanomaterials by microwave irradiation method. J. Alloys Compds 689, 41–47 (2016)
Kaminski, A., Sarma, S.D.: Polaron percolation in diluted magnetic semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 247202 (2002). 4 pages
Wolff, P.A., Bhatt, R.N., Durst, A.C.J.: Polaron-polaron interactions in diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 5196–5198 (1996)
Lewis, E.A., Le, D., Murphy, C.J., Jewell, A.D., Mattewra, M.F.G., Liriano, M.L., Rahman, T.S., Sykes, E.C.H.: Dissociative hydrogen adsorption on close-packed cobalt nanoparticle surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 25868–25873 (2012)
Pozzo, M., Alfe, D.: Hydrogen dissociation and diffusion on transition metal (= Ti, Zr, V, Fe, Ru, Co, Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu, Ag)-doped Mg (0001) surfaces. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34, 1922–1930 (2009)
Wua, E., Li, W., Li, J.: Extraordinary catalytic effect of Laves phase Cr and Mn alloys on hydrogen dissociation and absorption. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 37, 1509–1517 (2012)
Zaluska, A., Zaluski, L., Strom-Olsen, J.O.: Nanocrystalline magnesium for hydrogen storage. J. Alloys Compds 288, 217–225 (1999)
Lutterotti, L.: Introduction to diffraction and the Rietveld method, Corso: Laboratorio Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali. https://www.google.com.bh/search?source=hp&ei=OwYVWpykGNOiUo-6gtgI&q=Luca+Lutterotti%2C+Introduction+to+diffraction+and+the+Rietveld+method%2C+Corso%3A&oq=Luca+Lutterotti%2C+Introduction+to+diffraction+and+the+Rietveld+method%2C+Corso%3A&gsl=psy-ab.12...9880016.9880016.0.9881253.1.1.0.0.0.0.526.526.5-1.1.0....0...1c..64.psy-ab..0.0.0....0.lQn6vEOuryo. Accessed 22 Nov 2017
Shannon, R.D.: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976)
Kittel, C.: Introduction to solid state physics, 7th edn., p 425. Wiley, New York (1996)
Torrent, J., Barron, V.: Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York (2002)
Johansson, M.B., Baldissera, G., Valyukh, I., Persson, C., Arwin, H., Niklasson, G.A., Osterlund, L.: Electronic and optical properties of nanocrystalline WO3 thin films studied by optical spectroscopy and density functional calculations. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25, 205502 (2013). 11 pp
Tauc, J., Abelesn, F (eds.): Optical properties of solids. North Holland (1969)
Cole, B., Marsen, B., Miller, E., Yan, Y., To, B., Jones, K., Al-Jassim, M.: Evaluation of nitrogen doping of tungsten oxide for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 5213–5220 (2008)
Song, H., Li, Y., Lou, Z., Xiao, M., Hu, L., Ye, Z., Zhu, L.: Synthesis of Fe-doped WO3 nanostructures with high visible-light-driven photocatalytic activities. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 166–167, 112–120 (2015)
Shen, Y., Yan, P., Yang, Y., Hu, F., Xiao, Y., Pan, L., Li, Z.: Hydrothermal synthesis and studies on photochromic properties of Al doped WO3 powder. J. Alloys Compds 629, 27–31 (2015)
Hariharan, V., Aroulmoji, V., Prabakaran, K., Gnanavel, B., Parthibavarman, M., Sathyapriya, R., Kanagaraj, M.: Magnetic and electrochemical behaviour of cobalt doped tungsten oxide (WO3) nanomaterials by microwave irradiation method. J. Alloys Compds 689, 41–47 (2016)
Dakhel, A.A.: Hydrogenation tuned the created ferromagnetic properties of Ni-doped nano-ZnO. Appl. Phys. A 123, 214 (2017). 8 pages
Gerosa, M., Bottani, C.E., Caramella, L., Onida, G., Di Valentin, C., Pacchioni, G.: Defect calculations in semiconductors through a dielectric-dependent hybrid DFT functional: the case of oxygen vacancies in metal oxides. J. Chem. Phys. 143, 134702 (2015). 9 pages
Aguir, K., Lemire, C., Lollman, D.B.B.: Electrical properties of reactively sputtered WO3 thin films as ozone gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B 84, 1–5 (2002)
Wang, H., Dong, X., Peng, S., Dong, L., Wang, Y.: Improvement of thermoelectric properties of WO3 ceramics by ZnO addition. J. Alloys Compds 527, 204–209 (2012)
Polaczek, A., Pekala, M., Obuszko, Z.: Magnetic susceptibility and thermoelectric power of tungsten intermediary oxides. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 6, 7909–7919 (1994)
The official web page of the University of the West Indies at Mona, Jamaica. The Department of Chemistry. http://wwwchem.uwimona.edu.jm/spectra/MagMom.html. Accessed 22 Nov 2017
Seo, S.-Y., Kwak, C.-H., Kim, S.-H., Park, S.-H., Lee, I.-J., Han, S.-W.: Synthesis and characterization of ferromagnetic Zn1−x Co x O films. J. Cryst. Growth 346, 56–60 (2012)
Gao, Q., Dai, Y., Li, C., Yang, L., Li, X., Cui, C.: Correlation between oxygen vacancies and dopant concentration in Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation technique. Ixygen J. Alloys Compds 684, 669–676 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dakhel, A.A. Study of Semimagnetic Mn-Doped WO3 Nanoparticles Synthesised by Precipitation Method: Hydrogenation Creates a Promising DMS. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 2039–2046 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4430-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4430-9