Abstract
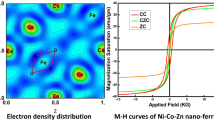
For the first time, rare-earth multi-doped Zn-Ni-Co spinel ferrite nanoparticles \({Zn}_{0.2}{Ni}_{0.3}{Co}_{0.5}{Fe}_{(2-x-y-z)}{Er}_{x}{Gd}_{y}{Sm}_{z}{O}_{4}\) (x = 0.1, y = 0.2, z = 0.1) were synthesized by the coprecipitation method in this paper. The thermal behavior of the obtained precipitate (uncalcined powder) was studied by thermogravimetric analysis. A single phase with space group Fd \(\overline{3 }\) m was confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and the average crystallite size was found to be 16 nm. The estimation of the cationic distribution indicates a mixed spinel structure. The effect of the rare-earth elements on the nanoparticles’ morphology was evaluated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis. Magnetic measurements were performed at three different temperatures 5, 80, and 300 K, and show a superparamagnetic behavior with a saturation magnetization of 21 emu/g at room temperature and a ferromagnetic behavior at 5 K. The saturation magnetization value obtained was interpreted by exchange interactions due to the presence of rare-earth elements in our structure. Therefore, the nanoparticles prepared in this work may be promising candidates for practical applications such as high-frequency electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression, electronics, communication, and future gigahertz antenna applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yousaf, M., Nazir, S., Akbar, M., Akhtar, M.N., Noor, A., Hu, E., Shah, M.A.K.Y., Lu, Y.: Structural, magnetic, and electrical evaluations of rare earth Gd3+ doped in mixed Co–Mn spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 48, 578–586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.09.136
Shao, L., Sun, A., Zhang, Y., Yu, L., Suo, N., Zuo, Z.: Comparative study on the structure and magnetic properties of Ni-Mg-Co ferrite doped with Al and rare earth elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 5339–5352 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05161-1
Suo, N., Sun, A., Yu, L., Zuo, Z., Pan, X., Zhang, W., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Shao, L.: Effect of different rare earth (RE = Y3+, Sm3+, La3+, and Yb3+) ions doped on the magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Co ferrite nanomagnetic materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 246–264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04762-0
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., Auwal, İA., Shirsath, S.E., Manikandan, A., Baykal, A., Özçelik, B., Ercan, İ, Trukhanov, S.V., Vinnik, D.A., Trukhanov, A.V.: Impact of Tm3+ and Tb3+ rare earth cations substitution on the structure and magnetic parameters of Co-Ni nanospinel ferrite. Nanomaterials 10, 2384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122384
Mouhib, Y., Belaiche, M., Ferdi, C.A., Lacham, M., Elacham, A.: New technique for elaboration and characterization of a high voltage spinel LiCo2O4 cathode and theoretical investigation. New J. Chem. 44, 2538–2546 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ06126F
Hirosawa, F., Iwasaki, T.: A comparative study of the magnetic induction heating properties of rare earth (RE = Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Gd and Yb)-substituted magnesium–zinc ferrites. Solid State Sci. 118, 106655 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2021.106655
Zhou, X., Zhou, Y., Zhou, L., Wei, J., Wu, J., Yao, D.: Effect of Gd and La doping on the structure, optical and magnetic properties of NiZnCo ferrites. Ceram. Int. 45, 6236–6242 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.102
Abdellatif, M.H., Azab, A.A., Salerno, M.: Effect of rare earth doping on the vibrational spectra of spinel Mn-Cr ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 260–264 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.09.012
Ahmad, D., Mehboob, N., Zaman, A., Ahmed, N., Ahmed, K., Mushtaq, M., Althubeiti, K., Ali, A., Sultana, F., Bashir, K.: Synthesis and characterization of Ce3+-doped Ni0.5Cd0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles by sol–gel auto-combustion method. Coatings. 11, 1156 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101156
Elius, I.B., Hossain, S., Aktar, M.S., Zakaria, A.K.M., Kamal, I., Hoque, S.M., Azad, A.K.: Structural and magnetic characterizations of NixCu0.8-x Zn0.2Fe2O4 spinel ferrites. Ferroelectrics. 572, 36–50 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2020.1868871
Mouhib, Y., Belaiche, M., Briche, S., Ferdi, C.A., Iffer, E.: Elaboration, characterization and first principle studies of MnCo2O4 nanomaterials prepared from non-standard raw materials. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 035508 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaf447
Almessiere, M.A. 2020, Slimani, Y., Rehman, S., Khan, F.A., Güngüneş, Ç.D., Güner, S., Shirsath, S.E., Baykal, A.: Magnetic properties, anticancer and antibacterial effectiveness of sonochemically produced Ce3+/Dy3+ co-activated Mn-Zn nanospinel ferrites. Arab. J. Chem. 13, 7403–7417 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.08.017
Almessiere, M.A. 2019, Ünal, B., Slimani, Y., Korkmaz, A.D., Baykal, A., Ercan, I.: Electrical properties of La3+ and Y3+ ions substituted Ni0.3Cu0.3Zn0.4Fe2O4 nanospinel ferrites. Results Phys. 15, 102755 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102755
Boda, N., Boda, G., Naidu, K.C.B., Srinivas, M., Batoo, K.M., Ravinder, D., Reddy, A.P.: Effect of rare earth elements on low temperature magnetic properties of Ni and Co-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 473, 228–235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.10.023
Li, S., Pan, J., Gao, F., Zeng, D., Qin, F., He, C., Dodbiba, G., Wei, Y., Fujita, T.: Structure and magnetic properties of coprecipitated nickel-zinc ferrite-doped rare earth elements of Sc, Dy, and Gd. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 13511–13526 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05928-0
Ali, A., Sarker, M.S.I., Islam, M., Khan, M.K.R., Khan, F.A., Khan, M.N.I., Rahman, M.M.: Effect of In on superparamagnetic CoInxFe2-xO4 (x = 0–0.15) synthesized through hydrothermal method. Results Phys. 25, 104251 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104251
Utomo, J., Agustina, A.K., Suharyadi, E.: Annealing temperature effect on structural, vibrational and optical properties of Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 nanoparticles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 432, 012033 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/432/1/012033
Simi Debnath: Effect of cobalt doping on structural parameters, cation distribution and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanocrystals | Elsevier Enhanced Reader, https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S0272884221004521?token=562877AC899F0DFA8B783E51CA0C20A1ECC5E967A2DB574D883D9BD9CA99043BC4D6EB94160B24CCCD32EC708D04B65C&originRegion=eu-west-1&originCreation=20211125114025
Almessiere, M.A. 2021, Unal, B., Slimani, Y., Gungunes, H., Toprak, M.S., Tashkandi, N., Baykal, A., Sertkol, M., Trukhanov, A.V., Yıldız, A., Manikandan, A.: Effects of Ce–Dy rare earths co-doping on various features of Ni–Co spinel ferrite microspheres prepared via hydrothermal approach. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14, 2534–2553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.142
Mouhib, Y., Belaiche, M.: Cobalt nano-ferrite synthesized by molten salt process: structural, morphological and magnetic studies. Appl. Phys. A. 127, 613 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04758-5
K. Elayakumar: Structural and magnetic characterization of rare earth element cerium-doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles (NiCexFe2-xO4) by sol-gel method with antibacterial activity | SpringerLink, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10948-020-05475-5
Mouhib, Y., Belaiche, M., Elansary, M., AhmaniFerdi, C.: Effect of heating temperature on structural and magnetic properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized for the first time in presence of Moroccan reagents. J. Alloys Compd. 895, 162634 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162634
Jadhav, J., Biswas, S., Yadav, A.K., Jha, S.N., Bhattacharyya, D.: Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline NiZn ferrites: In the context of cationic distribution. J. Alloys Compd. 696, 28–41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.163
Samad, R., Rather, M. ud D., Asokan, K., Want, B.: Dielectric and magnetic properties of rare-earth-doped cobalt ferrites and their first-order reversal curve analysis. Appl. Phys. A. 125, 503 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2804-5
Sharma, S., Verma, M.K., Sharma, N.D., Choudhary, N., Singh, S., Singh, D.: Rare-earth doped Ni–Co ferrites synthesized by Pechini method: cation distribution and high temperature magnetic studies. Ceram. Int. 47, 17510–17519 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.069
Zhang, Y., Sun, A., Suonan, Z.: Effect of rare-earth (Sm, Ce, and La) ions doping on the lattice structure and magnetic properties of Zn–Ba–Co ferrites by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 16505–16518 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06207-8
Rajesh Kanna, R., Lenin, N., Sakthipandi, K., Sivabharathy, M.: Impact of lanthanum on structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of Mn1-xCuxFe1.85La0.15O4 spinel nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 43, 15868–15879 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.160
Shahid, M., Shafi, S., AlyAboud, M.F., Warsi, M.F., Asghar, M., Shakir, I.: Impacts of Co2+ and Gd3+ co-doping on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized via micro-emulsion route. Ceram. Int. 43, 14096–14100 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.146
Pawar, R.A., Patange, S.M., Shitre, A.R., Gore, S.K., Jadhav, S.S., Shirsath, S.E.: Crystal chemistry and single-phase synthesis of Gd3+ substituted Co–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic properties. RSC Adv. 8, 25258–25267 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA04282A
Zhang, W., Sun, A., Zhao, X., Suo, N., Yu, L., Zuo, Z.: Structural and magnetic properties of La3+ ion doped Ni–Cu–Co nano ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 90, 599–610 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04941-4
Srinivasamurthy, K.M., Angadi, V.J., Kubrin, S.P., Matteppanavar, S., Kumar, P.M., Rudraswamy, B.: Evidence of enhanced ferromagnetic nature and hyperfine interaction studies of Ce-Sm doped Co-Ni ferrite nanoparticles for microphone applications. Ceram. Int. 44, 18878–18885 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.123
Hossain, M.D., Khan, M.N.I., Nahar, A., Ali, M.A., Matin, M.A., Hoque, S.M., Hakim, M.A., Jamil, A.T.M.K.: Tailoring the properties of Ni-Zn-Co ferrites by Gd3+ substitution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 497, 165978 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165978
Jahan, N., Khandaker, J.I., Liba, S.I., Hoque, S.M., Khan, M.N.I.: Structural analysis through cations distributions of diamagnetic Al3+ ions substituted Ni-Zn-Co ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 869, 159226 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159226
Aadil, M., Zulfiqar, S., Warsi, M.F., Agboola, P.O., Shakir, I.: Free-standing urchin-like nanoarchitectures of Co3O4 for advanced energy storage applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 12697–12706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.110
Lin, S., Pan, X., Meng, D., Zhang, T.: Electric conversion treatment of cobalt-containing wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 83, 1973–1986 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.101
Hwang, I., Jang, I., Lee, G., Tak, Y.: Binary cobalt and magnesium hydroxide catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water electrolysis. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 11, 6204–6214 (2016)
Pinto, P., Lanza, G., Ardisson, J., Lago, R.: Controlled dehydration of Fe(OH)3 to Fe2O3: developing mesopores with complexing iron species for the adsorption of β-Lactam antibiotics. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 30, (2018). https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180179
Carrasco, G.F., Portillo, M.C., Santiago, A.C., Diaz, A.R., Mora-Ramirez, M.A., Moreno, O.P.: Morphological and structural analysis of the Fe(OH)3 and CuS transitions to Fe2O3 and CuO. Optik 243, 167377 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167377
Yassine, M., Belaiche, M., Briche, S.: Elaboration, characterization, and magnetic properties of Ni 0.5 Zn 0.5 Fe 2 O 4 nanoparticles of high purity using molten salts technique. Phys. Status Solidi A. 215, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201800469
Abbas, S.A., Jung, K.-D.: Preparation of mesoporous microspheres of NiO with high surface area and analysis on their pseudocapacitive behavior. Electrochim. Acta 193, 145–153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.054
Muneer, I., Farrukh, M.A., Javaid, S., Shahid, M., Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, M.: Synthesis of Gd2O3/Sm2O3 nanocomposite via sonication and hydrothermal methods and its optical properties. Superlattices Microstruct. C, 256–266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.10.006
Li, G., Liang, Y., Zhang, M., Yu, D.: Size-tunable synthesis and luminescent properties of Gd(OH)3:Eu3+ and Gd2O3:Eu3+ hexagonal nano-/microprisms. CrystEngComm 16, 6670–6679 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00482E
Konyukhov, Y., Minh, N., Ryzhonkov, D.: Kinetics of reduction of α-Fe2O3 Nanopowder with hydrogen under power mechanical treatment in an electromagnetic field. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 10, 706–712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113319030171
Qin, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, X., Shen, W., Yu, J., Li, J.: A facile synthesis of three dimensional β-Ni(OH)2 composed of ultrathin nanosheets for high performance pseudocapacitor. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 2089–2097 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01360-4
Madern, N., Charbonnier, V., Monnier, J., Zhang, J., Paul-Boncour, V., Latroche, M.: Investigation of H sorption and corrosion properties of Sm2MnxNi7−x (0 ≤ x < 0.5) intermetallic compounds forming reversible hydrides. Energies. 13, 3470 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13133470
Yousefi, T., Mostaedi, M.T., Ghasemi, M., Ghadirifar, A.: A simple way to synthesize of samarium oxide nanoparticles: characterization and effect of ph on morphology. synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 46, 137–142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2014.900795
Kaur, G., Sharma, P., Priya, R., Pandey, O.P.: Thermal dehydration kinetics involved during the conversion of gadolinium hydroxide to gadolinium oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 822, 153450 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153450
Zhang, M., He, J., Deng, M., Gong, P., Zhang, X., Fan, M., Wang, K.: Rheological behaviours of guar gum derivatives with hydrophobic unsaturated long-chains. RSC Adv. 10, 32050–32057 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA04322B
Seyhan, M., Kucharczyk, W., Yarar, U.E., Rickard, K., Rende, D., Baysal, N., Bucak, S., Ozisik, R.: Interfacial surfactant competition and its impact on poly(ethylene oxide)/Au and poly(ethylene oxide)/Ag nanocomposite properties. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 10, 69–77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2147/NSA.S129468
Li, Y.-R., Li, Q.-Y., Wang, X.-D., Yu, L.-G., Yang, J.-J.: Aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil with ferric oleate catalyst. Pet. Sci. 15, 613–624 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12182-018-0246-x
Bužarovska, A., Dinescu, S., Chitoiu, L., Costache, M.: Porous poly(l-lactic acid) nanocomposite scaffolds with functionalized TiO2 nanoparticles: properties, cytocompatibility and drug release capability. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 11151–11166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2415-0
Hssaini, A., Belaiche, M., Elansary, M.: One-step synthesis of coated (Gd3+, Er3+) co-doped Co–Ni ferrite nanoparticles; structural and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05823-8
Jahan, N., Khan, M.N.I., Khandaker, J.I.: Exploration through structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of Al 3+ doped Ni–Zn–Co nanospinel ferrites. ACS Omega 6, 32852–32862 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c04832
Chen, W., Liu, D., Wu, W., Zhang, H., Wu, J.: Structure and magnetic properties evolution of rod-like Co0.5Ni0.25Zn0.25Dy Fe2−O4 synthesized by solvothermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 49–56 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.067
Mouli, K.C., Joseph, T., Ramam, K.: Synthesis and magnetic studies of Co-Ni-Zn ferrite nano crystals. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 5596–5599 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.1133
Salgaonkar, M., Gad, R.S.: Influence of B-site Gd+3 substitution on various properties of Co-ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A. 127, 867 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05026-2
Ramakrishna, K.S., Srinivas, Ch., Prasad, S.A.V., Kumar, E.R., Rao, K.R., Prajapat, C.L., Rao, T.V.C., Meena, S.S., Sastry, D.L.: Evaluation of structural, micro-structural, vibrational and elastic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn nanoferrites: role of Dopant Cu2+ at constant 0.1 mol% in Ni–Zn spinel structure. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 1336–1346 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01773-6
Narang, S.B., Pubby, K.: Nickel Spinel Ferrites: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 519, 167163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167163
Weil, L., Bertaut, F., Bochirol, L.: Propriétés magnétiques et structure de la phase quadratique du ferrite de cuivre. J. Phys. Radium. 11, 208–212 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1051/jphysrad:01950001105020800
Prabhakaran, T., Mangalaraja, R.V., Denardin, J.C., Jiménez, J.A.: The effect of calcination temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of co-precipitated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 716, 171–183 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.048
Majid, F., Wahid, I., Ata, S., Bibi, I., Ali, M.D., Malik, A., Alwadai, N., Iqbal, M., Nazir, A.: Cationic distribution of nickel doped NixCoX-1Fe2O4 nanparticles prepared by hydrothermal approach: Effect of doping on dielectric properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 264, 124451 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124451
Abouzir, E., Belaiche, M., Elansary, M., Ahmani Ferdi, C., Bsoul, I.: Novel magnetic nanomaterial Co0.7Zn0.3Fe2−xGdxO4 for nanotechnology applications: experimental and theoretical investigations. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1–18 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06913-3
Suresh, J., Trinadh, B., Vikram Babu, B., Reddy, P.V.S.S.S.N., Sathish Mohan, B., Rama Krishna, A., Samatha, K.: Evaluation of micro-structural and magnetic properties of nickel nano-ferrite and Mn2+ substituted nickel nano-ferrite. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 620, 413264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2021.413264
Debnath, S., Das, A., Das, R.: Effect of cobalt doping on structural parameters, cation distribution and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 47, 16467–16482 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.095
Kumar, L., Kumar, P., Kar, M.: Cation distribution by Rietveld technique and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Zn substituted nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 551, 72–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.009
Mallesh, S., Srinivas, V., Vasundhara, M., Kim, K.H.: Low-temperature magnetization behaviors of superparamagnetic MnZn ferrites nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 582, 411963 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411963
Devi, E.C., Singh, S.D.: Manifestation of magnetic characteristics of zinc ferrite nanoparticles using the Langevin function. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 34, 617–622 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05732-7
Monalisa, Sharma, S., Satyapal, H.K., Singh, R.K.: Correlation between lattice strain and magnetic properties enhancement of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite with controlled annealing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 23843–23853 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06795-5
Sinfrônio, F.S.M., Santana, P.Y.C., Coelho, S.F.N., Silva, F.C., de Menezes, A.S., Sharma, S.K.: Magnetic and structural properties of cobalt- and zinc-substituted nickel ferrite synthesized by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1145–1154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5081-5
Xu, Y., Sun, D., Hao, H., Gao, D., Sun, Y.: Non-stoichiometric Co( ii ), Ni( ii ), Zn( ii )-ferrite nanospheres: size controllable synthesis, excellent gas-sensing and magnetic properties. RSC Adv. 6, 98994–99002 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA21990J
Huili, H., Grindi, B., Viau, G., Tahar, L.B.: Influence of the stoichiometry and grain morphology on the magnetic properties of Co substituted Ni–Zn nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 17594–17604 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.073
Sharifianjazi, F., Moradi, M., Parvin, N., Nemati, A., Jafari Rad, A., Sheysi, N., Abouchenari, A., Mohammadi, A., Karbasi, S., Ahmadi, Z., Esmaeilkhanian, A., Irani, M., Pakseresht, A., Sahmani, S., ShahediAsl, M.: Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles doped with metal ions: a review. Ceram. Int. 46, 18391–18412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.202
Elansary, M., Belaiche, M., Ahmani Ferdi, C., Iffer, E., Bsoul, I.: Novel ferrimagnetic nanomaterial Sr (1−x) La x Gd y Sm z Fe (12−(z+y)) O 19 for recording media applications: experimental and theoretical investigations. New J. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ00938A
Lakhani, V.K., Pathak, T.K., Vasoya, N.H., Modi, K.B.: Structural parameters and X-ray Debye temperature determination study on copper-ferrite-aluminates. Solid State Sci. 13, 539–547 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.12.023
Sharma, R., Thakur, P., Kumar, M., Thakur, N., Negi, N.S., Sharma, P., Sharma, V.: Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via co-precipitation route. J. Alloys Compd. 684, 569–581 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.200
Mohapatra, J., Xing, M., Elkins, J., Beatty, J., Liu, J.P.: Size-dependent magnetic hardening in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles: effects of surface spin canting. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53, 504004 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/abb622
Marx, J., Huang, H., M. Salih, K.S., Thiel, W.R., Schünemann, V.: Spin canting in ferrite nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 237, 41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-016-1241-5
Yang, R., Yu, X., Li, H., Wang, C., Wu, C., Zhang, W., Guo, W.: Effect of Mg doping on magnetic induction heating of Zn–Co ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 851, 156907 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156907
Smart, J.S.: The Néel Theory of Ferrimagnetism. Am. J. Phys. 23, 356–370 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1119/1.1934006
Belaiche, Y., Minaoui, K., Ouadou, M., Elansary, M.: Preparation and study magnetic properties of the nanosized ferrite Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe1.95Mo0.02Tb0.01Sm0.01Gd0.01O4 with negative magnetization. A new result. Phase Transit. 0, 1–17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2021.1986041
Topkaya, R., Baykal, A., Demir, A.: Yafet–Kittel-type magnetic order in Zn-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with uniaxial anisotropy. J. Nanoparticle Res. 15, 1359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1359-6
Maaz, K., Mumtaz, A., Hasanain, S.K., Bertino, M.F.: Temperature dependent coercivity and magnetization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2199–2202 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.02.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belaiche, Y., Minaoui, K., Ouadou, M. et al. Elaboration and Experimental Investigation of Zn-Ni-Co Spinel Ferrite Multi-doped Rare-Earth (Gd, Er, and Sm) Prepared by Coprecipitation Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 35, 1269–1280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06189-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06189-6