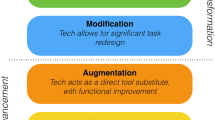
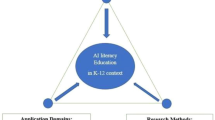
Abstract
In recent years, arguments have signalled the value of STEM education for building discipline knowledge and an array of capabilities, skills and dispositions, aligned with the needs of young people functioning productively and ethically in dynamic, complex and challenging future work, social and political environments. This combination has been termed STEM literacy and positioned as a desired outcome from STEM education programs. However, knowledge is limited on ways this can be developed in K-12 schools. This article introduces a framework that conceptualises the integrated nature of the characteristics of STEM education. It identifies and maps key characteristics of STEM education, recognising different entry points, curriculum designs and pedagogical strategies for school programs. The framework provides practical guidance for planning and implementing STEM education in schools.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Detailed explanations of the continuum can be found in Vasquez et al. (2013), p. 73–74, and at https://d41super.files.wordpress.com/2014/12/stem-beyond-the-acronym.pdf
See Cessnock Academy of STEM Excellence (https://chslccase.org/)
References
Anderson, S., Allen, P., Peckham, S., & Goodwin, N. (2008). Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems, 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-4505-6-7.
Arskey, H., & O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19–32.
Asghar, A., Ellington, R., Rice, E., Johnson, F., & Prime, G. (2012). Supporting STEM education in secondary science contexts. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 6(2), 85–125.
Australian Industry Group. (2015). Progressing STEM skills in Australia (final report). Sydney: AIGroup Retrieved from http://cdn.aigroup.com.au/Reports/2015/14571_STEM_Skills_Report_Final_-.pdf.
Balcar, J. (2016). Is it better to invest in hard or soft skills? The Economic and Labour Relations Review, 27(4), 453–470.
Becker, K., & Park, K. (2011). Effects of integrative approaches among science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) subjects on students’ learning: a preliminary meta-analysis. Journal of STEM Education Innovations and Research, 12(5–6), 23–37.
Bennett, D., & Monahan, P. (2013). NYSCI design lab: No bored kids! In M. Honey and D. Kanter (Eds), Design, Make, Play: Growing the Next Generation of STEM Innovators (pp. 34–50). New York: Routledge.
Bevan, B. (2017). The promise and promises of making in science education. Studies in Science Education, 53(1), 75–103.
Bissaker, K. (2014). Transforming STEM education in an innovative Australian school: the role of teachers’ and academics’ professional partnerships. Theory Into Practice, 53(1), 55–63.
Brears, L., MacIntrye, B., & O’Sullivan, G. (2011). Preparing teachers for the 21st century using PBL as an integrated strategy in science and technology education. Design and Technology Education: an International Journal, 16(1), 36–46.
Breiner, J., Johnson, C., Harkness, S., & Koehler, C. (2012). What is STEM? A discussion about conceptions of STEM in education and partnerships. School Science and Mathematics, 112(1), 3–11.
Bybee, R. (2010). Advancing STEM education: a 2020 vision. Technology and Engineering Teacher, (Sept.), 30-35.
Bybee. R. (2013). The case for STEM education: challenges and opportunities. National Science Teachers’ Association. Arlington: NSTA Press.
Capraro, M., & Jones, M. (2013). Interdisciplinary STEM project-based learning. In R. Capraro, M. Capraro, & J. Morgan (Eds.), STEM-project-based learning: an integrated science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) approach (pp. 51–58). Rotterdam: Sense.
Caprile, M., Palmén, R., Sanz, P. & Dente, G. (2015). Encouraging STEM Studies in the Labour Market. European Parliament Directorate General for Internal Policies [White Paper 542.199]. Retrieved from https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2015/542199/IPOL_STU(2015)542199_EN.pdf.
Daudt, H., van Mossel, C., & Scott, S. (2013). Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional experience with Arskey and O’Malley’s framework. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 13(48). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-48.
Edwards, D., Perkins, K., Pearce, J. & Hong, J. (2015). Work integrated learning in STEM in Australian universities. Final report submitted to the Office of the Chief Scientist. Retrieved from https://research.acer.edu.au/higher_education/44.
English, L. (2016). STEM Education K-12: Perspectives on integration. International Journal of STEM Education, 3(3), 1–8.
Falloon, G. (2013). Forging school-scientist partnerships: a case of easier said than done? Journal of Science Education and Technology, 22(1), 858–876.
Falloon, G. (2014). Using videoconferencing in a school-scientist partnership: students’ perspectives and scientists’ challenges. Research in Learning Technologies, 20, 1–18.
Hargrove, R. (2011). Fostering creativity in the design studio: a framework towards effective pedagogical practices. Art, Design and Communication in Higher Education, 10(1), 7–31.
Havice, W. (2009). The power and promise of a STEM Education: thriving in a complex technological world. In International Technology and Engineering Educators’ Association (ITEEA) (Ed.), The overlooked STEM imperatives: technology and engineering (pp. 10–17). Reston, VA: ITEEA Publications.
Heckman, J., & Kautz, T. (2012). Hard evidence on soft skills. Labour Economics, 19(4), 451–464.
Hoachlander, G. (2014). Integrating STE&M. Educational Leadership (December), 74–78.
Holmlund, T., Lesseeig, K., & Slavit, D. (2018). Making sense of STEM education in K-12 contexts. International Journal of STEM Education, 5(32), 1–18.
Honey, M., Pearson, G., & Schweingruber, H. (Eds.). (2014). STEM integration in K-12 education: status, prospects and an agenda for research. Washington DC: National Academies Press.
Johns, G., & Mentzer, N. (2016). STEM integration through design and inquiry (pp. 13–17). Nov: Technology and Engineering Teacher.
Kelley, T., & Knowles, J. (2016). A conceptual framework for integrated STEM education. International Journal of STEM Education, 3(11).
Khan, S. (2015). Another ‘M’ for STEM? Moral considerations for advancing STEM literacy. K-12 STEM Education, 1(4), 149–156.
LaForce, M., Noble, E., King, H., Holt, S., & Century, J. (2014). The 8 elements of inclusive STEM high schools. Chicago, IL: Outlier Research & Evaluation, CEMSE, The University of Chicago.
LaForce, M., Noble, E., King, H., Century, J., Blackwell, C., Holt, S., Ibrahim, A., & Loo, S. (2016). The eight essential elements of inclusive STEM high schools. International Journal of STEM Education, 3(21), 1–11.
Land, M. (2013). Full STEAM ahead: the benefits of integrating the arts into STEM. Procedia Computer Science, 20, 547–552.
Madden, M., Baxter, M., Beauchamp, H., Bouchard, K., Habermas, D., Huff, M., Pearon, J., & Plague, G. (2013). Rethinking STEM education: an interdisciplinary STEAM curriculum. Procedia Computer Science, 20, 541–546.
Marginson, S., Tytler, R., Freeman, B. & Kelly, R. (2013). STEM: country comparisons: international comparisons of science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Final report. Australian Council of Learned Academies. Retrieved from https://dro.deakin.edu.au/eserv/DU:30059041/tytler-stemcountry-2013.pdf.
Marrero, M., Gunning, A., & Germain-Williams, T. (2014). What is STEM Education? Global Education Review, 1(4), 1–6.
Marshall, J. & Harron, J. (2018). Making learners: a framework for evaluating making in STEM education. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 12(2), Article 2. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1749.
Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment. (2014). A nation of curious minds. A national strategic plan for science in society. Wellington: New Zealand Government.
Mohr-Schroeder, M., Cavalcanti, M., & Blyman, K. (2015). STEM education: understanding the changing landscape. In A. Sahin (Ed.), A practice-based model of STEM teaching (pp. 3–14). Rotterdam: Sense.
Moore, T., Stohlmann, M., Wang, H., Tank, K., Glancy, A., & Roehrig, G. (2014). Implementation and integration of engineering in K-12 STEM education. In Engineering in pre-college settings: synthesizing research, policy, and practices (pp. 35–60). West Lafayette, IN: Purdue University Press.
Morrison, J., & Bartlett, B. (2009). STEM as curriculum: An experimental approach. Education Week, 8(23), 28–31.
Morrison, J., McDuffie, A., & French, B. (2015). Identifying key concepts of teaching and learning in a STEM school. School Science and Mathematics, 115(5), 244–255.
Munn, Z., Peters, M., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 18(143), 1–7.
National Research Council. (2011). Successful K-12 STEM education: identifying effective approaches in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. Washington DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/13158.
National Science Board. (2015). Revisiting the STEM Workforce. National Science Foundation. Retrieved from https://www.nsf.gov/nsb/publications/2015/nsb201510.pdf.
Newhouse, C. (2017). STEM the boredom: Engage students in the Australian curriculum using ICT with problem-based learning and assessment. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 26(44), 44–57.
Oanh, D., Van Dung, L., Anh, T., & Trang, N. (2018). STEM education: organising high school students in Vietnam using engineering design process to fabricate water purification systems. American Journal of Educational Research, 6(9), 1289–1300.
Office of the Chief Scientist. (2016). Australia’s STEM workforce: science, technology, engineering and mathematics. Canberra: Australian Government Retrieved from https://www.chiefscientist.gov.au/wp-content/uploads/Australias-STEM-workforce_full-report.pdf.
Pham, M., Andrijana, R., Greig, J., Sargeant, J., Papadopoulos, A., & McEwan, S. (2014). A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Research Synthesis Methods, 5(4), 371–385.
Portz, S. (2015, April). The challenges of STEM education. Paper presented at the Space Congress, Florida. Retrieved from http://commons.erau.edu/space-congress-proceedings/proceedings-2015-43rd/proceedings-2015-43rd/3.
Quinn, H., & Bell, P. (2013). How designing, making and playing relate to the learning goals of K-12 science education. In M. Honey & D. Kanter (Eds.), Design, make, play: growing the next generation of STEM innovators (pp. 17–33). New York: Routledge.
Roberts, A. (2012). A justification for STEM education. Technology and Engineering Teacher (May-June), 1-5.
Sanders, M. (2012). Integrative STEM education as “best practice”. In H. Middleton (Ed.), Explorations of best practice in technology, design & engineering education (Vol. 2, pp. 103–117). Gold Coast: Australia. Griffith Institute for Educational Research.
Salami, M., Makela, C., & deMiranda, M. (2017). Assessing changes in teachers’ attitudes towards interdisciplinary STEM teaching. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 27, 63–88.
Shapiro, D. (2018). Connecting businesses and STEM students. National Science Teachers’ Association. Retrieved from http://nstacommunities.org/blog/2018/10/04/connecting-businesses-and-stem-students/.
Sleap, S. (2018). The Cessnock Academy of STEM Excellence. Retrieved from https://chslccase.org/.
STEM Education Coalition, (2014). Statement of core policy principles. Retrieved from http://www.stemedcoalition.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/Note-STEM-Education-Coalition-Core-Principles-2014-Final.pdf.
Task Force, S. T. E. M. (2014). Innovate: a blueprint for science, technology, engineering and mathematics in California public education. Dublin, CA: Californians Dedicated to Education Foundation Retrieved from http://www.cde.ca.gov/pd/ca/sc/documents/innovate.pdf.
Techakosit, S., & Nilsook, P. (2018). The development of STEM literacy using the learning process of scientific imagineering through AR. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 13(1), 230–238.
Timms, M., Moyle, K., Weldon, P. & Mitchell, P. (2018). Challenges in STEM learning in Australian schools. Policy insights 7. Victoria: Australian Council for Educational Research. Retrieved from https://research.acer.edu.au/policyinsights/7/.
Top, N., & Sahin, A. (2015). Make it happen: a study of a novel teaching style, STEM students on the stage (SOS), for increasing students’ STEM knowledge and interest. In A. Sahin (Ed.), A practice-based model of STEM teaching (pp. 43–62). Rotterdam: Sense.
Vasquez, J. (2014). STEM: beyond the acronym. Educational Leadership, (Dec-Jan 2014), 10-16.
Vasquez, J., Sneider, C., & Comer, M. (2013). STEM lesson essentials, grades 3–8: integrating science, technology, engineering and mathematics. New York: Heinemann.
Zeidler, D. L. (2016) STEM education: A deficit framework for the twenty first century? A sociocultural socioscientific response. Cultural Studies of Science Education, 11(1):11–26.
Zollman, A. (2012). Learning for STEM literacy: STEM literacy for learning. School Science and Mathematics, 112(1), 12–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics
Ethical clearance was not a requirement of this study.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was not a requirement of this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Appendix 3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falloon, G., Hatzigianni, M., Bower, M. et al. Understanding K-12 STEM Education: a Framework for Developing STEM Literacy. J Sci Educ Technol 29, 369–385 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-020-09823-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10956-020-09823-x