Abstract
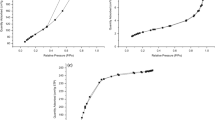
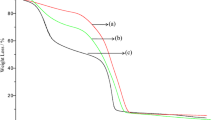
Silica-based materials were prepared by the acid catalyzed sol–gel method using different pharmaceuticals as a template. The template molecules investigated were fluoxetine, gentamicin, lidocaine, morphine, nifedipine, paracetamol and tetracycline. The resulting hybrid silicas underwent ultrasound extraction in the presence of several solvents and were characterized by elemental analysis, porosimetry by adsorption/desorption of nitrogen (BET method), small-angle X-ray scattering and X-ray diffraction. Drug extraction was carried out by the combination of solvent and ultra-sound. The textural characteristics of the hybrid xerogels and resulting imprinted materials were shown to be highly dependent on the molecular weight and molecular volume of the drug template. Increasing the molecular weight of the template results in a decrease in the encapsulation content of the resulting material. In the case of paracetamol and fluoxetine, the dimensions of the surface area are not sufficient to guarantee the adsorption of the smaller molecule. Instead, the shape generated through encapsulation and extraction during the production of the imprinted silica dictates the adsorption behavior.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner NW, Wright BE, Hlady V, Britt DW (2007) Formation of protein molecular imprints within Langmuir monolayers: a quartz crystal microbalance study. J Colloid Interface Sci 308:71–80
Feng L, Liu Y, Zhou X, Hu J (2005) The fabrication and characterization of a formaldehyde odor sensor using molecularly imprinted polymers. J Colloid Interface Sci 284(1):378–382
Dai CM, Dai SU, Zhang YL, Zhang YJ, Zhou XF (2011) Selective removal of diclofenac from contaminated water using molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres. Environ Pollut 159(6):1660–1666
Rebelo TSCR, Almeida SAA, Rafaela J, Guerreiro L, Conceição M, Montenegro BSM, Goreti M, Sales F (2011) Trimethoprim-selective electrodes with molecularly imprinted polymers acting as ionophores and potentiometric transduction on graphite solid-contact. Microchem J 98(1):21–28
Liu T, Liu Y, Wang Q, Li Q, Wang J, Yan Y (2011) Improving catalytic performance of Burkholderia cepacia lipase immobilized on macroporous resin NKA. J Mol Catal B Enzymatic 71(1–2):45–50
Venkatesh S, Saha J, Pass S, Byrne ME (2008) Transport and structural analysis of molecular imprinted hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Eu J Pharmaceutical Biopharmaceutical 69(3):852–860
Lee SW, Kunitake T (2006) Self-organized nanoescale materials, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Lieberzeit PA, Afzal A, Glanzing G, Dickert FL (2007) Molecularly imprinted sol–gel nanoparticles for mass-sensitive engine oil degradation sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 389(2):441–446
Titirici MM, Sellergren B (2004) Peptide recognition via hierarchical imprinting. Anal Bioanal Chem 378(8):1913–1921
Jin Y, Korean KHR (2005) Geological Review. J Chem Eng 51(3):264–267
Beltran A, Caro E, Marcé RM, Cormack PAG, Sherrington DC, Borrull F (2007) Synthesis and application of a carbamazepine-imprinted polymer for solid-phase extraction from urine and wastewater. Anal Chimica Acta 597(1):6–11
Mohajeri SA, Ebrahimi SA (2008) Preparation and characterization of a lamotrigine imprinted polymer and its application for drug assay in human serum. J Sep Sci 31(20):3595–3602
Amut E, Fu Q, Fang Q, Liu R, Xiao A, Zeng A, Chang C (2010) In situ polymerization preparation of chiral molecular imprinting polymers monolithic column for amlodipine and its recognition properties study. J Polym Res 17(3):401–409
Kan X, Geng Z, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Zhu J (2009) Processing and structure of carbon nanofiber paper. Nanotechnology 20(1):1–7
Fernández-González A, Laíño RB, Diaz-García ME, Guardia L, Viale A (2004) Assessment of molecularly imprinted sol–gel materials for selective room temperature phosphorescence recognition of nafcillin. J Chromatrogr B 804(1):247–254
Gonzáles GP, Hernando PF, Alegria JSD (2008) Determination of digoxin in serum samples using a flow-through fluorosensor based on a molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 23(11):1754–1758
Schubert U, Hüsing N (2005) Synthesis of inorganic materials, 2nd edn. Wiley, Weinheim
Costa Silva RG, Augusto F (2006) Sol–gel molecular imprinted ormosil for solid-phase extraction of methylxanthines. J Chromatogr A 1114(1):216–223
Ilavsky J, Jemian PR (2009) Irena: tool suite for modeling and analysis of small-angle scattering. J Appl Crystallogr 42(1):347–353
Kline SR (2006) Reduction and analysis of SANS and USANS data using IGOR Pro. J Appl Cryst 39(1):895–900
Beaucage G (1995) Approximations leading to a unified exponential/power-law approach to small-angle scattering. J Appl Crystallogr 28(1):717–728
Beaucage G (1996) Small-angle scattering from polymeric mass fractals of arbitrary mass-fractal dimension. J Appl Crystallogr 29(1):134–146
Becke AD (1993) Density-functional thermochemistry III. The role of exact exchange. J Chem Phys 98(1):5648–5652
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG (1988). Correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B 37(1):785–789
Gogonea V, Osawa E (1995) An improved algorithm for the analytical computation of solvent-excluded volume. The treatment of singularities in solvent-accessible surface area and volume functions. J Comput Chem 16(7):817–842
Pascual-Ahuir JL, Silla E (1990) Docking by least-squares fitting of molecular surface patterns. J Comput Chem 9(1):1047–1052
Silla E, Tunon I, Pascual-Ahuir JL (1991) GEPOL: an improved description of molecular surfaces. II computing the molecular area and volume. J Comput Chem 12(1):1077–1088
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Zakrzewski VG, Montgomery Jr JA, Stratmann RE, Burant JC, Dapprich S, Millam JM, Daniels AD, Kudin KN, Strain MC, Farkas O, Tomasi J, Barone V, Cossi M, Cammi R, Mennucci B, Pomelli C, Adamo C, Clifford S, Ochterski J, Petersson GA, Ayala PY, Cui, Q, Morokuma K, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Cioslowski J, Ortiz JV, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Gomperts R, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Gonzalez C, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Andres JL, Gonzalez C, Head-Gordon M, Replogle ES, Pople JA (1998) Gaussian 98, Revision A. 5. Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (1990) Sol–gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol–gel processing. Academic Press, New York
Löffler D, Ternes TA (2003) Analytical method for the determination of the aminoglycoside gentamicin in hospital wastewater via liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1000(1–2):583–588
Moffat AC, Osselton MD, Widdop B (2004) Analysis of Drugs and Poisons, 3rd edn. Pharmaceutical Press, London
Al-Amoud AI, Clark BJ, Chrystyn H (2002) Determination of gentamicin in urine samples after inhalation by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography using pre-column derivatisation with o-phthalaldehyde. J Chromatogr B 769(1):89–95
Kang L, Jun HW, McCall JW (1999) HPLC assay of Lidocaine in plasma with solid phase extraction and UV detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 19(5):737–745
Niopas I, Daftsios AC (2003) Determination of nifedipine in human plasma by solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography: validation and adaptation to pharmacokinetic studies. J Pharm Biomed Anal 32(1):1213–1218
Yang S, Cha J, Carlson K (2005) Simultaneous extraction and analysis of 11 tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics in influent and effluent domestic wastewater by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1097(1):40–53
Díaz-García ME, Laíño RB (2005) Molecular imprinting in sol–gel materials: recent developments and applications. Microchim Acta 149(1–2):19–36
Rouquerol J, Avnir D, Fairbridge CW, Everett DH, Haynes JH, Pernicone N, Ramsy JDF, Sing KSW, Unger KK (1994) Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids. Pure Appl Chem 66(8):1739–1758
Leirose GDS (2011) New nanoparticles data have been reported by G. D. S. Leirose and co-authors. J Pharm Sci 100(7):2826–2834
Cardoso MB (2010) Protein localization in silica nanospheres derived via biomimetic mineralization. Adv Funct Mater 20(1):3031–3038
Green DL, Lin JS, Lam Y, Hu MZ, Schaefer DW, Harris MT (2003) Size, volume fraction, and nucleation of Stober silica nanoparticles. J Colloid Interfaces Sci 266(2):346–358
Voronina NV, Meshkov IB, Myakushev VD, Laptinskaya TV, Papkov VS, Buzin MI, Il’Ina MN, Ozerin AN, Muzafarov AM (2010) Hybrid organo-inorganic globular nanospecies macromolecule to particle: transition from macromolecule to particle. J Polym Sci-b Part A Polym Chem 48(19):4310–4322
Dirè S, Facchin G, Ceccato R, Guarino L, Sassi A, Gleria M (2002) Hydroxylated cyclophosphazene/silica hybrid materials: synthesis and characterization. J Inorg Organomet Polym 12(3–4):59–78
Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE (2009) Multivariate Analysis, 7th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Acknowledgments
This project was partially financed by the CNPq. The authors are thankful to the LNLS (Project D11A-SAXS1-9926) for the measurements performed in the SAXS beamline.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morais, E.C., Correa, G.G., Brambilla, R. et al. Silica imprinted materials containing pharmaceuticals as a template: textural aspects. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 64, 324–334 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2861-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2861-0