Abstract
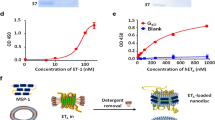
Since its discovery in 1989, there has been extensive research on endothelin (ET)-1 physiology, as well as pathology. Accordingly, there is considerable research on the discovery of therapeutics based around ET-1, amongst which current treatment options include endothelin receptor antagonists. These target the ET-1 receptors, which are G-protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs). We have effectively developed a soluble form of a GPCR that binds to ligands, by constructing a fusion polypeptide of different endothelin receptor ligand binding domains. Phage experiments identified strong binders to ET-1. We then constructed Fc-fusions of the top binders and further binding assays revealed a KD of 21.2 nM for the Fc-ETtr1 construct and KD of 77.3 nM for the Fc-ETtr2 construct. These constructs are soluble and have the ability to bind and potentially sequester elevated ET-1 levels that are prevalent in different diseases. These results provide a novel approach to targeting GPCR–binding ligands, and thereby to contribute to a very important class of therapeutics.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECL:
-
Extracellular loop
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- ETA:
-
Endothelin A
- ETB:
-
Endothelin B
- ETtr:
-
Endothelin-1 traps
- FFP:
-
Fc-fusion protein
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- HA:
-
Epitope human influenza hemagglutinin epitope
- LBD:
-
Ligand binding domain
- PBST:
-
Phosphate buffered saline tween
- SB:
-
Super broth medium
- STR:
-
Streptavidin
References
Adachi M et al (1993) Functional domains of human endothelin receptor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 22(Suppl 8):S121–S124
Aurora R et al (1997) Local interactions in protein folding: lessons from the alpha-helix. J Biol Chem 272(3):1413–1416
Beck A, Reichert JM (2011) Therapeutic Fc-fusion proteins and peptides as successful alternatives to antibodies. MAbs 3(5):415–416
Brazil M (2003) Setting a trap for cytokines. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2(2):90–90
Chaumais MC et al (2015) Clinical pharmacology of endothelin receptor antagonists used in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 15(1):13–26
Dinarello CA (2003) Setting the cytokine trap for autoimmunity. Nat Med 9(1):20–22
Fiore G et al (2005) Endothelin-1 triggers placental oxidative stress pathways: putative role in preeclampsia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(7):4205–4210
Gabbay E, Fraser J, McNeil K (2007) Review of bosentan in the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag 3(6):887–900
George EM, Granger JP (2011) Endothelin: key mediator of hypertension in preeclampsia. Am J Hypertens 24(9):964–969
George RA, Heringa J (2002) An analysis of protein domain linkers: their classification and role in protein folding. Protein Eng 15(11):871–879
Hiley CR et al (1992) BQ-123, cyclo(-D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu), is a non-competitive antagonist of the actions of endothelin-1 in SK-N-MC human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 184(1):504–510
Huovinen T et al (2013) Two ScFv antibody libraries derived from identical VL-VH framework with different binding site designs display distinct binding profiles. Protein Eng Des Sel 26(10):683–693
Jain A (2013) Endothelin-1-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 346(2):163–172
Jain A et al (2012) Endothelin-1 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress by activating the PLC-IP(3) pathway: implications for placental pathophysiology in preeclampsia. Am J Pathol 180(6):2309–2320
Karet F, Davenport A (1994) Endothelin and the human kidney: a potential target for new drugs. Nephrol Dial Transplant 9(5):4
Nelson J et al (2003) The endothelin axis: emerging role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3(2):110–116
Orry AJ, Wallace BA (2000) Modeling and docking the endothelin G-protein-coupled receptor. Biophys J 79(6):3083–3094
Patel S et al (2013) Selection of a high-affinity WW domain against the extracellular region of VEGF receptor isoform-2 from a combinatorial library using CIS display. Protein Eng Des Sel 26(4):307–315
Schneider MP, Boesen EI, Pollock DM (2007) Contrasting actions of endothelin ET(A) and ET(B) receptors in cardiovascular disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:731–759
Struck J, Morgenthaler NG, Bergmann A (2005) Proteolytic processing pattern of the endothelin-1 precursor in vivo. Peptides 26(12):2482–2486
Takasuka T et al (1992) Characterization of endothelin receptors ETA and ETB expressed in COS cells. J Biochem 112(3):396–400
Tam Tam KB et al (2011) Endothelin type A receptor antagonist attenuates placental ischemia-induced hypertension and uterine vascular resistance. Am J Obstet Gynecol 204(4):330e1–330e4
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank DM; Ms. Leela Jain for all her support. We also thank RC for funding this project.
Funding
This project was funded by private funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AJ and VM participated in the research design. AJ, VM and HY conducted the experiments. AJ, KH, AJ and IJ contributed new reagents or analytic tools. VM and AJ performed the data analysis. AJ, VM, KH, AJ, MJ and IJ wrote or contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, A., Mehrotra, V., Yong, H. et al. Creating a Soluble Binder to Endothelin-1 Based on the Natural Ligand Binding Domains of the Endothelin-1 (G-Protein-Coupled) Receptor. Int J Pept Res Ther 25, 107–114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9653-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9653-x