Abstract
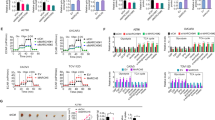
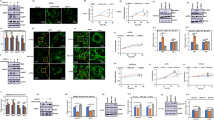
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is central to most adaptation responses of tumors to hypoxia, and consists of a hypoxia inducible HIF-1α or -2α subunit, and a constitutively expressed HIF-1β subunit. Previously, mitochondrial uncouplers, rottlerin and FCCP, were shown to increase the rate of cellular O2 consumption. In this study, we determined that mitochondrial uncouplers, rottlerin and FCCP, significantly decreased hypoxic as well as normoxic HIF-1 transcriptional activity which was in part mediated by down-regulation of the oxygen labile HIF-1α and HIF-2α protein levels in PC-3 and DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Our results also revealed that mitochondrial uncouplers decreased the expression of HIF target genes, VEGF and VEGF receptor-2. Taken together, our results indicate that functional mitochondria are important in HIF-1α and HIF-2α protein stability and transcriptional activity during normoxia as well as in hypoxia, and that mitochondrial uncouplers may be useful in the inhibition of HIF pathway in tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 721–732
Epstein AC, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O’Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI, Dhanda A, Tian YM, Masson N, Hamilton DL, Jaakkola P, Barstead R, Hodgkin J, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell 107: 43–54
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292: 468–472
Masson N, Willam C, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Independent function of two destruction domains in hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha chains activated by prolyl hydroxylation. EMBO J 20:5197–5206
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS, Kaelin Jr. WG (2001) HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 292: 464–468
Bruick RK, McKnight SL (2001) A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294: 1337–1340
Lando D, Peet DJ, Whelan DA, Gorman JJ, Whitelaw ML (2002) Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation domain a hypoxic switch. Science 295: 858–861
Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML, Bruick RK (2002) FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev 16: 1466–1471
Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL (1996) Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 271: 17771–17778
Bruick RK, McKnight SL (2002) Transcription. Oxygen sensing gets a second wind. Science 295: 807–808
Hopfl G, Ogunshola O, Gassmann M (2004) HIFs and tumors-causes and consequences. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286: R608–R623
Giaccia A, Siim BG, Johnson RS (2003) HIF-1 as a target for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2: 803–811
Zhong H, Semenza GL, Simons JW, De Marzo AM (2004) Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is an early event in prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Detect Prev 28: 88–93
Zhong H, Agani F, Baccala AA, Laughner E, Rioseco-Camacho N, Isaacs WB, Simons JW, Semenza GL (1998) Increased expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha in rat and human prostate cancer. Cancer Res 58: 5280–5284
Hao P, Chen X, Geng H, Gu L, Chen J, Lu G (2004) Expression and implication of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha in prostate neoplasm. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 24: 593–595
Schroedl C, McClintock DS, Budinger GR, Chandel NS (2002) Hypoxic but not anoxic stabilization of HIF-1alpha requires mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283: L922–L931
Hagen T, Taylor CT, Lam F, Moncada S (2003) Redistribution of intracellular oxygen in hypoxia by nitric oxide: effect on HIF1alpha. Science 302: 1975–1978
Mateo J, Garcia-Lecea M, Cadenas S, Hernandez C, Moncada S (2003) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by nitric oxide through mitochondria-dependent and -independent pathways. Biochem J 376: 537–544
Soltoff SP (2001) Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP levels and indirectly blocks protein kinase Cdelta tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 276: 37986–37992
Baby SM, Roy A, Lahiri S (2005) Role of mitochondria in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the rat carotid body glomus cells. Histochem Cell Biol 124: 69–76
Jiang BH, Semenza GL, Bauer C, Marti HH (1996) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 levels vary exponentially over a physiologically relevant range of O2 tension. Am J Physiol 271: C1172–C1180
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399: 271–275
Burroughs KD, Oh J, Barrett JC, DiAugustine RP (2003) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mek1/2 are necessary for insulin-like growth factor-I-induced vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in prostate epithelial cells: a role for hypoxia-inducible factor-1? Mol Cancer Res 1: 312–322
Palayoor ST, Tofilon PJ, Coleman CN (2003) Ibuprofen-mediated reduction of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 9: 3150–3157
Jiang BH, Zheng JZ, Leung SW, Roe R, Semenza GL (1997) Transactivation and inhibitory domains of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Modulation of transcriptional activity by oxygen tension. J Biol Chem 272: 19253–19260
Hirsila M, Koivunen P, Xu L, Seeley T, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J (2005) Effect of desferrioxamine and metals on the hydroxylases in the oxygen sensing pathway. Faseb J 19: 1308–1310
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE, Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM, Schumacker PT (2000) Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: a mechanism of O2 sensing. J Biol Chem 275: 25130–25138
Tirosh O, Aronis A, Melendez JA (2003) Mitochondrial state 3–4 respiration transition during Fas-mediated apoptosis controls cellular redox balance and rate of cell death. Biochem Pharmacol 66: 1331–1334
Vancurova I, Miskolci V, Davidson D (2001) NF-kappa B activation in tumor necrosis factor alpha-stimulated neutrophils is mediated by protein kinase Cdelta. Correlation to nuclear Ikappa Balpha. J Biol Chem 276: 19746–19752
Gschwendt M, Muller HJ, Kielbassa K, Zang R, Kittstein W, Rincke G, Marks F (1994) Rottlerin, a novel protein kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 199: 93–98
Kayali AG, Austin DA, Webster NJ (2002) Rottlerin inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by uncoupling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Endocrinology 143: 3884–3896
Tillman DM, Izeradjene K, Szucs KS, Douglas L, Houghton JA (2003) Rottlerin sensitizes colon carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis via uncoupling of the mitochondria independent of protein kinase C. Cancer Res 63: 5118–5125
Kalkhoven E (2004) CBP and p300: HATs for different occasions. Biochem Pharmacol 68: 1145–1155
Kappel A, Ronicke V, Damert A, Flamme I, Risau W, Breier G (1999) Identification of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-2 (Flk-1) promoter/enhancer sequences sufficient for angioblast and endothelial cell-specific transcription in transgenic mice. Blood 93: 4284–4292
Szewczyk A, Wojtczak L (2002) Mitochondria as a pharmacological target. Pharmacol Rev 54: 101–127
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Peter RatCliffe and Dr. Richard P. DiAugustine for providing us with the plasmid constructs. This work was supported by NIH grant # 1R21CA102382 to M. H. Kim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, R., Kim, M.H. Targeting the hypoxia inducible factor pathway with mitochondrial uncouplers. Mol Cell Biochem 296, 35–44 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9295-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9295-3