Abstract
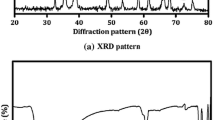
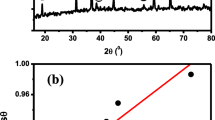
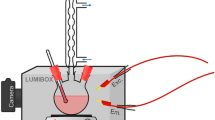
We investigated the synthesis of CdS nanoparticles via an optimized water-in-oil microemulsion route that used the non-ionic surfactant-based system H2O–n-octane–Brij30/1-octanol. For that purpose, a microemulsion that contained Cd(II) ions (μe1) and another microemulsion that contained S2− ions (μe2) were combined. To investigate the ways in which the non-ionic microemulsion characteristics controlled the size and emission properties of colloidal CdS quantum dots, μe1 and μe2 with tunable and robust similar structure were prepared. This requirement was fulfilled by matching the water emulsification failure boundary (wefb) of the two microemulsions and carrying out synthesis along this boundary. Dynamic light scattering and fluorescence probe techniques were used to investigate the size and interfacial organization of the microemulsion water droplets, and the CdS nanoparticles were characterized by UV–Vis and static fluorescence spectrometry, TEM and HRTEM. Nanoparticles of diameter 4.5–5.5 nm exhibiting enhanced band edge emission were produced by increasing the water content of the precursor microemulsions. The experimental results were combined with a Monte Carlo simulation approach to demonstrate that growth via coagulation of seed nuclei represented the driving mechanism for the CdS nanoparticle formation in the water-in-oil microemulsion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelescu DG, Magno L, Stubenrauch C (2010) Monte Carlo simulation of the size and composition of bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized in w/o-microemulsions. J Phys Chem C 114:22069–22078
Boutonnet M, Lögdberg S, Svensson EE (2008) Recent developments in the application of nanoparticles prepared from w/o microemulsions in heterogeneous catalysis. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 13:270–286
Caldararu H, Caragheorgheopol A, Vasilescu M, Dragutan I, Lemmetyinen H (1994) Structure of the polar core in reverse micelles of nonionic poly(oxyethylene) surfactants, as studied by spin probe and fluorescence probe techniques. J Phys Chem 98:5320–5331
Capek I (2004) Preparation of metal nanoparticles in water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 110:49–74
Caponetti E, Pedone L, Martino DC, Panto V, Liveri VT (2003) Synthesis, size control, and passivation of CdS nanoparticles in water/AOT/n-heptane microemulsions. Mater Sci Eng C 23:531–539
Chen DH, Chen CJ (2002) Formation and characterization of Au–Ag bimetallic nanoparticles in water-in-oil microemulsions. J Mater Chem 12:1557–1562
Dios M, Barroso F, Tojo C, Blanco MC, López-Quintela MA (2005) Effects of the reaction rate on the size control of nanoparticles synthesized in microemulsions. Colloid Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 270–271:83–87
Dios M, Barroso F, Tojo C, López-Quintela MA (2009) Simulation of the kinetics of nanoparticle formation in microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 333:741–748
Ethayaraja M, Bandyopadhyaya R (2006) Population balance models and Monte Carlo simulation for nanoparticle formation in water-in-oil microemulsions: implications for CdS synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 128:17102–17113
Ethayaraja M, Dutta K, Bandyopadhyaya R (2006) Mechanism of nanoparticle formation in self-assembled colloidal templates: population balance model and Monte Carlo simulation. J Phys Chem B 110:16471–16481
Ethayaraja M, Dutta K, Muthukumaran D, Bandyopadhyaya R (2007a) Nanoparticle formation in water-in-oil microemulsions: experiments, mechanism, and Monte Carlo simulation. Langmuir 23:3418–3423
Ethayaraja M, Ravikumar C, Muthukumaran D, Dutta K, Bandyopadhyaya R (2007b) CdS–ZnS core-shell nanoparticle formation: experiment, mechanism, and simulation. J Phys Chem C 111:3246–3252
Fletcher PDI, Horsup DI (1992) Droplet dynamics in water-in-oil microemulsions and macroemulsions stabilised by non-ionic surfactants. Correlation of measured rates with monolayer bending elasticity. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 88:855–864
Grabowski ZR, Rotkiewicz K, Seimiarczuk A, Cowley DJ, Baumann W (1979) Twisted intramolecular charge transfer states (TICT). A new class of excited states with a full charge separation. Nouveau J Chim 3:443–454
Holmberg K (2004) Surfactant-templated nanomaterials synthesis. J Colloid Interface Sci 274:355–364
Ingelsten HH, Bagwe R, Palmqvist A, Skoglundh M, Svanberg C, Holmberg K, Shah DO (2001) Kinetics of the formation of nano-sized platinum particles in water-in-oil microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 241:104–111
Karlstroem G (1985) A new model for upper and lower critical solution temperatures in poly(ethylene oxide) solutions. J Phys Chem 89:4962–4964
Lakowicz JR, Gryczynski I, Gryczynski Z, Nowaczyk K, Murphy CJ (2000) Time-resolved spectral observations of cadmium-enriched cadmium sulfide nanoparticles and the effects of DNA oligomer binding. Anal Biochem 280:128–136
Langevin D (1992) Micelles and microemulsions. Annu Rev Phys Chem 43:341–369
Lemyre J-L, Lamarre S, Beaupré A, Ritcey AM (2010) A new approach for the characterization of reverse micellar systems by dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 26:10524–10531
Li X, Coffer JL (1999) Effect of pressure on the photoluminescence of polynucleotide-stabilized cadmium sulfide nanocrystals. Chem Mater 11:2326–2330
Lin Y, Zhang J, Sargent EH, Kumacheva E (2002) Photonic pseudo-gap-based modification of photoluminescence from CdS nanocrystal satellites around polymer microspheres in a photonic crystal. Appl Phys Lett 81:3134–3136
López-Quintela MA (2003) Synthesis of nanomaterials in microemulsions: formation mechanism and growth control. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 8:137–144
López-Quintela MA, Tojo C, Blanco MC, Rio LG, Leis JR (2004) Microemulsion dynamics and reactions in microemulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 9:264–278
Ludolph B, Malik MA, O’Brien P, Revaprasadu N (1998) Novel single molecule precursor routes for the direct synthesis of highly monodispersed quantum dots of cadmium or zinc sulfide or selenide. Chem Commun 1849–1850
Magno M, Angelescu DG, Stubenrauch C (2009) Phase diagrams of non-ionic microemulsions containing reducing agents and metal salts as bases for the synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles. Colloid Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 348:116–123
Magno M, Sigle W, Aken PV, Angelescu D, Stubenrauch C (2010) Microemulsions as reaction media for the synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles: size and composition of particles. Chem Mater 22:6263–6271
Magno LM, Angelescu D, Sigle W, Stubenrauch C (2011a) Microemulsions as reaction media for the synthesis of Pt nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:3048–3058
Magno ML, Aken PAV, Sigle W, Angelescu DG, Stubenrauch C (2011b) Size control of PtPb intermetallic nanoparticles prepared via microemulsions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:9134–9136
Mandala D, Chatterjeeb U (2007) Synthesis and spectroscopy of CdS nanoparticles in amphiphilic diblock copolymer micelles. J Chem Phys 126:134507
Najjar R, Stubenrauch C (2009) Phase diagrams of microemulsions containing reducing agents and metal salts as bases for the synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:214–220
Nivaggioli T, Alexandridis P, Hatton TA, Yekta A, Winnik MA (1995) Fluorescence probe studies of Pluronic copolymer solutions as a function of temperature. Langmuir 11:730–737
Pandey G, Dixit S (2011) Growth mechanism and optical properties determination of CdS nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 115:17633–17642
Petit C, Lixon P, Pileni MP (1990) Synthesis of cadmium sulfide in situ in reverse micelles. 2. Influence of the interface on the growth of the particles. J Phys Chem 94:1598–1603
Pileni M-P (2000) II–VI semiconductors made by soft chemistry: syntheses and optical properties. Catal Today 58:151–166
Pileni M-P (2003) The role of soft colloidal templates in controlling the size and shape of inorganic nanocrystals. Nat Mater 2:145–150
Qi L, Ma J, Cheng H, Zhao Z (1996) Synthesis and characterization of mixed CdS–ZnS nanoparticles in reverse micelles. Colloid Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 111:195–202
Qiu S, Dong J, Chen G (1999) Preparation of Cu nanoparticles from water-in-oil microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 216:230
Ren B, Gao F, Tong Z, Yan Y (1999) Solvent polarity scale on the fluorescence spectra of a dansyl monomer copolymerizable in aqueous media. Chem Phys Lett 307:55–61
Rotkiewicz K, Grellmann K, Grabowski ZR (1973) Reinterpretation of the anomalous fluorescense of p–n, n-dimethylamino-benzonitrile. Chem Phys Lett 19:315
Sottmann T, Strey R (2005) Fundamentals in Interface and Colloid Science - Chapter 5. In: Lyklema J (ed) Soft Colloids V. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Steckel JS, Zimmer JP, Coe-Sullivan S, Stott NE, Bulovic V, Bawendi MG (2004) Blue luminescence from (CdS)ZnS core-shell nanocrystals. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:2154–2158
Stubenrauch C, Wielpütz T, Sottmann T, Roychowdhury C, DiSalvo FJ (2008) Microemulsions as templates for the synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Colloid Surf Chem Eng Aspects 317:328–338
Tata M, Banerjee S, John VT, Waguespack Y, McPherson GL (1997) Fluorescence quenching of CdS nanocrystallites in AOT water-in-oil microemulsions. Colloid Surf Chem Eng Aspects 127:39–46
Uskoković V, Drofenik M (2007) Reverse micelles: inert nano-reactors or physico-chemically active guides of the capped reactions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 133:23–34
Vasilescu M, Caragheorgheopol A, Caldararu H, Bandula R, Lemmetyinen H, Joela H (1998) Micropolarity and order in the reverse micelles of L62 and L64 Pluronic copolymers, as studied by molecular probe techniques. J Phys Chem 102:7740
Wang C-W, Moffitt MG (2004) Surface-tunable photoluminescence from block copolymer-stabilized cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Langmuir 20:11784–11796
Wu F, Zhang JZ, Kho R, Mehra RK (2000) Radiative and nonradiative lifetimes of band edge states and deep trap states of CdS nanoparticles determined by time-correlated single photon counting. Chem Phys Lett 330:237–242
Wu M-L, Chen D-H, Huang T-C (2001) Synthesis of Au/Pd bimetallic nanoparticles in reverse micelles. Langmuir 17:3877–3883
Xu W, Akins DL (2004) Reverse micellar synthesis of CdS nanoparticles and self-assembly into a superlattice. Mater Lett 58:2623–2626
Yao L, Xu G, Yang X, Luan Y (2009) CdS@SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized from polyoxyethylene (10) tertoctylphenyl ether based reverse microemulsion. Colloid Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 333:1–6
Zhang J, Sun L, Liao C, Yan C (2002) Size control and photoluminescence enhancement of CdS nanoparticles prepared via reverse micelle method. Solid State Commun 124:45–48
Zhang J, Di X-W, LIU Z-L, Gang GX, Zhou X-P (2007) Multicolored luminescent CdS nanocrystals. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 17:1367–1372
Acknowledgments
DA would like to thank the National University Research Council (CNCSIS) for financial support (Project PN-II-ID-PCE-2011-3-0328). POS-CCE O 2.2.1 Project INFRANANOCHEM-19/01.03.2009 funded by EU (ERDF) and Romanian Government is gratefully acknowledged for the light scattering equipment. DA thanks for the use of the HPC infrastructure developed under NASR Grant, Capacities Project CpI 84/2007. VST thanks to PN45N09 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelescu, D.G., Munteanu, G., Anghel, D.F. et al. Formation mechanism of CdS nanoparticles with tunable luminescence via a non-ionic microemulsion route. J Nanopart Res 15, 1376 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1376-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1376-5