Abstract
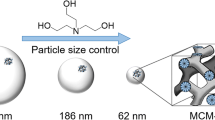
All variables affecting the morphology of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) should be carefully analyzed in order to truly tailored design their mesoporous structure according to their final use. Although complete control on MCM-41 synthesis has been already claimed, reproducibility and repeatability of results remain a big issue due to the lack of information reported in literature. Stirring rate, reaction volume, and system configuration (i.e., opened or closed reactor) are three variables that are usually omitted, making the comparison of product characteristics difficult. Specifically, the rate of solvent evaporation is seldom disclosed, and its influence has not been previously analyzed. These variables were systematically studied in this work, and they were proven to have a fundamental impact on final particle morphology. Hence, a high degree of circularity (C = 0.97) and monodispersed particle size distributions were only achieved when a stirring speed of 500 rpm and a reaction scale of 500 mL were used in a partially opened system, for a 2 h reaction at 80 °C. Well-shaped spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a diameter of 95 nm, a pore size of 2.8 nm, and a total surface area of 954 m2 g−1 were obtained. Final characteristics made this product suitable to be used in biomedicine and nanopharmaceutics, especially for the design of drug delivery systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrabino A (2011) Synthesis of mesoporous silica particles with control of both pore diameter and particle size. Master Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden
Bastos FS, Lima OA, Filho CR, Fernandes LD (2011) Mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41 synthesis from fluoride media. Brazilian. J Chem Eng 28:649–658
Beck JS, Vartuli JC, Roth WJ, Leonowicz ME, Kresge CT, Schmitt KD, Chu CTW, Olson DH, Sheppard EW, McCullen SB, Higgins JB, Schlenker JL (1992) A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J Am Chem Soc 114(27):10834–10843. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00053a020
Beltrán-Osuna AA, Perilla JE (2016) Colloidal and spherical mesoporous silica particles: synthesis and new technologies for delivery applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 77(2):480–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3874-2
Bernardos A, Mondragón L, Aznar E et al (2010) Enzyme-responsive intracellular controlled release using nanometric silica mesoporous supports capped with “saccharides”. ACS Nano 4(11):6353–6368. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn101499d
Bharti C, Nagaich U, Pal AK, Gulati N (2015) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in target drug delivery system: a review. Int J Pharm Investig 5(3):124–133. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-973X.160844
Brevet D, Hocine O, Delalande A, Raehm L, Charnay C, Midoux P, Durand JO, Pichon C (2014) Improved gene transfer with histidine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 471(1-2):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.05.020
Cai Q, Luo Z, Pang W et al (2001) Dilute solution routes to various controllable morphologies of MCM-41 silica with a basic medium. Chem Mater 13(2):258–263. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm990661z
Chakraborty I, Mascharak PK (2016) Mesoporous silica materials and nanoparticles as carriers for controlled and site-specific delivery of gaseous signaling molecules. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 234:409–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.07.028
Chen L, Zhang Z, Yao X, Chen X, Chen X (2015a) Intracellular pH-operated mechanized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as potential drug carries. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 201:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.09.023
Chen X, Yao X, Wang C, Chen L, Chen X (2015b) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with fluorescence-conjugated cyclodextrin for pH-activated controlled drug delivery and imaging. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 217:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.06.012
Chen Y, Chen H, Shi J (2013) In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic / therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv Mater 25(23):3144–3176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201205292
Chen Y, Shi X, Han B, Qin H, Li Z, Lu Y, Wang J, Kong Y (2012) The complete control for the nanosize of spherical MCM-41. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12(9):7239–7249. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2012.6459
Cheng Y-J, Zeng X, Cheng D-B, Xu XD, Zhang XZ, Zhuo RX, He F (2016) Functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) for highly controllable drug release and synergistic therapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 145:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.04.051
Crommelin DJA, Florence AT (2013) Towards more effective advanced drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm 454(1):496–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.02.020
Edler KJ (1997) Synthesis and characterisation of the mesoporous molecular sieve, MCM-41. Doctoral dissertation, The Australian National University, Australia
Guo Z, Liu X-M, Ma L, Li J, Zhang H, Gao YP, Yuan Y (2013) Effects of particle morphology, pore size and surface coating of mesoporous silica on naproxen dissolution rate enhancement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 101:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.06.026
Han N, Wang Y, Bai J, Liu J, Wang Y, Gao Y, Jiang T, Kang W, Wang S (2016) Facile synthesis of the lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanocomposites and their application in drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 219:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.08.006
Hu X, Wang Y, Peng B (2014) Chitosan-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-responsive nanocarriers for controlled drug release. Chem - An Asian J 9(1):319–327. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201301105
Huh S, Wiench JW, Yoo J et al (2003) Organic functionalization and morphology control of mesoporous silicas via a co-condensation synthesis method. Chem Mater 15(22):4247–4256. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0210041
Ikari K, Suzuki K, Imai H (2006) Structural control of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in a binary surfactant system. Langmuir 22(2):802–806. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0525527
Iliade P, Miletto I, Coluccia S, Berlier G (2012) Functionalization of mesoporous MCM-41 with aminopropyl groups by co-condensation and grafting: a physico-chemical characterization. Res Chem Intermed 38(3-5):785–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-011-0417-5
IUPAC (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
IUPAC (2014) Compendium of chemical terminology-gold book, 2.3.3. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
Khezri K, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Sarsabili M, Sobani M, Mirshafiei-Langari SA (2014) Spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles/tailor-made polystyrene nanocomposites by in situ reverse atom transfer radical polymerization. Polym Sci Ser B 56(6):909–918. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090414660026
Kresge CT, Leonowicz ME, Roth WJ, Vartuli JC, Beck JS (1992) Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 359(6397):710–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/359710a0
Lelong G, Bhattacharyya S, Kline S, Cacciaguerra T, Gonzalez MA, Saboungi ML (2008) Effect of surfactant concentration on the morphology and texture of MCM-41 materials. J Phys Chem C 112(29):10674–10680. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp800898n
Lv X, Zhang L, Xing F, Lin H (2016) Controlled synthesis of monodispersed mesoporous silica nanoparticles: particle size tuning and formation mechanism investigation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 225:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.12.024
Mamaeva V, Sahlgren C, Lindén M (2013) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine: recent advances. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(5):689–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.018
Manzano M, Aina V, Areán CO, Balas F, Cauda V, Colilla M, Delgado MR, Vallet-Regí M (2008) Studies on MCM-41 mesoporous silica for drug delivery: effect of particle morphology and amine functionalization. Chem Eng J 137(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.07.078
Merkus HG (2009) Particle size measurements: fundamentals, practice, quality. Springer Science +Businees Media B.V, The Netherlands
Morishige K, Fujii H, Uga M, Kinukawa D (1997) Capillary critical point of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, ethylene, and carbon dioxide in MCM-41. Langmuir 13(13):3494–3498. https://doi.org/10.1021/la970079u
de Padua Oliveira DC, de Barros ALB, Belardi RM et al (2016) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a potential vaccine adjuvant against Schistosoma mansoni. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 35:234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2016.07.002
Phillips E, Penate-Medina O, Zanzonico PB, Carvajal RD, Mohan P, Ye Y, Humm J, Gonen M, Kalaigian H, Schoder H, Strauss HW, Larson SM, Wiesner U, Bradbury MS (2014) Clinical translation of an ultrasmall inorganic optical-PET imaging nanoparticle probe. Sci Transl Med 6(260):260ra149. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009524
Qu F, Zhu G, Lin H, Zhang W, Sun J, Li S, Qiu S (2006) A controlled release of ibuprofen by systematically tailoring the morphology of mesoporous silica materials. J Solid State Chem 179(7):2027–2035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2006.04.002
Rafi AA, Mahkam M, Davaran S, Hamishehkar H (2016) A smart pH-responsive nano-carrier as a drug delivery system: a hybrid system comprised of mesoporous nanosilica MCM-41 (as a nano-container) & a pH-sensitive polymer (as smart reversible gatekeepers): preparation, characterization and in vitro releas. Eur J Pharm Sci 93:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2016.08.005
Rouquerol J, Rouquerol F, Llewellyn P, et al (2014) Adsorption by powders and porous solids: principles, methodology and applications. Elsevier Ltd.
Selvam P, Bhatia SK, Sonwane CG (2001) Recent advances in processing and characterization of periodic mesoporous MCM-41 silicate molecular sieves. Ind Eng Chem Res 40(15):3237–3261. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0010666
Shi YT, Cheng HY, Geng Y, Nan HM, Chen W, Cai Q, Chen BH, Sun XD, Yao YW, Li HD (2010) The size-controllable synthesis of nanometer-sized mesoporous silica in extremely dilute surfactant solution. Mater Chem Phys 120(1):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.10.045
Shibata H, Chiba Y, Kineri T, Matsumoto M, Nishio K (2010) The effect of heat treatment on the interplanar spacing of the mesostructure during the synthesis of mesoporous MCM-41 silica. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 358(1-3):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.12.020
Slowing II, Vivero-Escoto JL, Wu C-W, Lin VSY (2008) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(11):1278–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.03.012
Sun R, Wang W, Wen Y, Zhang X (2015) Recent advance on mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based controlled release system: intelligent switches open up. Nano 5(4):2019–2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5042019
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (2015) Cancer Nanotechnology Plan
Ukmar T, Maver U, Planinšek O, Kaučič V, Gaberšček M, Godec A (2011) Understanding controlled drug release from mesoporous silicates: theory and experiment. J Control Release 155(3):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.06.038
Vallet-Regi M, Arcos Navarrete D (2016) Nanoceramics in clinical use, 1st edn. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Vallet-Regi M, Rámila A, Del Real RP, Pérez-Pariente J (2001) A new property of MCM-41: drug delivery system. Chem Mater 13(2):308–311. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0011559
Varga N, Benko M, Sebok D et al (2015) Mesoporous silica core-shell composite functionalized with polyelectrolytes for drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 213:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.02.008
Wang Y, Zhao Q, Han N, Bai L, Li J, Liu J, Che E, Hu L, Zhang Q, Jiang T, Wang S (2015) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 11(2):313–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2014.09.014
Wanyika H, Gatebe E, Kioni P et al (2011) Synthesis and characterization of ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable physical properties by varying molar composition of reagents. African J Pharm Pharmacol 5(21):2402–2410. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPP11.592
Wu SH, Mou CY, Lin HP (2013) Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 42(9):3862–3875. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35405a
Xu X, Lü S, Gao C, Wang X, Bai X, Gao N, Liu M (2015a) Facile preparation of pH-sensitive and self-fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with PAMAM dendrimers for label-free imaging and drug delivery. Chem Eng J 266:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.075
Xu X, Lü S, Gao C, Wang X, Bai X, Duan H, Gao N, Feng C, Liu M (2015b) Polymeric micelle-coated mesop orous silica nanoparticle for enhanced fluorescent imaging and pH-responsive drug delivery. Chem Eng J 279:851–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.085
Xu X, Lü S, Gao C, Feng C, Wu C, Bai X, Gao N, Wang Z, Liu M (2016) Self-fluorescent and stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles using a double-role curcumin gatekeeper for drug delivery. Chem Eng J 300:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.087
Yang Y, Yu C (2015) Advances in silica based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Nanomedicine nanotechnology. Biol Med 12(2):317–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.10.018
Zhang H, Tong C, Sha J, Liu B, Lü C (2015) Fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized graphene oxide: a facile FRET-based ratiometric probe for Hg2+. Sensors Actuators B Chem 206:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.051
Zhou C, Yan C, Zhao J, Wang H, Zhou Q, Luo W (2016) Rapid synthesis of morphology-controlled mesoporous silica nanoparticles from silica fume. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 62:307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.01.031
Acknowledgements
José L. Gómez Ribelles acknowledges the support of the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, MINECO (research number MAT2016-76039-C4-1-R). CIBER-BBN is an initiative funded by the VI National R&D&i Plan 2008-2011, Iniciativa Ingenio 2010, Consolider Program, CIBER Actions and financed by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III with assistance from the European Regional Development Fund. This work was also supported by COLCIENCIAS (Departamento Administrativo de Ciencia Tecnología e Innovación, Convocatoria 567 Doctorados Nacionales) and Universidad Nacional de Colombia (grant number DIB 201010021438).
The authors would like to thank Professor Ramón Martínez Máñez, Scientific Director of CIBER’s Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN), and his research group at the Laboratory of Nanomedicine, from the Center for Molecular Recognition and Technological Development (UPV-IQMA), for their support and willingness. The authors acknowledge the assistance from the Microscopy Service at the UPV where all micrographs were taken.
Funding
This study was funded partially by Departamento Administrativo de Ciencia Tecnología e Innovación–COLCIENCIAS (recipient, Angela A. Beltrán-Osuna); Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, MINECO, research number MAT2016-76039-C4-1-R (Recipient, José L. Gómez-Ribelles); and Universidad Nacional de Colombia, grant number DIB 201010021438 (Recipient, Jairo E. Perilla).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 201 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beltrán-Osuna, Á.A., Gómez Ribelles, J.L. & Perilla, J.E. A study of some fundamental physicochemical variables on the morphology of mesoporous silica nanoparticles MCM-41 type. J Nanopart Res 19, 381 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4077-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4077-2