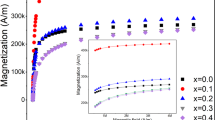
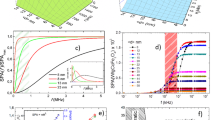
Abstract
Issues related to the optimization of heat transfer mechanisms dominated by superparamagnetic relaxation are considered in the case of AC (alternating current) magnetic field hyperthermia procedures. The key role in the conversion of electromagnetic energy to the thermal one via the superparamagnetic relaxation mechanism is played by the magnetic anisotropy of nanoparticles, easily to be controlled via the shape anisotropy component. The optimization process has been discussed in the case of magnetite (Fe3O4) ellipsoidal nanoparticles with dominant shape anisotropy dispersed in different media. Nanoparticles of different sizes and aspect ratios have been considered in correlation with those specific parameters of the actuating AC magnetic field which respect an established biological safely criterion. It has been proven that the dissipated power can be maximized for a given set of biological compatible RF (radiofrequency) field parameters (frequency and field amplitude at the sample space) only for specific pairs of particle sizes and aspect ratios. For instance, it has been shown that ellipsoidal magnetite nanoparticles with 10 nm equatorial size and aspect ratio of 2 are optimal for a maximum transferred power under radiofrequency excitations of 250 kHz and field amplitude of 20 kA/m, if high viscosity dispersion media are used. The methodology for deriving the optimal shape (geometrical) parameters of a specific type of nanoparticles in conditions of using available radiofrequency excitations, or vice versa, for deriving the optimal radiofrequency working parameters in the case of ferrofluids with specific nanoparticles (type and geometry) is described and discussed in detail.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanco-Andujar C, Walter A, Cotin G, Bordeianu C, Mertz D, Felder-Flesch D, Begin-Colin S (2016) Design of iron oxide-based nanoparticles for MRI and magnetic hyperthermia. Nanomedicine (Lond) 11(14):1889–1910. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2016-5001
Branquinho LC, Carriaõ MS, Costa AC, Zufelato N, Sousa MH, Miotto R, Ivkov R, Bakuzis AF (2013) Effect of magnetic dipolar interactions on nanoparticle heating efficiency: implications for cancer hyperthermia. Sci Rep 3:2887. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02887
Chang D, Lim M, Goos J, Qiao R, Ng YY, Mansfeld F, Jackson M, Davis TP, Kavallaris M (2018) Biologically targeted magnetic hyperthermia: potential and limitations. Front Pharmacol 9:831. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00831
Coïsson M, Barrera G, Celegato F, Martino L, Kane S N, Saroj Raghuvanshi S, Vinai F, Tiberto P (2017) Hysteresis losses and specific absorption rate measurements in magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia applications. 1861(6): 1545–1558. 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.12.006
Corato R, Espinosa A, Lartigue L, Tharaud M, Chat S, Pellegrino T, Ménager C, Gazeau F, Wilhelm C (2014) Magnetic hyperthermia efficiency in the cellular environment for different nanoparticle designs. Biomaterials 35:6400–6411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.036
Costas A, Florica C, Matei E, Toimil-Molares ME, Stavarache I, Kuncser A, Kuncser V, Enculescu I (2018) Magnetism and magnetoresistance of single Ni–Cu alloy nanowires. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:2345–2355. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.219
Diab DEH, Clerc P, Serhan N, Fourmy D, Gigoux V (2018) Combined treatments of magnetic intra-lysosomal hyperthermia with doxorubicin promotes synergistic anti-tumoral activity. Nanomaterials 8:468. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8070468
Donahue, M. J.; Porter, D. G. (1999) OOMMF User’s guide, version 1.0. National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg doi:https://doi.org/10.6028/nist.ir.6376 . The software is available at https://math.nist.gov/oommf/
Dortmund Data Bank (2019) http://ddbonline.ddbst.de/VogelCalculation/VogelCalculationCGI.exe?component=Water
Engelmann UM, Roeth AA, Eberbeck D, Buhl EM, Neumann UP, Schmitz-Rode T, Slabu I (2018) Combining bulk temperature and nanoheating enables advanced magnetic fluid hyperthermia efficacy on pancreatic tumor cells. Sci Rep 8:13210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31553-9
Espinosa A, Corato R, Kolosnjaj-Tabi J, Flaud P, Pellegrino P, Wilhelm C (2016) Duality of Iron oxide nanoparticles in Cancer therapy: amplification of heating efficiency by magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal bimodal treatment. ACS Nano 10:2436–2446. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b07249
Guardia P, Corato R, Lartigue L, Wilhelm C, Espinosa A, Garcia-Hernandez M, Gazeau F, Manna L, Pellegrino T (2012) Water-soluble Iron oxide nanocubes with high values of specific absorption rate for cancer cell hyperthermia treatment. ACS Nano 6(4):3080–3091. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2048137
Hedayatnasab Z, Abnisa F, Wan Daud WMA (2017) Review on magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic nanofluid hyperthermia application. Mater. Des 123:174–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.036
Hergt R, Dutz S (2007) Magnetic particle hyperthermia—biophysical limitations of a visionary tumour therapy. JMMM 311:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.10.1156
Huang HW, Liauth CT (2011) Review: therapeutical applications of heat in cancer therapy. J Med Biol Eng 32(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.5405/jmbe.932
Iacob N, Schinteie G, Palade P, Kuncser V (2015a) Approach for an improved experimental evaluation of the specific absorption rate in magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J Nanopart Res 17:190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2997-2
Iacob N, Schinteie G, Palade P, Ticos CM, Kuncser V (2015b) Stepped heating procedure for experimental SAR evaluation of ferrofluids. Eur Phys J E 38:57. https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2015-15057-8
Iacob N, Schinteie G, Bartha C, Palade P, Vekas L, Kuncser V (2016) Effects of magnetic dipolar interactions on the specific time constant in superparamagnetic nanoparticle systems. J Phys D 49(29):295001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/49/29/295001
Kuncser V, Palade P, Kuncser A, Greculeasa S, Schinteie G (2014) Engineering magnetic properties of nanostructures via size effects and interphase interactions. In: Kuncser V., Miu L. (eds) Size effects in nanostructures. Springer Series in Materials Science, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 169–237
Kuncser A, Antohe S, Kuncser V (2017) A general perspective on the magnetization reversal in cylindrical soft magnetic nanowires with dominant shape anisotropy. JMMM 423:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.066
Kuncser A, Iacob N, Kuncser V (2019) On the relaxation time of interacting superparamagnetic nanoparticles and implications for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. BJNANO 10:1280–1289
Lervik A, Bresme F, Kjelstrup S (2008) Heat transfer in soft nanoscale interfaces: the influence of interface curvature. Soft Matter 5:2407–2414. https://doi.org/10.1039/b817666c
Morrish AH (2001) The physical principles of magnetism. Wiley-IEE Press, New York
Nagayama G, Matsumoto T, Fukushima K, Tsuruta T (2017) Scale effect of slip boundary condition at solid–liquid interface. Sci Rep 7:43125. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43125
Palihawadana-Arachchige M, Nemala H, Naik VM, Naik R (2017) Effect of magnetic dipolar interactions on temperature dependent magnetic hyperthermia in ferrofluids. J Appl Phys 121:023901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4973879
Périgo EA, Hemery G, Sandre O, Ortega D, Garaio E, Plazaola F, Teran FJ (2015) Fundamentals and advances in magnetic hyperthermia. Appl PhysRev 2:041302. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935688
Rosensweig RE (2002) Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. JMMM 252:370–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00706-0
Spirou SV, Basini M, Lascialfari A, Sangregorio C, Innocenti C (2018) Magnetic hyperthermia and radiation therapy: radiobiological principles and current practice. Nanomaterials 8:401. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060401
Tang Y, Jin T, Flesch CR (2017) Numerical temperature analysis of magnetic hyperthermia considering nanoparticle clustering and blood vessels. IEEE Trans Magn 53:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2017.2722425
Tang Y, Flesch CR, Zhang C, Jin T (2018) Numerical analysis of the effect of non-uniformity of the magnetic field produced by a solenoid on temperature distribution during magnetic hyperthermia. JMMM 449:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.10.076
Thanh NTK (2018) Clinical applications of magnetic nanoparticles design to diagnosis manufacturing to medicine. CRC Press, New York
Tannous C, Gieraltowski J (2008) The Stoner–Wohlfarth model of ferromagnetism. Eur J Phys 29:475–487. https://doi.org/10.1088/0143-0807/29/3/008
Weaver JB, Kuehlert E (2012) Measurement of magnetic nanoparticle relaxation time. Med Phys 39(5):2765–2770. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3701775
Wang Q, Deng ZS, Liu J (2012) Theoretical evaluations of magnetic nanoparticle-enhanced heating on tumor embedded with large blood vessels during hyperthermia. J Nanopart Res 14:974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0974-6
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the Core Program PN18-110201/2018 at NIMP and the grant of the Romanian Ministry of Research and Innovation, 47PCCDI/2018 (PN-III-P1-1.2-PCCDI-2017-0871).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iacob, N., Kuncser, A., Comanescu, C. et al. Optimization of magnetic fluid hyperthermia with respect to nanoparticle shape-related parameters: case of magnetite ellipsoidal nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 22, 138 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04842-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04842-6