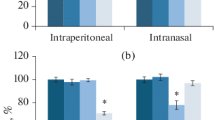
The actions of chronic i.p. administration of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β (IL-1β) on exploratory behavior and spatial memory were studied in rats. IL-1β was given at the weakly pyrogenic dose of 0.5 μg/kg daily for 14 days (starting seven days before and continuing through seven days of behavioral testing). Behavior was analyzed 23.5 h after sequential injections of cytokine. A battery of tests was used, including the open field test (on three sequential days), exploration of novel objects, and the Morris water maze. Experimental animals showed a significant decrease in motor activity, a minor increase in anxiety, and suppression of exploratory behavior. Impairments to spatial memory were not seen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. E. Zubareva, O. M. Efremov, A. S. Simbirtsev, and V. M. Klimenko, “Interleukin-1 beta and depressive states,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 87, No. 10, 1450–1456 (2001).
V. M. Klimenko, O. E. Zubareva, and S. V. Barabanova, “The actions of interleukin-1 on locomotor activity and spatial orientation,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., No. 4, 760–761 (1997).
Yu. N. Levashev, Immunotherapy with Betaleukin in the Complex Treatment of Patients with Localized Forms of Tuberculosis of the Respiratory Organs. Guidelines for Doctors, New Alternative Polygraphy, St. Petersburg (2008).
E. S. Romanova, N. I. Kuznetsov, and G. Yu. Startseva, “Betaleukin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C,” Zh. Infektol., 6, No. 3, 27–33 (2014).
E. S. Sokolova, V. I. Lyudyno, A. S. Simbirtsev, and V. M. Klimenko, “The psychostimulatory activity of subpyrogenic doses of interleukin-1β on chronic administration to rats,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 92, No. 3, 299–307 (2006).
A. N. Trofi mova, O. E. Zubareva, A. S. Simbirtsev, and V. M. Klimenko, “Effects of neonatal increases in interleukin-1β levels on the formation of spatial memory in adult rats,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 98, No. 6, 782–792 (2012).
S. J. Campbell, R. M. Deacon, T. Jiang, et al., “Overexpression of IL-1 beta by adenoviral-mediated gene transfer in the rat brain causes a prolonged hepatic chemokine response, axonal injury and the suppression of spontaneous behaviour,” Neurobiol. Dis., 27, No. 2, 151–163 (2007).
C. Cunningham and D. J. Sanderson, “Malaise in the water maze: untangling the effects of LPS and IL-1β on learning and memory,” Brain Behav. Immun., 22, No. 8, 1117–1127 (2008).
R. Dantzer and K. W. Kelley, “Twenty years of research on cytokine-induced sickness behavior,” Brain Behav. Immun., 21, No. 2, 153–160 (2007).
J. C. Felger and F. E. Lotrich, “Inflammatory cytokines in depression: neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic implications,” Neuroscience, 246, 199–229 (2013).
O. V. Forlenza, B. S. Diniz, L. L. Talib, et al., “Increased serum IL-1 level in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment,” Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord., 28, 507–512 (2009).
I. Goshen, T. Kreisel, H. Ounallah-Saad, et al., “A dual role for interleukin-1 in hippocampal-dependent memory processes,” Psycho-neuroendocrinology, 32, No. 8–10, 1106–1115 (2007).
M. Ifuku, S. M. Hossain, M. Noda, and T. Katafuchi, “Induction of interleukin-113 by activated microglia is a prerequisite for immunologically induced fatigue,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 40, No. 8, 3253–3263 (2014).
X. Monfrim, M. Gazal, P. B. De Leon, et al., “Immune dysfunction in bipolar disorder and suicide risk: is there an association between peripheral corticotropin-releasing hormone and interleukin-1β?” Bipolar Disord., 16, No. 7, 741–747 (2014).
A. H. Moore, M. Wu, S. S. Shaftel, et al., “Sustained expression of interleukin-lbeta in mouse hippocampus impairs spatial memory,” Neuroscience, 164, No. 4, 1484–1495 (2009).
K. Palin, R. M. Bluthé, D. Verrier, et al., “Interleukin-1 beta mediates the memory impairment associated with a delayed type hypersensitivity response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin in the rat hippocampus,” Brain Behav. Immun., 18, No. 3, 223–230 (2004).
J. N. Pearson, K. M. Schulz, and M. Patel, “Specific alterations in the performance of learning and memory tasks in models of chemoconvulsant-induced status epilepticus,” Epilepsy Res., 108, No. 6, 1032–1040 (2014).
S. Sakuma, D. Tokuhara, H. Otsubo, et al., “Dynamic change in cells expressing IL-1β in rat hippocampus after status epilepticus,” Jpn. Clin. Med., 13, No. 5, 25–32 (2014).
A. Simi, N. Tsakiri, P. Wang, and N. J. Rothwell, “Interleukin-1 and inflammatory neurodegeneration,” Biochem. Soc. Trans., 35, No. 5, 1122–1126 (2007).
A. J. Tarr, K. A. McLinden, D. Kraniac, et al., “The effects of age on lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive deficits and interleukin-1β expression,” Behav. Brain Res., 217, No. 2, 481–485 (2011).
M. Yamato, Y. Tamura, A. Eguchi, et al., “Brain interleukin-1β and the intrinsic receptor antagonist control peripheral Toll-like receptor 3-mediated suppression of spontaneous activity in rats,” PLoS One, 9, No. 3, e90950 (2014).
R. Yirmiya and I. Goshen, “Immune modulation of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis,” Brain Behav. Immun., 25, No. 2, 181–213 (2011).
J. J. Young, D. Bruno, and N. Pomara, “A review of the relationship between proinflammatory cytokines and major depressive disorder,” J. Affect. Disord., 169, No. 1, 15–20 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 101, No. 5, pp. 550–558, May, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalemenev, S.V., Sizov, V.V., Ishchenko, A.M. et al. Effects of Chronic Administration of Low-Dose Interleukin-1β on Exploratory Behavior and Spatial Memory in Rats. Neurosci Behav Physi 46, 903–907 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-016-0330-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-016-0330-x