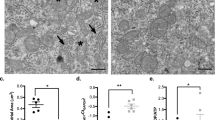
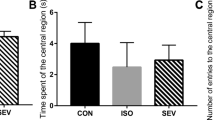
Abstract
This review summarizes recent research on the potential cognitive and behavioural abnormalities induced by exposure to volatile anesthetics and suggests a role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α in mediating these events. Volatile anesthetics are widely utilized in clinical and research settings, yet the long-term safety of exposure to these agents is under debate. Findings from various animal models suggest volatile anesthetics induce widespread apoptosis in the central nervous system (CNS) that correlates with lasting deficits in learning and memory. Longitudinal analysis of clinical data highlight an increased risk of developmental disorders later in life when children are exposed to volatile anesthetics, particularly when exposures occur over multiple sessions. However, the mechanisms underlying these events have yet to be established. Considering the extensive use of volatile anesthetics, it is crucial that these events are better understood. The possible role of HIF-1α in volatile anesthetic-induced CNS abnormalities will be suggested and areas requiring urgent attention will be outlined.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia PS, Kolesky SE, Jenkins A (2010) General anesthetic actions of GABAA receptors. Curr Neuropharmacol 8(1):2–9
Zuo Z (2012) Are volatile anesthetics neuroprotective or neurotoxic? Med Gas Res. doi:10.1186/2045-9912-2-10
Jiang Y, Xu H, Sun Y, Han N, Li QF (2012) Hypoxia inducible factor-1α is involved in the neurodegeneration induced by isoflurane in the brain of neonatal rats. J Neurochem 120(3):453–460
Mellidis K, Ordodi V, Galatou E, Sandesc D, Bubenek S, Duicu O, Muntean D, Lazou A (2014) Activation of prosurvival signalling pathways during the memory phase of volatile anesthetic preconditioning in human myocardium: a pilot study. Mol Cell Biochem 388(1–2):195–201
Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW et al (1999) Basic neurochemistry: molecular, cellular and medical aspects, 6th edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Hemmings HC, Akabas MH, Goldstein PA, Trudell JR, Orser BA, Harrison NL (2005) Emerging molecular mechanisms of general anesthetic action. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(10):503–510
Nishikawa K, Harrison NL (2003) The actions of sevoflurane and desflurane on the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor type A: effects of TM2 mutations in the alpha and beta subunit. Anesthesiology 99(3):678–684
Hemmings HC Jr (2009) Sodium channels and the synaptic mechanisms of inhaled anaesthetics. Br J Anaesth 103:61–69
Li L, Deng J, Zuo Z (2013) Glutamate transporter type 3 mediates isoflurane preconditioning-induced acute phase of neuroprotection in mice. Brain Res Bull 98:23–29
Qu X, Xu C, Wang H, Xu J, Liu W, Wang Y, Jia X, Xie Z, Xu Z, Ji C, Wu A, Yue Y (2013) Hippocampal glutamate level and glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST) are up-regulated in senior rat associated with isoflurane-induced spatial learning/memory impairment. Neurochem Res 38(1):59–73
Weir CJ (2006) The molecular mechanisms of general anesthesia: dissecting the GABAA receptor. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain 6(2):49–53
Sonner JM, Cantor RS (2013) Molecular mechanisms of drug action: an emerging view. Annu Rev Biophys 42:143–167
Rudolph U, Antkowiak B (2004) Molecular and neuronal substrates for general anaesthetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:709–720
Yon JH, Daniel-Johnson J, Carter LB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2005) Anesthesia induces neuronal cell death in the developing rat brain via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Neuroscience 135(3):815–827
Sprung J, Flick RP, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Barbaresi WJ, Bojanic K, Welch TL, Olson MD, Hanson AC, Schroeder DR, Wilder RT, Warner DO (2012) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder after early exposure to procedures requiring general anesthesia. Mayo Clin Proc 87(2):120–129
Flick RP, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Wilder RT, Voigt RG, Olson MD, Sprung J, Weaver AL, Schroeder DR, Warner DO (2011) Cognitive and behavioural outcomes after early exposure to anesthesia and surgery. Pediatrics 128(5):1053–1061
Ing C, DiMaggio C, Whitehouse A, Hegarty MK, Brady J, von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Davidson A, Wood AJJ, Li G, Sun LS (2012) Long-term differences in language and cognitive function after childhood exposure to anesthesia. Pediatrics 130(3):476–485
Monk TG, Weldon BC, Garvan CW, Dede DE, van der Aa MT, Heilman KM, Gravenstein JS (2008) Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 108(1):18–30
Kodama M, Satoh Y, Otsubo Y, Araki Y, Yonamine R, Masui K, Kazama T (2011) Neonatal desflurane exposure induces more robust neuroapoptosis than do isoflurane and sevoflurane and impairs working memory. Anesthesiology 115(5):979–991
Xiong W, Zhou G, Wang B, Xue Z, Wang L, Sun H, Ge S (2013) Impaired spatial learning and memory after sevoflurane–nitrous oxide anesthesia in aged rats is associated with down-regulated cAMP/CREB signaling. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079408
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW, Wozniak DF (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23(3):876–882
Istanphanous GK, Howard J, Nan X, Hughes EA, McCann JC, McAuliffe JJ, Danzer SC, Loepke AW (2011) Comparison of the neuroapoptotic properties of equipotent anesthetic concentrations of desflurane, isoflurane, or sevoflurane in neonatal mice. Anesthesiology 114(3):578–587
Creeley CE, Dikranian KT, Dissen GA, Back SA, Olney JW, Brambrink AM (2014) Isoflurane-induced apoptosis of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the fetal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology 120(3):626–638
Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber NB, Smith DJ, Zhang X, Dissen GA, Creeley CE, Olney JW (2010) Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Anesthesiology 112(4):834–841
Brambrink AM, Back SA, Riddle A, Gong X, Moravec MD, Dissen GA, Creeley CE, Dikranian KT, Olney JW (2012) Isoflurane-induced apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in the neonatal primate brain. Ann Neurol 72(4):525–535
Semenza GL, Prabhaker NR (2013) The role of hpoxia-inducible factors in oxygen sensing by the carotid body. Adv Exp Med Biol 785:1–5
Sutter CH, Laughner E, Semenza GL (2000) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α protein expression is controlled by oxygen-regulated ubiquitination that is disrupted by deletions and missense mutations. PNAS 97(9):4748–4753
Miyazaki K, Kawamoto T, Tanimoto K, Nishiyama M, Honda H, Kato Y (2002) Identification of functional hypoxia response elements in the promotor region of the DEC1 and DEC2 genes. J Biol Chem 277(4):47014–47021
Schafer ST, Frede S, Winning S, Bick A, Roshanger P, Fandrey J, Peters J, Adamzik M (2013) Hypoxia-inducible factor and target gene expression are decreased in patients with sepsis. Anaesthesiology 118(6):1426–1436
Ke Q, Costa M (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol 70(5):1469–1480
Carroll VA, Ashcroft M (2005) Targeting the molecular basis for tumour hypoxia. Expert Rev Mol Med 7(6):1–16
Hong S, Lee H, Kim K (2004) HIF-1α: a valid therapeutic target for tumor therapy. Cancer Res Treat 36(6):343–353
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD, Semenza GL (1996) Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol 12(12):5447–5454
Kind KL, Collett RA, Harvey AJ, Thompson JG (2004) Oxygen-regulated expression of GLUT-1, GLUT-3, and VEGF in the mouse blastocyte. Mol Reprod Dev 70(1):37–44
Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM (1995) Vascular permeability/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 146(5):1029–1039
Josko J, Gwozdz B, Jedrzejowska-Szypulka H, Hendryk S (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its effect on angiogenesis. Med Sci Monit 6(5):1047–1052
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. APS 79:1431–1568
Jewell UR, Kvietikova I, Scheid A, Bauer C, Wenger RH, Gassmann M (2001) Induction of HIF-1α in response to hypoxia is instantaneous. FASEB J 15(7):1312–1314
Mu D, Jiang X, Sheldon RA, Fox CK, Hamrick SEG, Vexler ZS, Ferriero DM (2003) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and induction of vascular endothelial growth factor in a rat neonatal stroke model. Neurobiol Dis 14(3):524–534
Chavez JC, LaManna JC (2002) Activation of hypoxia-inducible facotr-1 in the rat cerebral cortex after transient global ischemia: potential role of insulin-like growth factor-1. J Neurosci 22(20):8922–8931
Vannucci SJ, Seaman LB, Vannucci RC (1996) Effects of hypoxia–ischemia on GLUT1 and GLUT3 glucose transporters in immature rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16(1):77–81
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Zhang Y, Ling EA (2006) Hypoxia-induced astrocytic reaction and increased vascular permeability in the rat cerebellum. Glia 54(8):826–839
Lopez-Hernandez B, Posadas I, Podlesniy P, Abad MA, Trullas R, Cena V (2012) HIF-1α is neuroprotective during the early phases of mild hypoxia in rat cortical neurons. Exp Neurol 233(1):543–554
Halterman MW, Federoff HJ (1999) HIF-1alpha and p53 promote hypoxia-induced delayed neuronal death in models of CNS ischemia. Exp Neurol 159:65–72
Piret JP, Mottet D, Raes M, Michiels C (2002) Is HIF-1 alpha a pro- or an anti-apoptotic protein? Biochem Pharm 64(5–6):889–892
Wu C, Hu Q, Chen J, Yan F, Li J, Wang L, Mo H, Gu C, Zhang P, Chen G (2013) Inhibiting HIF-1α by 2ME2 ameliorates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 437:469–474
Saraf PG, Miller CL (2014) HIF-1α downregulation and apoptosis in hypoxic prostate tumor cells infected with oncolytic mammalian orthoreovirus. Oncotarget 5(2):561–574
Feng L, Tao L, Dawei H, Xuliang L, Xiaodong L (2013) HIF-1α expression correlates with cellular apoptosis, angiogenesis, and clinical prognosis in rectal carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. doi:10.1007/s12253-013-9738-6
Aminova LR, Chavez JC, Lee J, Ryu H, Kung A, LaManna JC, Ratan RR (2005) Prosurvival and prodeath effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α stabilization in a murine hippocampal cell line. J Biol Chem 280(5):3996–4003
Aminova LR, Siddiq A, Ratan RR (2008) Antioxidants, HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors or short interfering RNAs to BNIP3 or PUMA, can prevent prodeath effects of the transcriptional activator, HIF-1α, in a mouse hippocampal neuronal line. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(12):1989–1998
Suzuki H, Tomida A, Tsuruo T (2001) Dephosphorylated hypoxia-inducible factor 1α as a mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis during hypoxia. Oncogene 20:5779–5788
Amaral JD, Xavier JM, Steer CJ, Rodriques CM (2010) The role of p53 in apoptosis. Discov Med 9(45):145–152
Bagnall J, Leedale J, Taylor SE, Spiller DG, White MRH, Sharkey KJ, Bearon RN, See V (2014) Tight control of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-alpha transient dynamics is essential for cell survival in hypoxia. J Biol Chem 289(9):5549–5564
Fei P, Wang W, Kim S, Wang S, Burns TF, Sax JK, Buzzai M, Dicker DT, McKenna WG, Bernhard EJ, ElDeiry WS (2004) Bnip3L is induced by p53 under hypoxia, and its knockdown promotes tumor growth. Cancer Cell 6(6):597–609
Li QF, Wang XR, Yang YW, Su DS (2006) Up-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha by isoflurane in Hep3B cells. Anesthesiology 105(6):1211–1219
Raphael J, Zuo Z, Abedat S, Beeri R, Gozal Y (2008) Isoflurane preconditioning decreases myocardial infarction in rabbits via up-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 that is mediated by a mammalian target of rapamycin. Anesthesiology 108:415–425
Ye Z, Guo Q, Xia P, Wang N, Wang E, Yuan Y (2012) Sevoflurane postconditioning involves an up-regulation of HIF-1α and HO-1 expression via PI3 K/Akt pathway in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1463(29):63–74
Mellidis K, Ordodi V, Galatou E, Sandesc D, Bubenek S, Duicu O, Muntean D, Lazou A (2014) Activation of prosurvival signaling pathways during the memory phase of volatile anesthetic preconditioning in human myocardium: a pilot study. Mol Cell Biochem 388:195–201
Datta K, Li J, Bhattacharya R, Gasparian L, Wang E, Mukhopadhyay D (2004) Protein kinase C ζ transactivates hypoxia-inducible factor α by promoting its association with p300 in renal cancer. Cancer Res 64:456–462
Tanaka T, Takabuchi S, Nishi K, Oda S, Wakamatsu T, Daijo H, Fukuda K, Hirota K (2010) The intravenous anesthetic propofol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation and suppresses the glucose metabolism in macrophages. J Anesth 24(1):54–60
He XY, Shi XY, Yuan HB, Xu HT, Li YK, Zou Z (2012) Propofol attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis in alveolar epithelial type II cells through down-regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Injury 43(3):279–283
Benzonana LL, Perry NJ, Watts HR, Yang B, Perry IA, Coombes C, Takata M, Ma D (2013) Isoflurane, a commonly used volatile anesthetic, enhances renal cancer growth and malignant potential via the hypoxia-inducible factor cellular signalling pathway in vitro. Anesthesiology 119(3):593–605
Xie Z (2013) Cancer prognosis: can anesthesia play a role? Anesthesiology 9(3):501–503
Bedirli N, Bagriacik EU, Emmez H, Yilmaz G, Unal Y, Ozkose Z (2012) Sevoflurane and isoflurane preconditioning provides neuroprotection by inhibition of apoptosis-related mRNA expression in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 34(4):336–344
Zhao P, Peng L, Li L, Xu X, Zuo Z (2007) Isoflurane preconditioning improves long-term neurologic outcome after hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology 107(6):963–970
Murray CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74(5):1124–1136
Wei H, Liang G, Yang H (2007) Isoflurane preconditioning inhibited isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity. Neurosci Lett 425:59–62
Vutskits L, Davis PJ, Hansen TG (2012) Anesthetics and the developing brain: time for a change in practice? A pro/con debate. Pediatr Anesth 20(5):408–413
Acknowledgments
These studies were supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia of which Andrew John Lawrence is a Principal Research Fellow and the Australian Research Council of which Jhodie Rubina Duncan is a Future Fellow. Financial support from the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program is also acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giles, E.K., Lawrence, A.J. & Duncan, J.R. Exploring the Modulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1α by Volatile Anesthetics as a Possible Mechanism Underlying Volatile Anesthetic-Induced CNS Injury. Neurochem Res 39, 1640–1647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1379-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1379-y