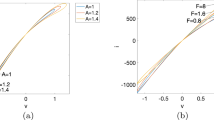
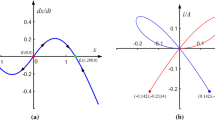
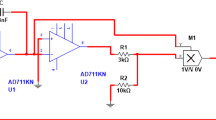
Abstract
Neural networks are favored by academia and industry because of their diversity of dynamics. However, it is difficult for ring neural networks to generate complex dynamical behaviors due to their special structure. In this paper, we present a memristive ring neural network (MRNN) with four neurons and one non-ideal flux-controlled memristor. The memristor is used to describe the effect of external electromagnetic radiation on neurons. The chaotic dynamics of the MRNN is investigated in detail by employing phase portraits, bifurcation diagrams, Lyapunov exponents and attraction basins. Research results show that the MRNN not only can generate abundant chaotic and hyperchaotic attractors but also exhibits complex multistability dynamics. Meanwhile, an analog MRNN circuit is experimentally implemented to verify the numerical simulation results. Moreover, a medical image encryption scheme is constructed based on the MRNN from a perspective of practical engineering application. Performance evaluations demonstrate that the proposed medical image cryptosystem has several advantages in terms of keyspace, information entropy and key sensitivity, compared with cryptosystems based on other chaotic systems. Finally, hardware experiment using the field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is carried out to verify the designed cryptosystem.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files
References
Hopfield, J.J.: Neural network and physical system with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 79, 2554–2558 (1982)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 1569–1578 (2017)
Yang, H., Wang, B., Yao, Q., et al.: Efficient hybrid multi-faults location based on hopfield neural network in 5G coexisting radio and optical wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 5(4), 1218–1228 (2019)
Wang, X., Li, Z.: A color image encryption algorithm based on Hopfield chaotic neural network. Opt. Lasers Eng. 115, 107–118 (2019)
Yang, X., Yuan, Q.: Chaos and transient chaos in simple Hopfield neural networks. Neurocomputing 69(1—-3), 232–241 (2005)
Rech, P.: Chaos and hyperchaos in a Hopfield neural network. Neurocomputing 74(17), 3361–3364 (2011)
Bao, B., Chen, C., Bao, H., et al.: Dynamical effects of neuron activation gradient on Hopfield neural network: numerical analyses and hardware experiments. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 29(4), 1930010 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Chen, C., et al.: Neural bursting and synchronization emulated by neural networks and circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 68(08), 3397–3410 (2021)
Njitacke, Z., Isaac, S., Kengne, J., et al.: Extremely rich dynamics from hyperchaotic Hopfield neural network: hysteretic dynamics, parallel bifurcation branches, coexistence of multiple stable states and its analog circuit implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 229(6), 1133–1154 (2020)
Strukov, D., Snider, G., Stewart, D., et al.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191), 80–83 (2008)
Wu, J., Ma, S.: Coherence resonance of the spiking regularity in a neuron under electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(3), 1895–1908 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yao, W., et al.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 90, 105390 (2020)
Etémé, A., Tabi, C., Beyala, J., et al.: Chaos break and synchrony enrichment within Hindmarsh-Rose-type memristive neural models. Nonlinear Dyn. 105(1), 785–795 (2021)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: A novel no-equilibrium HR neuron model with hidden homogeneous extreme multistability. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 145, 110761 (2021)
Li, Q., Tang, S., Zeng, H., et al.: On hyperchaos in a small memristive neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 78(2), 1087–1099 (2014)
Chen, C., Bao, H., Chen, M., et al.: Non-ideal memristor synapse-coupled bi-neuron Hopfield neural network: Numerical simulations and breadboard experiments. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 111, 152894 (2019)
Bao, B., Yang, Q., Zhu, L., et al.: Chaotic bursting dynamics and coexisting multistable firing patterns in 3D autonomous Morris-Lecar model and microcontroller-based validations. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos. 29(10), 1950134 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Cui, Li., et al.: Brain-like initial-boosted hyperchaos and application in biomedical image encryption. Ind. Inform, IEEE Trans (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2022.3155599
Leng, Y., Yu, D., Hu, Y., et al.: Dynamic behaviors of hyperbolic-type memristor-based Hopfield neural network considering synaptic crosstalk. Chaos 30(3), 033108 (2020)
Wang, Z., Parastesh, F., Rajagopal, K., et al.: Delay-induced synchronization in two coupled chaotic memristive Hopfield neural networks. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 134, 109702 (2020)
Chen, C., Min, F., Zhang, Y., et al.: Memristive electromagnetic induction effects on Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106, 2559–2576 (2021)
Njitacke, Z., Tsafack, N., Ramakrishnan, B., et al.: Complex dynamics from heterogeneous coupling and electromagnetic effect on two neurons: application in images encryption. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 153, 111577 (2021)
Pham, V., Jafari, S., Vaidyuanathan, S., et al.: A novel memristive neural network with hidden attractors and its circuitry implementation. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59(3), 358–363 (2016)
Bao, B., Qian, H., Xu, Q., et al.: Coexisting behaviors of asymmetric attractors in hyperbolic-type memristor based Hopfield neural network. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 81 (2017)
Chen, C., Chen, J., Bao, H., et al.: Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 3385–3399 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Hong, Q., et al.: A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 67(12), 3472–3476 (2020)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: Initial offset boosting coexisting attractors in memristive multi-double-scroll Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(4), 2821–2841 (2020)
Xu, X.: Complicated dynamics of a ring neural network with time delays. J. Phys. A-Math. Theor. 41(3), 035102 (2008)
Khokhlova, T., Kipnis, M.: The breaking of a delayed ring neural network contributes to stability: the rule and exceptions. Neural Netw. 48, 148–152 (2013)
Zhao, D., Wang, J.: Exponential stability and spectral analysis of a delayed ring neural network with a small-world connection. Nonlinear Dyn. 68(1), 77–93 (2012)
Kaslik, E., Balint, S.: Complex and chaotic dynamics in a discrete-time-delayed Hopfield neural network with ring architecture. Neural Netw. 22(10), 1411–1418 (2009)
Panayides, A.S., Amini, A., Filipovic, N.D., et al.: AI in medical imaging informatics: current challenges and future directions. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24(7), 1837–1857 (2020)
Ravichandran, D., Praveenkumar, P., Rayappan, J.: DNA chaos blend to secure medical privacy. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 16(8), 850–858 (2017)
Dzwonkowski, M., Rykaczewski, R.: Secure quaternion feistel cipher for DICOM images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(1), 371–380 (2018)
Ding, Y., Tan, F., Qin, Z., et al.: DeepKeyGen: a deep learning-based stream cipher generator for medical image encryption and decryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3062754
Belazi, A., Talha, M., Kharbech, S., et al.: Novel medical image encryption scheme based on chaos and DNA encoding. IEEE Access 7, 36667–36681 (2019)
Sambas, A., Vaidyanathan, S., Tlelo-Cuautle, E., et al.: A 3-D multi-stable system with a peanut-shaped equilibrium curve: Circuit design, FPGA realization, and an application to image encryption. IEEE Access 8, 137116–137132 (2020)
Telem, A., Fotsin, H., Kengne, J.: Image encryption algorithm based on dynamic DNA coding operations and 3D chaotic systems. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80(12), 19011–19041 (2021)
Zhao, C., Ren, H.: Image encryption based on hyper-chaotic multi-attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(1), 679–698 (2020)
Cao, W., Zhou, Y., Chen, C., et al.: Medical image encryption using edge maps. Signal Process. 132, 96–109 (2017)
Amirtharajan, A.: A robust medical image encryption in dual domain: chaos-DNA-IWT combined approach. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 58(7), 1445–1458 (2020)
Sangavi, V., Thangavel, P.: An exotic multi-dimensional conceptualization for medical image encryption exerting Rossler system and Sine map. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 55, 102626 (2020)
Kamal, S.T., Hosny, K.M., Elgindy, T.M., et al.: A new image encryption algorithm for grey and color medical images. IEEE Access. 9, 37855–37865 (2021)
Njitacke, Z.T., Isaac, S.D., Nestor, T., et al.: Window of multistability and its control in a simple 3D Hopfield neural network: application to biomedical image encryption. Neural Comput. Appl. 33(12), 6733–6752 (2021)
Doubla, I.S., Njitacke, Z.T., Ekonde, S., et al.: Multistability and circuit implementation of tabu learning two-neuron model: application to secure biomedical images in IoMT. Neural Comput. Appl. 33, 14945–14973 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Deng, Q., et al.: Review on chaotic dynamics of memristive neuron and neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 959–973 (2021)
Pham, V.T., Volos, C., Jafari, S., et al.: Coexistence of hidden chaotic attractors in a novel no-equilibrium system. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(3), 2001–2010 (2017)
Mannan, Z.I., Adhikari, S.P., Kim, H., et al.: Global dynamics of Chua Corsage Memristor circuit family: fixed-point loci, Hopf bifurcation, and coexisting dynamic attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(4), 3169–3196 (2020)
Moon, S., Baik, J.J., Hong, S.H.: Coexisting attractors in a physically extended Lorenz system. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos. 31(05), 2130016 (2021)
Veeman, D., Mehrabbeik, M., Natiq, H., et al.: A new chaotic system with coexisting attractors. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos. 32(03), 2230007 (2022)
Rajagopal, K., Karthikeyan, A., Srinivasan, A.: Dynamical analysis and FPGA implementation of a chaotic oscillator with fractional-order memristor components. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(3), 1491–1512 (2018)
Kengne, Z., Jafari, S., Njitacke, Z.T., et al.: Dynamic analysis and electronic circuit implementation of a novel 3d autonomous system without linear terms. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 52, 62–76 (2017)
Wang, N., Li, C., Bao, H., et al.: Generating multi-scroll Chua’s attractors via simplified piecewise-linear Chua’s diode. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 66(12), 4767–4779 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yu, F., et al.: An extremely simple multi-wing chaotic system: dynamics analysis, encryption application and hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(12), 12708–12719 (2021)
Stankevich, N., Kuznetsov, A., Popova, E., et al.: Chaos and hyperchaos via secondary Neimark-Sacker bifurcation in a model of radiophysical generator. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2355–2370 (2019)
Zhang, S., Li, C., Zheng, J., et al.: Generating any number of initial offset-boosted coexisting Chua’s double-scroll attractors via piecewise-nonlinear memristor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 69(07), 7202–7212 (2021)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(04), 600–612 (2004)
Wang, F., Wang, R., Iu, H.H.C., et al.: A novel multi-shape chaotic attractor and its FPGA implementation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 66(12), 2062–2066 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Major Research Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91964108), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61971185, 62101182), The Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020JJ4218), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M682552) and the Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (21C0200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Wang, C., Cui, L. et al. Hyperchaotic memristive ring neural network and application in medical image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn 110, 841–855 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07630-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07630-0