Abstract
Purpose
The aims of this study were (1) to determine whether amino acid and dipeptide loading can improve the effective permeability of gabapentin and (2) to characterize the underlying mechanism that is responsible for this interaction.
Materials and Methods
An in situ single-pass rat intestinal perfusion model was used to assess the effective permeability of gabapentin in rat, in the absence and presence of cellular loading by amino acid and dipeptide mixtures.
Results
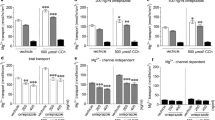
Compared to gabapentin alone, cellular loading with amino acid and dipeptide mixtures significantly improved the effective permeability of gabapentin by 46–79% in jejunum and by 67–72% in ileum (p ≤ 0.01). However, coperfusion of glycylsarcosine (i.e., PEPT1 substrate), methionine sulfoximine (i.e., glutamine synthase inhibitor), or lysine and arginine (i.e., b0,+ substrates) with the amino acid and dipeptide mixtures compromised the intestinal uptake of gabapentin.
Conclusions
These findings demonstrate, for the first time, a direct relationship between the PEPT1-mediated uptake of a dipeptide and the trans-stimulated uptake of gabapentin (an amino acid-like drug) through the transport system b0,+.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ala:
-
alanine
- arg:
-
arginine
- GABA:
-
γ-amino butyric acid
- gln:
-
glutamine
- glu:
-
glutamate
- GlyGlu:
-
glycylglutamate
- GlyGly:
-
glycylglycine
- GlySar:
-
glycylsarcosine
- GS:
-
glutamine synthase
- leu:
-
leucine
- lys:
-
lysine
- MS:
-
methionine sulfoximine
- P eff :
-
effective permeability
- SLC:
-
solute carrier family
References
N. S. Gee, J. P. Brown, V. U. K. Dissanayake, J. Offord, R. Thurlow, and G. N.Woodruff. The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of a calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 5768–5776 (1996).
J. S. Bryans and D. J. Wustrow. 3-Substituted GABA analogs with central nervous system activity: a review. Med. Res. Rev. 19: 149–177 (1999).
M. V. Ameringen, C. Mancini, B. Pipe, and M. Bennett. Antiepileptic drugs in the treatment of anxiety disorders: role in therapy. Drugs 64: 2199–220 (2004).
D. M. Treiman. GABAergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Epilepsia 42: 8–12 (2001).
T. Z. Su, E. Lunney, G. Campbell, and D. L. Oxender. Transport of gabapentin, a gamma-amino acid drug, by system L alpha-amino acid transporters: a comparative study in astrocytes, synaptosomes and CHO cells. J. Neurochem. 64: 2125–2131 (1995).
M. S. Luer, C. Hamani, M. Dujovny, B. Gidal, M. Cwik, K. Deyo, and J. H. Fischer. Saturable transport of gabapentin at the blood–brain barrier. Neurol. Res. 21: 559–562 (1999).
M. H. Dave, N. Schulz, M. Zecevic, C. A. Wagner, and F. Verrey. Expression of heteromeric amino acid transporters along the murine intestine. J. Physiol. 558: 597–610 (2004).
B. H. Stewart, A. R. Kugler, P. R. Thompson, and H. N. Bockbrader. A saturable transport mechanism in the intestinal absorption of gabapentin is the underlying cause of the lack of proportionality between increasing dose and drug levels in plasma. Pharm. Res. 10: 276–281 (1993).
N. Piyapolrungroj, C. Li, H. Bockbrader, G. Liu, and D. Fleisher. Mucosal uptake of gabapentin (Neurontin) vs. pregabalin in the small intestine. Pharm. Res. 18: 1126–1130 (2001).
N. Jezyk, C. Li, B. H. Stewart, X. Wu, H. N. Bockbrader, and D. Fleisher. Transport of pregabalin in rat intestine and Caco-2 monolayers. Pharm. Res. 16: 519–526 (1999).
C. M. Stevenson, L. L. Radulovic, H. N. Bockbrader, and D. Fleisher. Contrasting nutrient effects on the plasma levels of an amino acid-like antiepileptic agent from jejunal administration in dogs. J. Pharm. Sci. 86: 953–957 (1997).
F. Verrey, E. I. Closs, C. A. Wagner, M. Palacin, H. Endou, and Y. Kanai. CATs and HATs: the SLC7 family of amino acid transporters. Pflugers. Arch. 447: 532–542 (2004).
M. Pineda, E. Fernandez, D. Terrents, R. Estevez, C. Lopez, M. Camps, J. Lloberas, A. Zorzano, and M. Palacin. Identification of a membrane protein, LAT-2, that co-expresses with 4F2 heavy chain, an L-type amino acid transport activity with broad specificity for small and large zwitterionic amino acids. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 19738–19744 (1999).
U. Wenzel, B. Meissner, F. Doring, and H. Daniel. PEPT1-mediated uptake of dipeptides enhances the intestinal absorption of amino acids via transport system b0,+. J. Cell. Physiol. 186: 251–259 (2001).
Y. Kanai and M. A. Hediger. The glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter family SLC1: molecular, physiological and pharmacological aspects. Pflugers. Arch. 447: 469–479 (2004).
S. A. Adibi. The oligopeptide transporter (Pept-1) in human intestine: biology and function. Gastroenterology 113:332–340 (1997).
I. Komiya, J. Y. Park, A. Kamani, N. F. H. Ho, and W. I. Higuchi. Quantitative mechanistic studies in simultaneous fluid flow and intestinal absorption using steriods as model solutes. Int. J. Pharm. 4:249–262 (1980).
H. Lu, H. J. Thomas, and D. Fleisher. Influence of D-glucose-induced water absorption on rat jejunal uptake of two passively absorbed drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 81:21–25 (1992).
A. Howard, R. A. Goodlad, J. R. F. Walters, D. Ford, and B. Hirst. Increased expression of specific intestinal amino acid and peptide transporter mRNA in rats fed by TPN is reversed by GLP-2. J. Nutr. 134:2957–2964 (2004).
C. Gamboa and A. Ortega. Insulin-like growth factor-1 increases activity and surface levels of the GLAST subtype of glutamate transporter. Neurochem Int 40: 397–403 (2002).
F. Gouyon, L. Caillaud, V. Carrière, C. Klein, V. Dalet, D. Citadelle, G. L. Kellett, B. Thorens, A. Leturque, and E. B. Laroche. Simple-sugar meals target GLUT2 at enterocyte apical membranes to improve sugar absorption: a study in GLUT2-null mice. J. Physiol. 552:823–832 (2003).
R. A. Ronzio, W. B. Rowe, and A. Meister. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glutamine synthetase by methionine sulfoximine. Biochemistry 8:1066–1075 (1969).
V. DeMarco, K. Dyess, D. Strauss, C. M. West, and J. Neu. Inhibition of glutamine synthetase decreases proliferation of cultured rat intestinal epithelial cells. J. Nutr. 129:57–62 (1999).
K. Mizoguchi, S. Cha, A. Chairoungdua, D. K. Kim, Y. Shigeta, H. Matsuo, J. Fukushima, Y. Awa, K. Akakura, T. Goya, H. Ito, H. Endou, and Y. Kanai. Human cystinuria-related transporter: localization and functional characterization. Kidney Int. 59:1821–1833 (2001).
B. E. Gidal, M. M. Maly, J. Budde, G. L. Lensmeyer, M. E. Pitterle, and J. C. Jones. Effect of a high-protein meal on gabapentin pharmacokinetics. Epilepsy. Res. 23:71–76 (1996).
M. L. Hogerle and D. Winne. Drug absorption by the rat jejunum perfused in situ. Dissociation from the pH-partition theory and role of microclimate-pH and unstirred layer. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 322:249–255 (1983).
Y. Shiau, P. Fernandez, M. J. Jackson, and S. McMonagle. Mechanisms maintaining a low pH microclimate in the intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 248:G608–G617 (1985).
L. Salphati, K. Childers, L. Pan, K. Tsutsui, and L. Takahashi. Evaluation of single-pass intestinal-perfusion method in rat for the prediction of absorption in man. J Pharm Pharmacol 53: 1007–1013 (2001).
R. Hakkak, M. J. Ronis, and T. M. Badger. Effects of enteral nutrition and ethanol on cytochrome P450 distribution in small intestine of male rats. Gastroenterology 104:1611–1618 (1993).
Q. Y. Zhang, J. Wikoff, D. Dunbar, and L. Kaminsk. Characterization of rat small intestinal cytochrome P450 composition and inducibility. Drug Metab. Dispos. 24: 322–328 (1996).
L. K. Munck and B. G. Munck. Variation in amino acid transport along the rabbit small intestine. Mutual jejunal carriers of leucine and lysine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1116:83–90 (1992).
T. Terada, Y. Shimada, X. Pan, K. Kishimoto, T. Sakurai, R. Doi, H. Onodera, T. Katsura, M. Imamura, and K. I. Inui. Expression profiles of various transporters for oligopeptides, amino acids and organic ions along the human digestive tract. Biochem Pharmacol 70: 1756–1763 (2005).
G. L. Amidon, P. J. Sinko, and D. Fleisher. Estimating human oral fraction dose absorbed: a correlation using rat intestinal membrane permeability for passive and carrier mediated compounds. Pharm. Res. 5:651–654 (1988).
U. Fagerholm, M. Johansson, and H. Lennernas. Comparison between permeability coefficients in rat and human jejunum. Pharm. Res. 13:1336–1342 (1996).
W. L. Chiou and A. Barve. Linear correlation of the fraction of oral dose absorbed of 64 drugs between humans and rats. Pharm. Res. 15:1792–1795 (1998).
H. J. Steinhardt and S. A. Adibi. Kinetics and characteristics of absorption from an equimolar mixture of 12 glycyl-dipeptides in human jejunum. Gastroenterology 90:577–582 (1986).
Y. S. Kim, W. Birthwhistle, and Y. W. Kim. Peptide hydrolases in the brush border and soluble fractions of small intestinal mucosa of rat and man. J. Clin. Invest. 51: 1419–1430 (1972).
S. A. Adibi and D. W. Mercer. Protein digestion in human intestine as reflected in luminal, mucosal, and plasma amino acid concentrations after meals. J. Clin. Invest. 52:1586–1594 (1973).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grant R01 GM035498 (D.E.S.) from the National Institutes of Health. Theresa V. Nguyen was supported by an American Foundation for Pharmaceutical Education Fellowship, a Pharmacological Sciences Training Program from the National Institutes of Health (Grant T32 GM007767), and by the College of Pharmacy (Pfizer and Lyons Fellowships).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is posthumous for David Fleisher.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.V., Smith, D.E. & Fleisher, D. PEPT1 Enhances the Uptake of Gabapentin via Trans-Stimulation of b0,+ Exchange. Pharm Res 24, 353–360 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9155-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9155-6