Abstract
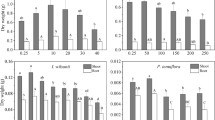
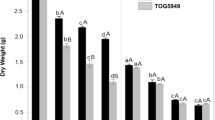
Many metal hyperaccumulating plants have to tolerate abiotic stresses in their native soils such as high metal concentrations, low nutrient status and drought. This paper tests the ability of the Ni-hyperaccumulator Alyssum murale and two races of the Zn-hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Prayon and Close House) to tolerate salinity. The plants were exposed to salt (NaCl) solutions ranging between 0 mM and 100 mM in conjunction with either high or low concentrations of Ni or Zn. Alyssum murale was most resistant to salt in terms of seedling emergence and survival of emerged seedlings. The two races of T. caerulescensand T. arvense were salt sensitive. High Ni or Zn concentrations did not have a clear effect on the salt tolerance of any of the plants tested. The implications of the findings are discussed for the development of metal phytoremediation/phytomining technologies on saline soils or where brackish water (e.g., mining wastewater) could be used to irrigate phytoremediation ‘crops’.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T S Al-Niemi W F Campbell M D Rumbaugh (1992) ArticleTitleResponse of alfalfa cultivars to salinity during germination and post germination growth Crop Sci. 32 979–980
J S Angle A J M Baker S N Whiting R L Chaney (2003) ArticleTitleSoil moisture effects on uptake of metal by Thlaspi and Alyssum Plant Soil 256 325–332 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1026137624250 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXotV2jtrs%3D
M Ashraf N Nazir T McNeilly (2001) ArticleTitleComparative salt tolerance of amphiploid and diploid Brassica species Plant Science 160 683–689 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00449-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXivFKms7o%3D Occurrence Handle11448743
A J M Baker P L Walker (1990) Ecophysiology of metal uptake by tolerant plants A J Shaw (Eds) Heavy metal tolerance in plants: Evolutionary aspects CRC Press Boca Raton 155–177
R S Boyd S N Martens (1992) The raison d’être for metal hyperaccumulation in plants A J M Baker J Proctor R D Reeves (Eds) The vegetation of ultramafic (serpentine) soils Intercept Ltd Andover 279–289
P E V Charman B W Murphy (Eds) (2000) Soils: their properties and management Oxford University Press Melbourne
C Croser S Renault J Franklin Zwiazek (2001) ArticleTitleThe effect of salinity on the emergence and seedling growth of Picea mariana,Picea glauca, and Pinus banksiana Environ. Pollut. 115 9–16 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00097-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmt1yisrw%3D Occurrence Handle11586777
D Evlagon I Ravina P M Neumann (1990) ArticleTitleInteractive effects of salinity and calcium on osmotic adjustment, hydraulic conductivity and growth in primary roots of maize seedlings Israel J. Bot. 39 239–247 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtl2qtr4%3D
H Greenway R Munns (1980) ArticleTitleMechanism of salt tolerance in nonhalohytes Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31 149–190 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.001053 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXksVWntb4%3D
U Krämer J D Cotter-Howells J M Charnock A J M Baker J A C Smith (1996) ArticleTitleFree histidine as a metal chelator in plants that accumulate nickel Nature 379 635–638 Occurrence Handle10.1038/379635a0
M M Lasat (2002) ArticleTitlePhytoextraction of toxic metals: A review of biological mechanisms J. Environ. Qual. 31 109–120 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvVCgurs%3D Occurrence Handle11837415
D H LloydThomas (1995) Hyperaccumulation of heavy metals by Thlaspi caerulescens J.& C. Presl Ph.D. thesis University of Sheffield UK
E Lombi K L Tearall J R Howarth F J Zhao M J Hawkesford S P McGrath (2002) ArticleTitleInfluence of iron status on cadmium and zinc uptake by different ecotypes of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens Plant Physiol. 128 1359–1367 Occurrence Handle10.1104/pp.010731 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivFylu70%3D Occurrence Handle11950984
E V Maas (1985) ArticleTitleCrop tolerance to saline sprinkling water Plant Soil 89 372–384
H Marschner (1995) The Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants Academic Press London
S P McGrath F J Zhao E Lombi (2002) ArticleTitlePhytoremediation of metals, metalloids and radionuclides Adv. Agron. 75 1–56 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitVSjsLw%3D
P Meerts P Duchene W Gruber C Lefèbvre (2003) ArticleTitleMetal accumulation and competitive ability in metallicolous and non-metallicolous Thlaspi caerulescens fed with different Zn salts Plant Soil 249 1–8 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1022510130148 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsVyrsrc%3D
P Meerts C Grommesch (2002) ArticleTitleSoil seed banks in a heavy-metal polluted grassland at Prayon (Belgium) Plant Ecol. 155 35–45 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1013234418314
K H Mühling A Läuchli (2003) ArticleTitleInteraction of NaCl and Cd stress on compartmentation pattern of cations, antioxidant enzymes and proteins in leaves of two wheat genotypes differing in salt tolerance Plant Soil 253 219–231 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1024517919764
R Munns (2002) ArticleTitleComparative physiology of salt and water stress Plant Cell Environ. 25 239–250 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.0016-8025.2001.00808.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xhslakurw%3D Occurrence Handle11841667
P M Neumann (1995) of root growth by salinity stress: Toxicity or an adaptive biophysical response? F Baluska M Ciamporova O Gasparikova P W Barlow (Eds) Structure and function of roots Developments in plant and soil sciences Kluwer AcademicPublishers Dordrecht 299–304
P M Neumann (1997) ArticleTitleSalinity resistance and plant growth revisited Plant Cell Environ. 20 1193–1198 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.1997.d01-139.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmsVersLY%3D
A J Pollard K Dandridge Powell F A Harper J A C Smith (2002) ArticleTitleThe genetics of metal hyperaccumulation in plants Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 21 539–566 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhtlKitrY%3D
A J Richards C Lefèbvre M G Macklin A Nicholson X Vekemans (1989) ArticleTitleThe population-genetics of Armeria maritima (Mill) Willd.On the River South Tyne, UK New Phytol. 112 281–293
B C Severne (1974) ArticleTitleNickel accumulation by Hybanthus floribundus Nature 248 807–808 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2cXks1Sku7g%3D Occurrence Handle4835556
Z G Shen F J Zhao S P McGrath (1997) ArticleTitleUptake and transport of Zn in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens and the non-hyperaccumulator Thlaspi ochroleucum Plant Cell Environ. 20 898–906 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.1997.d01-134.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXlt1Wmt7g%3D
R P Tolrà C Poschenrieder J Barceló (1996) ArticleTitleZinc hyperaccumulation in Thlaspi caerulescens. I. Influence on growth and mineral nutrition J. Plant Nutrit. 19 1531–1540
S N Whiting J R Leake S P McGrath A J M Baker (2000) ArticleTitlePositive responses to Zn and Cd by roots of the Zn and Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens New Phytol. 145 199–210 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00570.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisVarsb4%3D
S N Whiting P M Neumann A J M Baker (2003) ArticleTitleNickel and zinc hyperaccumulation by Alyssum murale and Thlaspi caerulescens (Brassicaceae) do not enhance survival and whole-plant growth under drought stress Plant Cell Environ. 26 351–360 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.00959.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtVylt7s%3D
S N Whiting R D Reeves A J M Baker (2002) ArticleTitleConservation of biodiversity: mining, metallophytes and land reclamation Mining Environ. Manage. 10 11–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comino, E., Whiting, S.N., Neumann, P.M. et al. Salt (NaCl) tolerance in the Ni hyperaccumulator Alyssum murale and the Zn hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 270, 91–99 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-1233-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-1233-0