Abstract
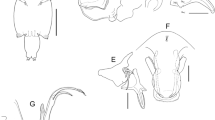
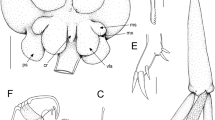
Two new species of the parasitic copepod genus Dissonus Wilson, 1906 are described: D. excavatus n. sp. from the gills of a labrid, Bodianus perditio, and a lutjanid, Macolor niger, collected off New Caledonia and Taiwan, and D. inaequalis n. sp. from a hemiscylliid elasmobranch, Chiloscyllium punctatum, collected off Sarawak (Malaysia) and the Philippines. Material of D. heronensis Kabata, 1966 is described from a balistid host, Pseudobalistes fuscus, off New Caledonia, and this constitutes a new host record for this parasite. D. manteri Kabata, 1966 was collected from four serranid host species off New Caledonia and from one of the same hosts off Taiwan. Two of the hosts from New Caledonia, Plectropomus laevis and Epinephelus cyanopodus, represent new host records. D. pastinum Deets & Dojiri, 1990 was recognised as a new synonym of D. nudiventris Kabata, 1966, so the total number of valid species is now twelve. Material from museum collections of D. nudiventris, D. similis Kabata, 1966 and D. spinifer Wilson, 1906 was re-examined and provided new information which is utilised in a key to all valid species of Dissonus.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Not Dissonus Skoracki, 1999.
References
Boxshall, G. A. (1990). The skeletomusculature of siphonostomatoid copepods, with an analysis of adaptive radiation in structure of the oral cone. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B, 328, 167–212.
Boxshall, G. A., & Halsey, S. H. (2004). An Introduction to copepod diversity (966 pp). London: The Ray Society.
Boxshall, G. A., & Justine, J.-L. (2005). A new genus of parasitic copepod (Siphonostomatoida: Caligidae) from a Razorback Scabbardfish, Assurger anzac Alexander (Trichiuridae) off New Caledonia. Folia Parasitologica, 52, 349–358.
Deets, G. B., & Dojiri, M. (1990). Dissonus pastinum n. sp. (Siphonostomatoida: Dissonidae), a copepod parasitic on a horn shark from Japan. Beaufortia, 41, 49–54.
Dojiri, M., & Cressey, R. F. (1987). Revision of the Taeniacanthidae (Copepoda: Poecilostomatoida) parasitic on fishes and sea urchins. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology, 447, 1–250.
Ho, J.-S., & Dojiri, M. (1977). Parasitic copepods on the fishes of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia Part II. Caligoida: Dissonus, Lepeophtheirus and Dentigryps. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory, 24, 77–97.
Huys, R., & Boxshall, G. A. (1991). Copepod evolution (468 pp). London: The Ray Society.
Kabata, Z. (1965). Parasitic Copepoda of fishes. Report B.A.N.Z. Antarctic Research Expedition (B), 8(6), 1–16, 1–7.
Kabata, Z. (1966). Copepoda parasitic on Australian fishes, V. Genus Dissonus (Dissonidae). Annals and Magazine of Natural History, (series 13), 9, 211–226.
Kabata, Z. (1979). Parasitic Copepoda of British fishes (468 pp). London: The Ray Society.
Kirtisinghe, P. (1950). Parasitic copepods of fish from Ceylon. III. Parasitology, 40, 77–86.
Kurtz, H. (1924). Parasitische Copepoden aus der Sammlung des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien. I. Pholidopus (Achtheinus) intermedius und Dissonus glaber, zwei neue Arten aus der Familie der Caligidae. Sitzungberichte Akademie der Wissenschaften. Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Classe. Wien, Abt. I, 133, 613–624.
Lewis, A. G. (1968). Copepod crustaceans parasitic on the fishes of Enewetok Atoll. Proceedings of the US National Museum, 125, 1–78.
Lim, L. H. S., & Justine, J.-L. (2007). Haliotrema banana sp. n. (Monogenea, Ancyrocephalidae) from Bodianus perditio (Perciformes: Labridae) off New Caledonia. Folia Parasitologica, 54, 203–207.
Matsuura, K., & Yoshino, T. (2004). A New Triggerfish of the Genus Abalistes (Tetraodontiformes: Balistidae) from the Western Pacific. Records of the Australian Museum, 56, 189–194.
Nunes-Ruivo, L., & Fourmanoir, P. (1956). Copepodes parasites de poissons de Madagascar I. Memoires de l’Institut Scientifique de Madagascar, Series A, 10, 69–80.
Ogawa, K. (1991). Ectoparasites of sawfish, Pristis microdon, caught in fresh waters of Australia and Papua New Guinea. University Museum, University of Tokyo, Nature and Culture, 3, 91–101.
Pillai, N. K. (1968). Additions to the copepod parasites of South Indian fishes. Parasitology, 58, 9–36.
Pillai, N. K. (1985). Fauna of India. Parasitic copepods of marine fishes (900 pp). Calcutta: Zoological Survey of India.
Randall, J. E., & Justine, J.-L. (2007). The triggerfish Abalistes filamentosus from New Caledonia, a first record for the South Pacific. Cybium, in press.
Skoracki, M. (1999). New genus and species of Syringophilidae from Eurasian Reed-Warbler, Acrocephalus scirpaceus (Sylviidae: Passeriformes) (Acari: Prostigmata). Genus (Wroclaw), 10, 155–162.
Skoracki, M. (2004). A new name for Dissonus Skoracki, 1999 not Wilson, 1906 (Acari: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae). Genus (Wroclaw), 15, 445–446.
Tang, D., & Kalman, J. E. (2005). A new caligiform copepod (Siphonostomatoida: Dissonidae) parasitic on Seriola hippos from western Australian waters, with new records and morphological variation for Dissonus nudiventris and Dissonus similis and an updated key to the species of Dissonus. Journal of Parasitology, 91, 427–437.
Ummerkutty, A. N. P. (1970). Studies on the crustacean fauna of Mysore coast – 3. Description of Caligotrogus kapuri n. gen. and n. sp. with remarks on its affinities. Journal of the Kerala Academy of Biology, 2, 3–14.
Wilson, C. B. (1906). Report on some parasitic Copepoda collected by Professor Herdman, at Ceylon, in 1902. In W. A. Herdman (Ed.), Report to Government of Ceylon on the Pearl Oyster Fisheries of the Gulf of Manaar, 5, 189–210, 1–5.
Wilson, C. B. (1907). North American parasitic copepods belonging to the family Caligidae. Part 2. The Trebinae and Euryphorinae. Proceedings of the United States National Museum, 31(1504), 669–720, 15–20.
Yamaguti, S. (1963). Parasitic Copepoda and Branchiura of fishes (1104 pp). New York: Interscience Publishers.
Acknowledgements
The type-material of Dissonus inaequalis n. sp. was collected by Janine Caira under collecting permit No. UPE:40/2001/19SJ.924 from the Economic Planning Unit in Kuala Lumpur, and under research agreement No. SBC-RA-0050-JNC from the Sarawak Biodiversity Centre in Kuching. This work was supported in part with funds from US National Science Foundation (NSF) grants Nos DEB 0103640 and DEB 0542846. Field collections in Taiwan were supported in part by a grant from the Paramitas Foundation to JSH. CLL acknowledges support from projects NSC 91-2313-B-415-010 and NSC 94-2311-B-415-004 from the National Science of Council of Taiwan. The collaboration between GAB and SO was supported by a short term invitation fellowship from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. We are grateful to T Chad Walter for arranging the loan of the D. spinifer material from the USNM. We would like to thank Danny Tang for his careful review and for his suggested improvements to the manuscript. Prof. C. Chauvet (University of New Caledonia) kindly provided several of the groupers examined. Identification of all Bodianus specimens mentioned in this paper was kindly confirmed (from photographs) by Martin Gomon (Museum Victoria, Melbourne, Australia), who also provided comments and literature; identification of most other labrids was kindly confirmed (from photographs) by Ronald Fricke (Staatliches Museum für Naturkunde, Stuttgart, Germany). In New Caledonia, Julie Mounier, volunteer technician, and Charles Beaufrère, Audrey Guérin, Anaïs Guillou, Amandine Marie, Chloé Journo, Violette Justine, Eric Bureau, Maya Robert, Damien Hinsinger, Géraldine Colli, Lenaïg Hemery and Aude Sigura, all students, participated in the fishing operations and parasitological survey. Sam Tereua, Miguel Clarque and Napoléon Colombani, captains of the RV ‘Coris’ provided safe navigation. Angelo di Matteo (IRD) provided technical help. This paper is a contribution to the EU funded network of Excellence, EDIT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boxshall, G.A., Lin, CL., Ho, JS. et al. A revision of the family Dissonidae Kurtz, 1924 (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida). Syst Parasitol 70, 81–106 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-008-9132-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-008-9132-z