Abstract
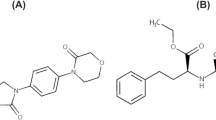
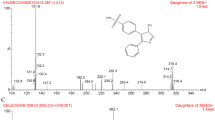
To establish a rapid and sensitive ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS/MS) method for the determination of rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban in rat plasma. The analytes and the internal standard (diazepam) were separated on an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 chromatography column (2.1 mm × 50 mm, 1.7 μm) using gradient elution with a mobile phase of acetonitrile and 0.1 % formic acid in water at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. The detection was performed on a triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer by multiple reaction monitoring mode to monitor the precursor-to-product ion transitions of m/z 436.1 → 145.1 for rivaroxaban, m/z 460.0 → 443.1 for apixaban, m/z 548.2 → 366.1 for edoxaban and m/z 285.2 → 193.1 for diazepam (IS) using a positive electrospray ionization interface. The method was validated over a concentration range of 1.0–200 ng/mL for rivaroxaban, 1.0–100 ng/mL for apixaban and 1.0–500 ng/mL for edoxaban. Total time for each chromatograph was 3.5 min. The intra- and inter-day precision and accuracy of the quality control samples at low, medium, and high concentration levels exhibited relative standard deviations <10.5 % and the accuracy values ranged from −9.9 to 11.3 %. The method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban in rats.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perzborn E, Roehrig S, Straub A, Kubitza D, Misselwitz F (2011) The discovery and development of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:61–75
Watson J, Whiteside G, Perry C (2011) Apixaban: first global approval. Drugs 71:2079–2089
Bounameaux H, Camm AJ (2014) Edoxaban: an update on the new oral direct factor Xa inhibitor. Drugs 74:1209–1231
Bassand JP (2012) Review of atrial fibrillation outcome trials of oral anticoagulant and antiplatelet agents. Europace 14:312–324
Mendell J, Tachibana M, Shi M, Kunitada S (2011) Effects of food on the pharmacokinetics of edoxaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 51:687–694
Frost C, Wang J, Nepal S, Schuster A, Barrett YC, Mosqueda-Garcia R et al (2013) Apixaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor: single dose safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and food effect in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 75:476–487
Stampfuss J, Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W (2013) The effect of food on the absorption and pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 51:549–561
Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti G et al (2012) Oral anticoagulant therapy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 141:e44S–e88S
Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH et al (2012) 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 33:2719–2747
Samama MM, Guinet C (2011) Laboratory assessment of new anticoagulants. Clin Chem Lab Med 49:761–772
Barrett YC, Wang Z, Knabb RM (2013) A novel prothrombin time assay for assessing the anticoagulant activity of oral factor Xa inhibitors. Clin Appl Thromb/Hemost 19:522–528
Schmitz EM, Boonen K, van den Heuvel DJ, van Dongen JL, Schellings MW, Emmen JM et al (2014) Determination of dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban by ultra-performance liquid chromatography: tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) and coagulation assays for therapy monitoring of novel direct oral anticoagulants. J Thromb Haemost 12:1636–1646
Korostelev M, Bihan K, Ferreol L, Tissot N, Hulot JS, Funck-Brentano C et al (2014) Simultaneous determination of rivaroxaban and dabigatran levels in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 100:230–235
Iqbal M, Khalil NY, Imam F, Khalid Anwer M (2015) A validated high-throughput UHPLC-MS/MS assay for accurate determination of rivaroxaban in plasma sample. J Thromb Thrombolysis 39:79–88
Rohde G (2008) Determination of rivaroxaban–a novel, oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor–in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 872:43–50
Pursley J, Shen JX, Schuster A, Dang OT, Lehman J, Buonarati MH et al (2014) LC-MS/MS determination of apixaban (BMS-562247) and its major metabolite in human plasma: an application of polarity switching and monolithic HPLC column. Bioanalysis 6:2071–2082
Delavenne X, Mismetti P, Basset T (2013) Rapid determination of apixaban concentration in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: application to pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 78–79:150–153
Zheng N, Yuan L, Ji QC, Mangus H, Song Y, Frost C et al (2015) “Center punch” and “whole spot” bioanalysis of apixaban in human dried blood spot samples by UHPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B 988:66–74
Gous T, Couchman L, Patel JP, Paradzai C, Arya R, Flanagan RJ (2014) Measurement of the direct oral anticoagulants apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban in human plasma using turbulent flow liquid chromatography with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Ther Drug Monit 36:597–605
Qiu X, Wang Z, Wang B, Zhan H, Pan X, Xu RA (2014) Simultaneous determination of irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide in human plasma by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a bioequivalence study. J Chromatogr B 957:110–115
Qiu X, Zhao JL, Hao C, Yuan C, Tian N, Xu ZS et al (2016) Simultaneous determination of mangiferin and neomangiferin in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and its application for pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 124:138–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Wl., Lou, D., Zhang, Dt. et al. Determination of rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban in rat plasma by UPLC–MS/MS method. J Thromb Thrombolysis 42, 205–211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1367-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1367-y