Abstract
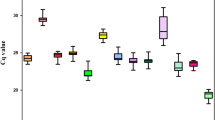
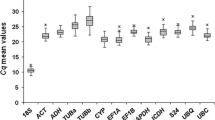
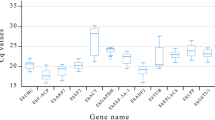
Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) is a sensitive method used to investigate relevant changes in gene expression during somatic embryogenesis. Understanding its regulatory network might be helpful to the process of induction of embryos and facilitate the development of efficient plant regeneration procedures. In this study, a set of 12 genes was selected and their stability was assessed in different tissues of somatic embryogenesis-related cultures of Coffea arabica. Analyses of gene expression stability were performed using the RefFinder tool that integrates the geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and Delta-Ct algorithms. Among the all candidate reference genes studied, APRT/EF1a, UBQ/ACT, ACT/24S, RPL39/24S, PP2A/RPL39, PP2A/AP47, emerged as the most stable for normalization of qPCR analyses of embryogenic cell suspensions, non-embryogenic calli, embryogenic calli, combined embryogenic and non-embryogenic calli, somatic embryos and plantlet, respectively. A combination of two genes, 24S and PP2A, was identified as most suitable reference genes across all samples for the C. arabica tissues studied. The commonly employed reference gene encoding glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was found to be inappropriate as a reference gene for embryogenic tissues of C. arabica. In addition, Baby boom (BBM) gene expression was investigated to confirm the validity of the selected reference genes, the transcript levels of gene were overestimated when unsuitable reference genes were used for normalization. The results shown herein will permit a more precise and reliable normalization of qPCR in experiments involving somatic embryogenesis of C. arabica.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64(15):5245–5250. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Barsalobres-Cavallari CF, Severino FE, Maluf MP, Maia IG (2009) Identification of suitable internal control genes for expression studies in Coffea arabica under different experimental conditions. BMC Mol Biol 10:1–11. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-10-1
Borowski JM, Galli V, da Silva Messias R, Perin EC, Buss JH, dos Anjos e Silva SD et al (2014) Selection of candidate reference genes for real-time PCR studies in lettuce under abiotic stresses. Planta 239(6):1187–1200. doi:10.1007/s00425-014-2041-2
Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L et al (2002) Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 14(8):1737–1749. doi:10.1105/tpc.001941
Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW (2005) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR—a perspective. J Mol Endocrinol 34(3):597–601. doi:10.1677/jme.1.01755
Cardoso DC, Martinati JC, Giachetto PF, Vidal RO, Carazzolle MF, Padilha L et al (2014) Large-scale analysis of differential gene expression in coffee genotypes resistant and susceptible to leaf miner–toward the identification of candidate genes for marker assisted-selection. BMC Genomics 15:66. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-66
Carvalho CHS, Paiva ACRS, Silva EQ, Custódio AA (2013a) Custo de produção de mudas clonais de café arábica produzidas por embriogênese somática. Circular Técnica 3, Embrapa, Brasília. http://www.sapc.embrapa.br/arquivos/consorcio/circulartecnica/circular_tecnica_03.pdf. Accessed 1 June 2015
Carvalho K, Bespalhok Filho JC, Dos Santos TB, De Souza SGH, Vieira LGE, Pereira LFP et al (2013b) Nitrogen starvation, salt and heat stress in coffee (Coffea arabica L.): identification and validation of new genes for qPCR normalization. Mol Biotechnol 53(3):315–325. doi:10.1007/s12033-012-9529-4
Chao WS, Doğramaci M, Foley ME, Horvath DP, Anderson JV (2012) Selection and validation of endogenous reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis in leafy spurge (Euphorbia esula). PLoS One 7:e42839. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042839
Chen L, Zhong H-Y, Kuang J-F, Li J-G, Lu W-J, Chen J-Y (2011) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies of gene expression in banana fruit under different experimental conditions. Planta 234(2):377–390. doi:10.1007/s00425-011-1410-3
Cheng D, Zhang Z, He X, Liang G (2013) Validation of reference genes in Solenopsis invicta in different developmental stages, castes and tissues. PLoS One 8(2):e57718. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057718
Cruz F, Kalaoun S, Nobile P, Colombo C, Almeida J, Barros LMG et al (2009) Evaluation of coffee reference genes for relative expression studies by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Mol Breed 23(4):607–616. doi:10.1007/s11032-009-9259-x
Docimo T, Schmidt GW, Luck K, Delaney SK, D’Auria JC (2013) Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative gene expression studies in Erythroxylum coca. F1000Res 2:37. doi:10.3410/f1000research.2-37.v1
Fan C, Ma J, Guo Q, Li X, Wang H, Lu M (2013) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS One 8(2):e56573. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056573
Figueiredo A, Loureiro A, Batista D, Monteiro F, Várzea V, Pais MS et al (2013) Validation of reference genes for normalization of qPCR gene expression data from Coffea spp. hypocotyls inoculated with Colletotrichum kahawae. BMC Res Notes 6:388. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-6-388
Florez SL, Erwin RL, Maximova SN, Guiltinan M, Curtis WR (2015) Enhanced somatic embryogenesis in Theobroma cacao using the homologous BABY BOOM transcription factor. BMC Plant Biol 15:121. doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0479-4
Galli V, da Silva Messias R, dos Anjos e Silva e SD, Rombaldi CV (2013) Selection of reliable reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction studies in maize grains. Plant Cell Rep 32(12):1869–1877. doi:10.1007/s00299-013-1499-x
Galli V, Borowski JM, Perin EC, da Silva Messias R, Labonde J, Pereira IS et al (2015) Validation of reference genes for accurate normalization of gene expression for real time-quantitative PCR in strawberry fruits using different cultivars and osmotic stresses. Gene 554(2):205–214. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2014.10.049
Gatica-Arias AM, Arrieta-Espinoza G, Espinoza Esquivel AM (2008) Plant regeneration via indirect somatic embryogenesis and optimisation of genetic transformation in Coffea arabica L. cvs. Caturra and Catuaí. Electron J Biotech 11(1):1–11. doi:10.2225/vol11-issue1-fulltext-9
Goulao LF, Fortunato AS, Ramalho JC (2012) Selection of reference genes for normalizing quantitative real-time PCR gene expression data with multiple variables in Coffea spp. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30(3):741–759. doi:10.1007/s11105-011-0382-6
Gruszczyńska A, Rakoczy-Trojanowska M (2011) Expression analysis of somatic embryogenesis-related SERK, LEC1, VP1 and NiR ortologues in rye (Secale cereale L.). J Appl Genet 52(1):1–8. doi:10.1007/s13353-010-0015-z
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Guénin S, Pelloux J, Lefebvre JF, Louvet R et al (2008a) The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6(6):609–618. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00346.x
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Pelloux J, Bellini C, Van Wuytswinkel O (2008b) Towards a systematic validation of references in real-time RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20(7):1734–1735. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.059774
Imai T, Ubi BE, Saito T, Moriguchi T (2014) Evaluation of reference genes for accurate normalization of gene expression for real time-quantitative PCR in Pyrus pyrifolia using different tissue samples and seasonal conditions. PLoS One 9(1):e86492. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086492
International Coffee Organization World coffee trade (1963–2013) (2014) A review of the markets, challenges and opportunities facing the sector. London, International Coffee Council. http://www.ico.org/news/icc-111-5-r1e-world-coffee-outlook.pdf. Accessed 1 June 2015.
Ivamoto ST, Domingues DS, Vieira LGE, Pereira LFP (2015) Identification of the transcriptionally active cytochrome P450 repertoire inCoffea arabica. Genet Mol Res 14(1):2399–2412. doi:10.4238/2015.March.27.25
Kong Q, Yuan J, Niu P, Xie J, Jiang W, Huang Y et al (2014) Screening suitable reference genes for normalization in reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR analysis in melon. PLoS One 9(1):e87197. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0087197
Kulinska-Lukaszek K, Tobojka M, Adamiok A, Kurczynska EU (2012) Expression of the BBM gene during somatic embryogenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol Plant 56(2):389–394. doi:10.1007/s10535-012-0105-
Kumar V, Sharma R, Trivedi PC, Vyas GK, Khandelwal V (2011) Traditional and novel references towards systematic normalization of qRT-PCR data in plants. Aust J Crop Sci 5(11):1455–1468
Li J, Han J, Hu Y, Yang J (2016) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR during flower development in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.). Front Plant Sci 7:516. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00516
Lin L, Han X, Chen Y, Wu Q, Wang Y (2013) Identification of appropriate reference genes for normalizing transcript expression by quantitative real-time PCR in Litsea cubeba. Mol Genet Genomics 288(12):727–737. doi:10.1007/s00438-013-0785-1
Lin Y, Zhang C, Lan H, Gao S, Liu H, Liu J et al (2014) Validation of potential reference genes for qPCR in maize across abiotic stresses, hormone treatments, and tissue types. PLoS One 9(2):e95445. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095445
Ling H, Wu Q, Guo J, Xu L, Que Y (2014) Comprehensive selection of reference genes for gene expression normalization in sugarcane by real time quantitative RT-PCR. PLoS One 9(5):e97469. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097469
Liu M, Wu Z, Jiang F (2015) Selection and validation of garlic reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 122:435. doi:10.1007/s11240-015-0780-9
Lland H, Hertzberg M, Marlton P (2006) Myeloid leukemia: methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa
Logan J, Edwards K, Saunders N (2009) Real-time PCR: current technology and applications. Poole. Caister Academic Press, Wymondham
Ma J, He Y, Wu C, Liu H, Hu Z, Sun G (2012) Cloning and molecular characterization of a SERK gene transcriptionally induced during somatic embryogenesis in Ananas comosus cv. Shenwan. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30(1):195–203. doi:10.1007/s11105-011-0330-5
Mamo S, Gal AB, Bodo S, Dinnyes A (2007) Quantitative evaluation and selection of reference genes in mouse oocytes and embryos cultured in vivo and in vitro. BMC Dev Biol 7:14. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-7-14
Marraccini P, Freire LP, Alves GSC, Vieira NG, Vinecky F, Elbelt S et al (2011) RBCS1expression in coffee: Coffea orthologs, Coffea arabica homeologs, and expression variability between genotypes and under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 11:85. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-85
Namasivayam P (2007) Acquisition of embryogenic competence during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90:1. doi:10.1007/s11240-007-9249-9
Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006) Quantification of mRNA using real-time PCR. Nat Protoc 1(3):1559–1582. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.236
Passarinho P, Ketelaar T, Xing M, Van Arkel J, Maliepaard C, Hendriks MW et al (2008) BABY BOOM target genes provide diverse entry points into cell proliferation and cell growth pathways. Plant Mol Biol 68(3):225–237. doi:10.1007/s11103-008-9364-y
Pathi KM, Tula S, Tuteja N (2013) High frequency regeneration via direct somatic embryogenesis and efficient Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of tobacco. Plant Signal Behav 8:e24354. doi:10.4161/psb.24354
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45–e45. doi:10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper—Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26(6):509–515. doi:10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
RefFinder (2016). Evaluating reference genes expression. Greenville, B. Zhang, East Carolina University. http://fulxie.0fees.us. Accessed 9 Nov 2016
Ribas AF, Dechamp E, Champion A, Bertrand B, Combes MC, Verdeil JL et al (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Coffea arabica (L.) is greatly enhanced by using established embryogenic callus cultures. BMC Plant Biol 11:92. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-92
Rodrigues TB, Khajuria C, Wang H, Matz N, Cardoso DC, Valicente FH et al (2014) Validation of reference housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera). PLoS One 9(10):e109825. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109825
Ságio SA, Barreto HG, Lima AA, Moreira RO, Rezende PM, Paiva LV et al (2014) Identification and expression analysis of ethylene biosynthesis and signaling genes provides insights into the early and late coffee cultivars ripening pathway. Planta 239(5):951–963. doi:10.1007/s00425-014-2026-1
Santis C, Smith-Keune C, Jerry DR (2011) Normalizing RT-qPCR data: are we getting the right answers? An appraisal of normalization approaches and internal reference genes from a case study in the finfish Lates calcarifer. Mar Biotechnol 13(2):170–180. doi:10.1007/s10126-010-9277-z
Silva AT, Barduche D, Livramento KG, Ligterink W, Paiva LV (2014) Characterization of a putative serk-like ortholog in embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Coffea arabica L. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32(1):176–184. doi:10.1007/s11105-013-0632-x
Silva AT, Barduche D, Livramento KG, Paiva LV (2015) A putative BABY BOOM -like gene (CaBBM) is expressed in embryogenic calli and embryogenic cell suspension culture ofCoffea arabica L. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 51(1):93–101. doi:10.1007/s11627-014-9643-z
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Spiegelaere W, Dern-Wieloch J, Weigel R, Schumacher V, Schorle H, Nettersheim D et al (2015) Reference gene validation for RT-qPCR, a note on different available software packages. PLoS One 10(3):e0122515. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122515
Spinsanti G, Panti C, Lazzeri E, Marsili L, Casini S, Frati F et al (2006) Selection of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies in striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) skin biopsies. BMC Mol Biol 7:32. doi:10.1186/1471-2199-7-32
Stolf-Moreira R, Lemos EGM, Abdelnoor RV, Beneventi MA, Rolla AAP, Pereira SS, et al (2011) Identification of reference genes for expression analysis by real-time quantitative PCR in drought-stressed soybean. Pesq Agropec Bras 46(1):58–65. doi:10.1590/S0100-204X2011000100008
Teixeira JB, Junqueira CS, Costa Pereira AJC, Mello RIS, Silva APD, Mundim DA (2004) Multiplicação clonal de café (Coffea arabica L.) via embriogênese somática. Documentos 121. Brasília, Embrapa. http://www.embrapa.br/documents/1355163/2021185/doc121.pdf/8b7b0ff2-9308-4485-a32d-34cb4bdcda4d. Accessed 1 June 2015
Van Boxtel J, Berthouly M (1996) High frequency somatic embryogenesis from coffee leaves. Factors influencing embryogenesis and subsequent proliferation and regeneration in liquid medium. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 44(1):4–17. doi:10.1007/BF00045907
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy R, De Paepe A et al (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Vandesompele J, Kubista M, Pfaffl MW (2009) Reference gene validation software for improved normalization. In: Logan J, Edwards K, Saunders N (eds) Real-time PCR: current technology and applications. Poole, Caister Academic Press, pp 47–64
Vieira LGE, Andrade AC, Colombo CA, Moraes AHA, Metha A, Oliveira AC et al (2006) Brazilian coffee genome project: an EST-based genomic resource. Braz J Plant Physiol 18(1):95–108
Volland M, Blasco J, Hampel M (2016) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR in marine bivalve ecotoxicology: systematic review and case study. BioRxiv. doi:10.1101/074542
Wan H, Zhao Z, Qian C, Sui Y, Malik AA, Chen J (2010) Selection of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in cucumber. Anal Biochem 399(2):257–261. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2009.12.008
Winkelmann T (2010) Clonal propagation of Cyclamen persicum via somatic embryogenesis. Methods Mol Biol 589:281–290. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-114-1_26
Yeap W, Loo JM, Wong YC, Kulaveerasingam H (2014) Evaluation of suitable reference genes for qRT-PCR gene expression normalization in reproductive, vegetative tissues and during fruit development in oil palm. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 116:55. doi:10.1007/s11240-013-0382-3
Zaffagnini M, Fermani S, Costa A, Lemaire SD, Trost P (2013) Plant cytoplasmic GAPDH: redox post-translational modifications and moonlighting properties. Front Plant Sci 4:450. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00450
Zamarripa A, Ducos JP, Bollon H, Dufour M, Pétiard V (1991) Production d’embryons somatiques de caféier en milieu liquide: effets densité d’inoculation et renouvellement du milieu. Café Cacao Thé 35(4): 233–244
Zeng S, Liu Y, Wu M, Liu X, Shen X, Liu C et al (2014) Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization and its applications in Lycium. PLoS One 9(5):e97039. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097039
Zhang Y, Clemens A, Maximova SN, Guiltinan MJ (2014) The Theobroma cacao B3 domain transcription factor TcLEC2 plays a duel role in control of embryo development and maturation. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):106. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-14-106
Acknowledgements
We thank especially MSc Wesley Pires Flausino Máximo for helpful comments on this manuscript. The authors also would like to thank Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for their financial support. These funding programs did not play a role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments NCF, HGB, LVP, ACJ. Performed the experiments NCF, CNF, ROM. Analyzed and interpreted the data NCF, CNF. Contributed with reagents and materials LVP, ACJ. Wrote the paper NCF. Made critical revisions of the content of the paper LVP, HGB, ACJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freitas, N.C., Barreto, H.G., Fernandes-Brum, C.N. et al. Validation of reference genes for qPCR analysis of Coffea arabica L. somatic embryogenesis-related tissues. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 128, 663–678 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1147-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1147-6