Abstract
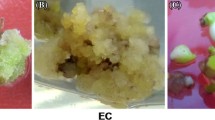
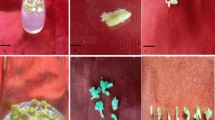
Somatic embryogenesis (SE) is an intricate in vitro multi-step biotechnological tool used to develop embryos/plants from a single or a group of somatic cells. It is a model technique for understanding various plant developmental pathways. A lot of research is going on to elucidate the mechanism underlying the process of SE. This study was aimed at the identification of SE related proteins in a medicinally important plant, Catharanthus roseus via label free liquid chromatography–mass spectroscopy (LC–MS). LC–MS is a sensitive and reliable technique than the gel based techniques, using LC–MSMS in tandem for separation and identification of proteins. Here, we are reporting for the first time SE related proteins in C. roseus by using gel free shotgun proteomic approach. The non embryogenic and embryogenic calli of C. roseus were used for comparative proteome analysis. A total of 3573 proteins were identified in both embryogenic and non embryogenic calli of which 1511 proteins were found to be common in both the calli. In non embryogenic callus 982 proteins while in embryogenic callus 1079 proteins were exclusively identified, which were associated with varied cellular functions. The most of these proteins function in different metabolic processes and stress responses. More than 72 stress responsive proteins and isoforms were observed exclusively in embryogenic callus including glutathione S transferase, ascorbate peroxidase, catalase, superoxide dismutase, alkylhydro peroxidase, SOD Fe N domain containing protein, pyridine nucleotide disulphide oxidoreductase, thioredoxin reductase. The role of plant growth regulators (PGRs) in inducing stress cause switching on/off of several genes has been discussed, led biochemical and molecular alterations in acquiring somatic embryogenic competence.
Key message
Proteomic map of Catharanthus roseus was prepared. A total of 3573 proteins were identified, of which 1079 were embryogenic. These proteins have role in metabolic and stress responses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campos NA, Panis B, Carpentier SC (2017) Somatic embryogenesis in coffee: the evolution of biotechnology and the integration of omics technologies offer great opportunities. Front Plant Sci 8:1460. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01460
Chen SL, Yu H, Luo HM, Wu Q, Li CF, Steinmetz A (2016) Conservation and sustainable use of medicinal plants: problems, progress, and prospects. Chin Med 11:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-016-0108-7
Eng JK, McCormack AL, Yates JR (1994) An approach to correlate MS/MS data to amino acid sequences in a protein database. J Am Soc Mass Spectrum 5:976–989
Feher A (2015) Somatic embryogenesis—stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. Biochem Biophys Acta 1849:385–402
Fehér A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 74:201–228
Fraga HP, Vieria LN, Heringer AS, Puttkammer CC, Silveira V, Guerra MP (2016) DNA methylation and proteome profiles of Araucaria angustfolia (Bertol) Kuntzeembryogenic cultures as affected by plant growth regulators supplementation. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 125(2):353–374
Ge F, Hu H, Huang X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li Z, Zou C, Peng H, Li L, Gao S, Pan G, Shen Y (2017) Metabolomic and proteomic analysis of maize embryonic callus induced from immature embryo. Sci Rep 7(1):1004. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01280-8
Guerra DD, Callis J (2012) Ubiquitin on the move: the ubiquitin modification system plays diverse roles in the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum- and plasma membrane-localized proteins. Plant Physiol 160(1):56–64. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.199869
Helleboid S, Hendriks T, Bauw G, Inze D, Vasseur J, Hilbert JL (2000) Three major somatic embryogenesis related proteins in Cichorium identified as PR proteins. J Exp Bot 51:1189–1200
Heringer AS, Barroso T, Macedo AF, Santa-Catarina C, Souza GHMF, Floh EIS, Souza-Filho GA, Silveira V (2015) Label-free quantitative proteomics of embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus during sugarcane somatic embryogenesis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127803
Heringer AS, Reis RS, Passaman LZ, de Souza-Filho GA, Santa-Catarina C, Silveira V (2017) Comparative proteomics analysis of the effect of combined red and blue lights on sugarcane somatic embryogenesis. Acta Physiol Plant 39:52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2349-1
Heringer AS, Santa-Catarina C, Silveira V (2018) Insights from proteomic studies into plant somatic embryogenesis. Proteomics. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201700265
Hincha DK, Thalhammer A (2012) LEA proteins: IDPs with versatile functions in cellular dehydration tolerance. Biochem Soc T 40:1000–1003
Hoenemann C, Ambold J, Hohe A (2012) Gene expression of a putative glutathione S-transferase is responsive to abiotic stress in embryogenic cell cultures of Cyclamen persicum.. Electronic J Biotechnol 15:1–6
Horstman A, Li M, Heidmann I, Weemen M, Chen B, Muino JM, Angenent GC, Boutilier K (2017) The Baby Boom transcription factor activates the LEC1-ABI3-FUS3-LEC2 network to induce somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol 175:848–857
https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFSAssets/LSG/manuals/MAN0011495_Pierce_C18_SpinCol_UG.pdf
Ikeda M, Umehara M, Kamada H (2006) Embryogenesis-related genes; its expression and roles during somatic and zygotic embryogenesis in carrot and Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol 23:153–161
Imin N, Nizamidin M, Daniher D, Nolan KE, Rose RJ, Rolfe BG (2005) Proteomic analysis of somatic embryogenesis in Medicago truncatula. Explant cultures grown under 6-benzylaminopurine and 1-naphthaleneacetic acid treatments. Plant Physiol 137:1250–1260. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.055277
Isaacson T, Damasceno CM, Saravanan RS, He Y, Catala C, Saladie M, Rose JK (2006) Sample extraction techniques for enhanced proteomic analysis of plant tissues. Nat Protoc 1(2):769–774
Jiménez VM (2005) Involvement of plant hormones and plant growth regulators on in vitro somatic embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul 47:91–110
Jing D, Zhang J, Xia Y, Kong L, OuYang F, Zhang S, Zhang H, Wang J (2016) Proteomic analysis of stress-related proteins and metabolic pathways in Picea asperata somatic embryos during partial desiccation. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12588
Junaid A, Mujib A, Fatima S, Sharma MP (2008) Cultural conditions affect somatic embryogenesis in Catharanthus roseus L. (G.) Don. Plant Biotechnol Rep 2:179–189
Karpievitch YV, Ashoka DP, Gordon AA, Richard DS, Alan RD (2010) Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry-based proteomics: biological and technological aspects. Ann Appl Stat 4(4):1797–1823. https://doi.org/10.1214/10-AOAS341
Lu D, Wei W, Zhou W, Linda D, Xiao J, Yu L (2017) Establishment of a somatic embryo regeneration system and expression analysis of somatic embryogenesis-related genes in Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume). Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 130(3):601–616
Mahdavi-Darvari F, Noor NM, Ismanizan I (2014) Epigenetic regulation and gene markers as signals of early somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 120(2):407–422
Mordhorst AP, Toonen MAJ, deVries SC (1997) Plant embryogenesis. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16(6):535–576
Mujib A, Ali M, Isah T, Dipti T (2014) Somatic embryo mediated mass production of Catharanthus roseus in culture vessel (bioreactor)—a comparative study. Saudi J Biol Sci 21(5):442–449
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497
Nolan KE, Irwanto RR, Rose RJ (2003) Auxin up-regulates MtSERK1 expression in both Medicago truncatula root-forming and embryogenic cultures. Plant Physiol 133:218–230. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.020917
Oh CS (2010) Characteristics of 14-3-3 proteins and their role in plant immunity. Plant Pathol J 26(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-016-0108-7
Orłowska A, Igielski R, Łagowska K, Pczyska EK (2017) Identification of LEC1, L1L and polycomb repressive Complex2 genes and their expression during the induction phase of Medicago truncatula Gaertn. somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 129:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1161-8
Park CJ, Seo YS (2015) A review of the molecular chaperones for plant immunity. Plant Pathol J 31(4):323–333. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.RW.08.2015.0150
Pulianmackal AJ, Kareem AV, Durgaprasad K, Trivedi ZB, Prasad K (2014) Competence and regulatory interactions during regeneration in plants. Front Plant Sci 5:142
Rupps A, Raschke J, Rümmler M, Linke B, Zoglauer K (2016) Identification of putative homologs of Larix decidua to Babyboom (BBM), leafy cotyledon1 (LEC1), Wuschel-related Homeobox2 (WOX2) and somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) during somatic embryogenesis. Planta 243:473–488
Schmidt ED, Guzzo F, Toonen MA, de Vries SC (1997) A leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Tolleter D, Hincha DK, Macherel D (2010) A mitochondrial late embryogenesis abundant protein stabilizes model membranes in the dry state. BBA Gen Sub 1798:1926–1933
Verdeil JL, Alemanno L, Niemenak N, Tranbarger TJ (2007) Pluripotent versus totipotent plant stem cells: dependence versus autonomy? Trends Plant Sci 12:245–252
Washburn MP, Wolters D, Yates JR (2001) Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multidimensional protein identification technology. Nat Biotechnol 19(3):242–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/85686
Zhao J, Li H, Fu S, Chen B, Sun W, Zhang J (2015) An iTRAQ-based proteomics approach to clarify the molecular physiology of somatic embryo development in Prince Rupprecht’s larch (Larix principis-rupprechtii Mayr). PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119987
Acknowledgements
The first author is thankful to University Grant Commission (UGC) for providing financial assistance with (Grant No. 2061530497). The authors are also thankful to the Department of Botany, Jamia Hamdard, and University of Delhi for providing laboratory and other research facilities for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BG, AF, NZ conducted most of the experiments. BG also made the draft of article. AM and MVR edited the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this research.
Additional information
Communicated by Francisco de Assis Alves Mourão Filho.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11240_2019_1563_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary Table 1. Proteins/isoforms (accession numbers) exclusively found in F1 i.e. embryogenic tissue of Catharanthus roseus—Supplementary material 1 (XLSX 102 KB)
11240_2019_1563_MOESM2_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary Table 2. Accession numbers of the proteins found in embrogenic callus (F1) having high abundance (twice or more) than that of non embryogenic callus (F2). The ratio (F1/F2) protein abundances are listed in decreasing order—Supplementary material 2 (XLSX 45 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulzar, B., Mujib, A., Rajam, M.V. et al. Identification of somatic embryogenesis (SE) related proteins through label-free shotgun proteomic method and cellular role in Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 137, 225–237 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01563-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01563-0