Abstract
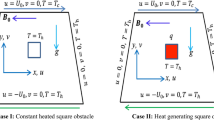
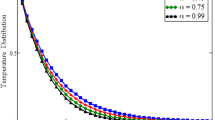
We present the benchmarking of a new finite element – finite volume (FEFV) solution technique capable of modeling transient multiphase thermohaline convection for geological realistic p-T-X conditions. The algorithm embeds a new and accurate equation of state for the NaCl–H2O system. Benchmarks are carried out to compare the numerical results for the various component-processes of multiphase thermohaline convection. They include simulations of (i) convection driven by temperature and/or concentration gradients in a single-phase fluid (i.e., the Elder problem, thermal convection at different Rayleigh numbers, and a free thermohaline convection example), (ii) multiphase flow (i.e., the Buckley–Leverett problem), and (iii) energy transport in a pure H2O fluid at liquid, vapor, supercritical, and two-phase conditions (i.e., comparison to the U.S. Geological Survey Code HYDROTHERM). The results produced with the new FEFV technique are in good agreement with the reference solutions. We further present the application of the FEFV technique to the simulation of thermohaline convection of a 400°C hot and 10 wt.% saline fluid rising from 4 km depth. During the buoyant rise, the fluid boils and separates into a high-density, high-salinity liquid phase and a low-density, low-salinity vapor phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Ackerer A. Younes R. Mosé (1999) ArticleTitleModeling variable density flow and solute transport in porous medium: 1. Numerical model and verification Transport Porous Media 35 245–373 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1006564309167
S.E. Buckley M.C. Leverett (1942) ArticleTitleMechanisms of fluid displacement in sands TAIME 146 107–116
J.P. Caltagirone (1975) ArticleTitleThermoconvection instabilities in a horizontal porous layer J. Fluid Mech. 72 269–287 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112075003345
J.P. Caltagirone P. Fabrie (1989) ArticleTitleNatural convection in a porous medium at high numbers. Part I - Darcy’s model Part I - Darcy’s model. Eur. J. Mech. B - Fluids 8 207–227
L.M. Cathles (1977) ArticleTitleAn analysis of the cooling of intrusives by groundwater convection which includes boiling Econ. Geol. 72 804–826
A.S.M. Cherkaoui W.S.D. Wilcock (1999) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of high Rayleigh number two-dimensional convection in an open-top porous layer heated from below J. Fluid Mech. 394 241–260 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0022112099005716
Christie M. A. and Blunt M. J. (2001). Tenth SPE comparative solution project: A comparison of upscaling techniques. SPE Paper presented at the SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium Houston, Texas, U.S.A., SPE66599.
D. Coumou S. Geiger T. Driesner C.A. Heinrich (2004) ArticleTitleNumerical modelling of MOR hydrothermal systems: The need to use compressible fluids, realistic EOS and high-resolution meshes EOS Transactions AGU, Fall Meeting Supplement 85 B13A–0210
P.T. Delaney (1982) ArticleTitleRapid intrusion of magma into wet rock: Groundwater flow due to pore pressure increases J. Geophys. Res. 87 7739–7756
E.M. Dicks (1983) Higher order Godounov black-oil simulations for compressible flow in porous media University of Reading U.K.
T. Driesner C.A. Heinrich (2003) ArticleTitleAccurate P-T-X-V-H correlations for the system NaCl-H2O from 0 to 800 °C, 0 to 500 Mpa, and 0 to 1 XNaCl Acta Mineralogica–Petrographica Abstract Ser. 2 55–56
Driesner T. and Heinrich C. A.: The system NaCl–H2O. I. Correlation formulae for phase relations in temperature-pressure-composition space from 0 to 1000°C, 0 to 5000 bar, and 0 to 1 X NaCl . Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta, in revision.
Driesner, T.: The system NaCl–H2O. II. Molar volume, enthalpy, and isobaric heat capacity from 0 to 1000°C, 0 to 5000 bar, and 0 to 1 X NaCl . Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta, in revision.
B. Dutrow D. Norton (1995) ArticleTitleEvolution of fluid pressure and fracture propagation during contact metamorphism J. Metamorphic Geol. 13 677–686
C.J. Eastoe (1982) ArticleTitlePhysics and chemistry of the hydrothermal system at the Panguna porphyry copper deposit Bougainville, Papua New Guinea, Econ. Geol. 77 127–153
J.W. Elder (1967) ArticleTitleTransient convection in a porous medium J. Fluid Mech. 27 609–623
S. Geiger S. Roberts S.K. Matthäi C. Zoppou A. Burri (2004) ArticleTitleCombining Finite element and finite volume methods for efficient multiphase flow simulations in highly heterogeneous and structurally complex geologic media Geofluids 4 284–299 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1468-8123.2004.00093.x
S. Geiger T. Driesner C.A. Heinrich S.K. Matthäi (2006) ArticleTitleMultiphase thermohaline convection in the Earth’s crust: I. A new finite element – finite volume solution technique combined with a new equation of state for NaCl–H2O Transport Porous Media 63 399–434
L. Haar J.S. Gallagher G.S. Kell (1984) NBS/NRC Steam Tables Hemisphere Publishing Corporation Washington, DC
Hayba, D. O. and Ingebritsen, S. E.: 1994, The Computer Model HYDROTHERM, A Three-Dimensional Finite-Difference Model to Simulate Ground-Water Flow and Heat Transport in the Temperature Range of 0 to 1200°C. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 94–4045.
D.O. Hayba S.E. Ingebritsen (1997) ArticleTitleMultiphase groundwater flow near cooling plutons J. Geophys. Res. 102 12235–12252 Occurrence Handle10.1029/97JB00552
C.A. Heinrich D. Günther A. Audétat T. Ulrich R. Frischknecht (1999) ArticleTitleMetal fractionation between magmatic brine and vapor, determined by microanalysis of fluid inclusions Geology 27 755–758 Occurrence Handle10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0755:MFBMBA>2.3.CO;2
Helmig R. (1997). Multi-phase Flow and Transport Processes in the Subsurface, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
R.W. Henley A. McNabb (1978) ArticleTitleMagmatic vapor plumes and ground-water interaction in porphyry copper emplacement Econ. Geol. 73 1–20
T. Jupp A. Schultz (2000) ArticleTitleA thermodynamic explanation for black smoker temperatures Nature 403 880–883 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35002552
S. Kimura G. Schubert J.M. Straus (1986) ArticleTitleRoute to chaos in porous-medium thermal convection J. Fluid Mech. 116 305–324
O. Kolditz R. Ratke H. J. Diersch W. Zielke (1998) ArticleTitleCoupled groundwater flow and transport: 1. Verification of variable density flow and transport models Adv. Water 21 27–46
Matthäi S. K., Geiger, S. and Roberts S.: 2001, Complex Systems Platform: CSP3D3.0: User’s Guide. http://e-collection.ethbib.ethz.ch/show?type=bericht&nr=239, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule Zürich, Switzerland.
P. Nehlig (1991) ArticleTitleSalinity of oceanic hydrothermal fluids – a fluid inclusion study Earth and Planetary Sci. Lett. 102 310–325
D. Norton J. E. Knight (1977) ArticleTitleTransport phenomena in hydrothermal systems: Cooling plutons Amer. J. Sci. 277 937–981
Ogata A. and Banks R. B. (1961). A solution of the differential equation of longitudinal dispersion in porous media, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 411-A.
C. Oldenburg K. Pruess (1999) ArticleTitlePlume separation by transient thermohaline convection in porous media Geophys. Res. Lett. 26 2997–3000 Occurrence Handle10.1029/1999GL002360
O.M. Phillips (1991) Flow and Reactions in Permeable Rocks Cambridge University Press Cambridge
Pruess K.: 1987, TOUGH User’s Guide. U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Report NUREG/CR –4645.
Pruess, K.: 1991, TOUGH2 - A General Purpose Numerical Simulator for Multiphase Fluid and Heat Flow, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Report, LBL–29400.
E. Roedder (1971) ArticleTitleFluid inclusion studies on porphyry-type ore deposits at Bingham. Utah, Butte, Montana, and Climax, Colorado Econ. Geol. 66 98–120
Schoofs S.: 1999, Thermochemical convection in porous media. An application to hydrothermal systems and magmatic intrusions, Geologica Ultraiectina 179.
S. Schoofs F.J. Spera U. Hansen (1999) ArticleTitleChaotic thermohaline convection in hydrothermal systems Earth and Planetary Sci. Lett. 174 213–229
M.J. Simpson T.P. Clement (2003) ArticleTitleTheoretical analysis of the worthiness of the Henry and Elder problems as benchmarks of density-dependent groundwater flow Adv. Water Resour. 26 17–31 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00085-4
S Spivak H.S. Price A. Settari (1977) ArticleTitleSolution of the equations for multidimensional. two-phase, immiscible flow by variational methods Soc. Petrol. Eng. J. 17 27–41
P.H. Steen C.K. Aidun (1988) ArticleTitleTime-periodic convection in porous media: transition mechanism J. Fluid Mech. 196 263–290
G. Strang (1968) ArticleTitleOn construction and comparison of difference schemes SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 5 506–517 Occurrence Handle10.1137/0705041
S. Sourirajan G.C. Kennedy (1962) ArticleTitleThe system H2O-NaCl at elevated temperatures and pressures Amer. J. Sci. 260 115–141
Von Damm K. L. (1995). Controls on the chemistry and temporal variability of seafloor hydrothermal fluids, in: S. E. Humphris, R. A. Zierenberg, L. S. Mullineaux, and R. E. Thomson (eds.), Seafloor Hydrothermal Systems. Geophysical Monograph, 91:222–247.
W.S.D. Wilcock (1998) ArticleTitleCellular convection models of mid-ocean ridge hydrothermal circulation and temperatures of black-smoker fluids J. Geophys. Res. 103 2585–2596 Occurrence Handle10.1029/97JB03252
R. Young (1993) ArticleTitleTwo-phase geothermal flows with conduction and the connection with Buckley-Leverett theory Transport Porous Media 12 261–278 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00624461
Zyvoloski G. A., Robinson B. A., Dash Z. V. and Trease L. L.: 1996, Users Manual for the FEHMN Application. Los Alamos National Laboratory, LA–UR–94–3788.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geiger, S., Driesner, T., Heinrich, C.A. et al. Multiphase Thermohaline Convection in the Earth’s Crust: II. Benchmarking and Application of a Finite Element – Finite Volume Solution Technique with a NaCl–H2O Equation of State. Transp Porous Med 63, 435–461 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-005-0109-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-005-0109-y