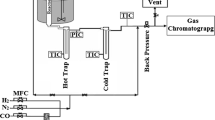
Abstract
The effect of silylation in the performance of cobalt catalysts supported on mesoporous silica MCM-41 and non-porous silica in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) at process conditions (240 °C, 10 bar, H2/CO ratio = 2.15) was evaluated. Catalysts with a concentration of 5 % metallic phase were synthesized by wet impregnation on silylated and non-silylated supports. The catalysts were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray diffraction, N2-adsorption/desorption, temperature programmed reduction, diffuse reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet visible region and high resolution transmission electron microscope. The characterization analyses showed the silylation treatment cause disorganization and partial blockage in the structure of MCM-41 support. Consequently, it were observed less CO overall conversion and selectivity towards C5+ hydrocarbons compared with the FTS catalyst prepared with non-silylated support. Also, according to the results of the catalytic evaluation, CO overall conversion seems to be related to the accessibility of the reactants, whereas log-chain hydrocarbons selectivity relates to the ability to reinsert olefins, in conjunction with metal particle size, which is directly connected with metal-support interaction.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anuário Estatístico Brasileiro do Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis (2014) BR, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro. http://www.anp.gov.br. Accessed 22 Jan 2015
Ramos ALD, Marques JJ, Santos V, Freitas LS, Santos RGVM, Souza MMVM (2011) Atual estágio de desenvolvimento da tecnologia GTL e perspectivas para o Brasil. Quim Nova 34:1704–1716
Gaspari A (2008) ‘Saída liquefeita’, Retrospectiva oil and gas. Brasil Energia 335:8–10
O Renascimento de uma Tecnologia Madura: O processo Fischer-Tropsch de Conversão de Gás em Combustíveis Líquidos (2002) BR, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro. http://www.gee.ie.ufrj.br/publicacoes/pdf/2002_renasc_tec_madura.pdf. Accessed 4 Aug 2012
Davis BH (2003) Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: relationship between iron catalyst composition and process variables. Catal Today 84:83–98
Martínez A, Prieto G (2007) The key role of the support surface tuning during the preparation of catalysts from reverse micellar—synthesized metal nanoparticles. Catal Commun 8:1479–1486
Martínez A, Prieto G (2007) Breaking the dispersion-reducibility dependence in oxide-supported cobalt nanoparticles. J Catal 245:470–476
JungáKim D, ManáKim J (2005) Enhancement in the reducibility of cobalt oxides on a mesoporous silica supported cobalt catalyst. Chem Commun 11:1462–1464
Fu T, Lv J, Li Z (2014) Effect of carbon porosity and cobalt particle size on the catalytic performance of carbon supported cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:1342–1350
Tao CL, Li JL, Liew KY (2010) Effect of the pore size of Co/SBA-15 isomorphically substituted with zirconium on its catalytic performance in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Sci China Chem 53:2552–2559
Khodakov AY, Bechara R, Griboval-Constant A (2003) Fische–Tropsch synthesis over silica supported cobalt catalysts: mesoporous structure versus cobalt surface density. Appl Catal A 254:273–288
Khodakov AY, Griboval-Constant A, Bechara R, Zholobenko VL (2002) Pore size effects in Fischer Tropsch synthesis over cobalt-supported mesoporous sílicas. J Catal 206:230–241
Lualdi M, Lögdberg S, Carlo G, Järas S, Boutonnet M, Venezia AM, Blekkan ED, Holmen A (2011) Evidence for diffusion-controlled hydrocarbon selectivities in the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over cobalt supported on ordered mesoporous silica. Top Catal 54:1175–1184
Martínez A, Prieto G, Rollan J (2009) Nanofibrous γ-Al2O3 as support for Co-based Fischer–Tropsch catalysts: pondering the relevance of diffusional and dispersion effects on catalytic performance. J Catal 263:292–305
Zola AS, Bidart AMF, Fraga AC, Hori CE, Sousa-Aguiar EF, Arroyo PA (2007) Cobalt supported on different zeolites for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Stud Surf Sci Catal 167:129–134
Szegedi A, Kónya Z, Méhn D, Solymar E, Pál-Borbély G, Horváth ZE, Biró AP, Kiricsi I (2004) Spherical mesoporous MCM-41 materials containing transition metals: synthesis and characterization. Appl Catal A 272:257–266
Tang Q, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Wan H (2003) Preparation of metallic cobalt inside NaY zeolite with high catalytic activity in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Catal Commun 4:253–258
Bessell S (1995) Investigation of bifunctional zeolite supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. Appl Catal A 126:235–244
Matsumoto A, Chen H, Tsutsumi K, Grün M, Unger K (1999) Novel route in the synthesis of MCM-41 containing framework aluminum and its characterization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 32:55–62
Kresge CT, Leonowicz ME, Roth WJ, Vartulli JC, Beck JS (1992) Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 359:710–712
Gregg SJ, Sing KSW (1982) Adsorption, surface area and porosity. Academic Press, London
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquérol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Diaz JF, Balkus KJ, Bedioui F, Kurshev V, Kevan L (1997) Synthesis and characterization of cobalt-complex functionalized MCM-41. Chem Mater 9:61–67
Rodrigues EL, Bueno JMC (2002) Co/SiO 2 catalysts for selective hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde II: influence of the Co surface structure on selectivity. Appl Catal A 232:147–158
Backman LB, Rautiainen A, Lindblad M, Krause AOI (2000) Effect of support and calcination on the properties of cobalt catalysts prepared by gas phase deposition. Appl Catal A 191:55–68
Prieto G, Martínez A, Concepción P, Moreno-Tost R (2009) Cobalt particle size effects in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: structural and in situ spectroscopic characterisation on reverse micelle-synthesised Co/ITQ-2 model catalysts. J Catal 266:129–144
Su YK, Shen CM, Yang TZ, Yang HT, Gao HJ, Li HL (2005) The dependence of Co nanoparticle sizes on the ratio of surfactants and the influence of different crystal sizes on magnetic properties. Appl Phys A 81:569–572
Lim S, Ciuparu D, Pak C, Dobek F, Chen Y, Harding D, Pfefferle L, Haller G (2003) Synthesis and characterization of highly ordered Co-MCM-41 for production of aligned single walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT). J Phys Chem B 107:11048–11056
Girardon J-S, Quinet E, Griboval-Constant A, Chernavskii PA, Gengembre L, Khodakov AY (2007) Cobalt dispersion, reducibility, and surface sites in promoted silica-supported Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. J Catal 248:143–157
Katsoulidis AP, Petrakis DE, Armatas GS, Trikalitis PN, Pomonis PJ (2006) Ordered mesoporous CoO x/MCM-41 materials exhibiting long-range self-organized nanostructured morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 92:71–80
Szegedi A, Popova M, Minchev C (2009) Catalytic activity of Co/MCM-41 and Co/SBA-15 materials in toluene oxidation. J Mater Sci 44:6710–6716
Lou Z, Wang R, Sun H, Chen Y, Yang Y (2008) Direct synthesis of highly ordered Co-SBA-15 mesoporous materials by the pH-adjusting approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 110:347–354
Jia L, Jia L, Li D, Hou B, Wang J, Sun Y (2011) Silylated Co/SBA-15 catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J Solid State Chem 184:488–493
Tang HQ, Liew KY, Li JL (2012) Cobalt catalysts supported on silica nanotubes for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Sci China Chem 55:145–150
Friedel RA, Anderson RB (1950) Composition of synthetic liquid fuels. I. product distribution and analysis of C5—C8 paraffin isomers from cobalt catalyst1. J Am Chem Soc 72:1212–1215
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES/Brazil), National Council of Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq/Brazil) for financial support and The Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory (LNNano) for HRTEM analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zola, A.S., da Silva, L.S., Moretti, A.L. et al. Effect of Silylation and Support Porosity of Co/MCM-41 and Co/SiO2 Catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Top Catal 59, 219–229 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-015-0446-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-015-0446-1