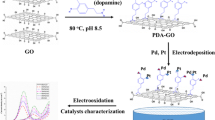
Abstract
Pd-based catalysts supported on high-surface-area carbon are widely used in formic acid fuel cells. The composition, structure, and support can be modified to maximize the capabilities of Pd-based catalysts in terms of catalytic activity, durability, and cost. Various studies have investigated tuning the properties of Pd-based catalysts by alloying Pd with other metals. In this study, Cr, Ni, Cu, and Zn were incorporated into Pd-based catalysts. First, the effects of mole ratios were studied between Pd and the metals. The PdnNi ratios on a reduced graphene oxide support (PdnNi/rGO) were prepared using the one-pot method without the use of any surfactants. All obtained rGO-supported PdnNi catalysts (n = 1, 2, 4, with diameter of 5 nm) were used for the electrocatalytic oxidation of formic acid. The electro-oxidation measurements revealed that the PdnNi/rGO samples had superior electrocatalytic performance both in current densities and stabilities for formic acid oxidation (FAO) compared to Pd/rGO. Furthermore, Pd4Ni/rGO had greater electrocatalytic activity than the other PdnNi/rGO samples. In addition, with the same mole ratio of metals, Pd4Cr/rGO had higher efficiency toward FAO than the other series in the order: Pd4Cr/rGO > Pd4Ni/rGO > Pd4Cu/rGO > Pd4Zn/rGO.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available within the paper and its supplementary information files (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-023-01821-8). Any additional information is available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bianchini C, Shen PK (2009) Palladium-based electrocatalysts for alcohol oxidation in half cells and in direct alcohol fuel cells. Chem Rev 109(9):4183–4206. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr9000995
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306(5696):666–669. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6(3):183–191
Habas SE, Lee H, Radmilovic V, Somorjai GA, Yang P (2007) Shaping binary metal nanocrystals through epitaxial seeded growth. Nat Mater 6(9):692–697
Wang X, Meng Q, Gao L, Jin Z, Ge J, Liu C, Xing W (2018) Recent progress in hydrogen production from formic acid decomposition. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43(14):7055–7071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.146
Zeng T, Zheng L, Chen H, Wang Y, Ling M, Sun S, Zhang F, Yuan W, Zhang LY (2023) One-pot controllable epitaxial growth of Pd-based heterostructures for enhanced formic acid oxidation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 656:130358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130358
Qin YL, Wang JW, Zhang LL, Wang LM (2014) Synthesis and electrocatalytic properties of uniform palladium nanocubes by using graphene oxide as surfactant and support. ChemCatChem 6(8):2215–2218. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201402084
Hu S, Munoz F, Noborikawa J, Haan J, Scudiero L, Ha S (2016) Carbon supported Pd-based bimetallic and trimetallic catalyst for formic acid electrochemical oxidation. Appl Catal B 180:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.023
Meng X, Zeng T, Ma S, Zheng L, Chen H, Yuan W, Zhang LY (2022) Surface Nitridation of PdCu nanosheets to promote charge transfer and suppress CO poisoning toward ethanol electrooxidation. Adv Mater Interfaces 9(7):2101849. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202101849
Zeng T, Meng X, Huang H, Zheng L, Chen H, Zhang Y, Yuan W, Zhang LY (2022) Controllable synthesis of web-footed PdCu nanosheets and their electrocatalytic applications. Small 18(14):2107623. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202107623
Zhang LY, Guo CX, Cao H, Wang S, Ouyang Y, Xu B, Guo P, Li CM (2022) Highly wrinkled palladium nanosheets as advanced electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in acidic medium. Chem Eng J 431:133237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133237
Li H, Zhang X, Pang H, Huang C, Chen J (2010) PMo12-functionalized Graphene nanosheet-supported PtRu nanocatalysts for methanol electro-oxidation. J Solid State Electrochem 14(12):2267–2274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1067-z
Kim J, Cote LJ, Kim F, Yuan W, Shull KR, Huang J (2010) Graphene oxide sheets at interfaces. J Am Chem Soc 132(23):8180–8186. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja102777p
Wang R, Wu Z, Chen C, Qin Z, Zhu H, Wang G, Wang H, Wu C, Dong W, Fan W, Wang J (2013) Graphene-supported Au–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles with excellent catalytic performance in selective oxidation of methanol to methyl formate. Chem Commun 49(74):8250–8252. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC43948H
Mazumder V, Chi M, Mankin MN, Liu Y, Metin Ö, Sun D, More KL, Sun S (2012) A facile synthesis of MPd (M = Co, Cu) nanoparticles and their catalysis for formic acid oxidation. Nano Lett 12(2):1102–1106. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl2045588
Matin MA, Jang J-H, Kwon Y-U (2014) PdM nanoparticles (M = Ni, Co, Fe, Mn) with high activity and stability in formic acid oxidation synthesized by sonochemical reactions. Journal of Power Sources 262 (Supplement C):356–363. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.03.109
Hammer B, Nørskov JK (1995) Electronic factors determining the reactivity of metal surfaces. Surf Sci 343(3):211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(96)80007-0
Hammer B, Norskov JK (1995) Why gold is the noblest of all the metals. Nature 376(6537):238–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/376238a0
Hammer B, Nørskov JK (2000) Theoretical surface science and catalysis—calculations and concepts. Adv Catal 45:71–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-0564(02)45013-4
Groß A (2009) Electronic structure methods and total energies. In: Groß A (ed) Theoretical surface science: a microscopic perspective. Springer, Berlin, pp 21–58
Nilsson A, Pettersson LGM (2008) Chapter 2 - Adsorbate electronic structure and bonding on metal surfaces. In: Nilsson A, Pettersson LGM, Nørskov JK (eds) Chemical bonding at surfaces and interfaces. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 57–142
Lu L, Shen L, Shi Y, Chen T, Jiang G, Ge C, Tang Y, Chen Y, Lu T (2012) New insights into enhanced electrocatalytic performance of carbon supported Pd–Cu catalyst for formic acid oxidation. Electrochim Acta 85:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.08.113
He F, Li K, Xie G, Wang Y, Jiao M, Tang H, Wu Z (2016) Understanding the enhanced catalytic activity of Cu1@Pd3(111) in formic acid dissociation, a theoretical perspective. J Power Sources 316:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.03.062
Liu M, Zhang R, Chen W (2014) Graphene-supported nanoelectrocatalysts for fuel cells: synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem Rev 114(10):5117–5160. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400523y
Kankla P, Limtrakul J, Green MLH, Chanlek N, Luksirikul P (2019) Electrooxidation of formic acid enhanced by surfactant-free palladium nanocubes on surface modified graphene catalyst. Appl Surf Sci 471:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.001
Li Y, Li Y, Zhu E, McLouth T, Chiu C-Y, Huang X, Huang Y (2012) Stabilization of high-performance oxygen reduction reaction Pt electrocatalyst supported on reduced graphene oxide/carbon black composite. J Am Chem Soc 134(30):12326–12329. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3031449
Hummers WS, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80(6):1339–1339. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01539a017
Gao Y, Wang G, Wu B, Deng C, Gao Y (2011) Highly active carbon-supported PdNi catalyst for formic acid electrooxidation. J Appl Electrochem 41(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-010-0201-z
Moraes LPR, Matos BR, Radtke C, Santiago EI, Fonseca FC, Amico SC, Malfatti CF (2016) Synthesis and performance of palladium-based electrocatalysts in alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41(15):6457–6468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.02.150
Chen L, Guo H, Fujita T, Hirata A, Zhang W, Inoue A, Chen M (2011) Nanoporous PdNi bimetallic catalyst with enhanced electrocatalytic performances for electro-oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions. Adv Func Mater 21(22):4364–4370. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201101227
Shobha T, Aravinda CL, Bera P, Devi LG, Mayanna SM (2003) Characterization of Ni–Pd alloy as anode for methanol oxidative fuel cell. Mater Chem Phys 80(3):656–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(03)00087-7
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Piner RD, Kohlhaas KA, Kleinhammes A, Jia Y, Wu Y, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS (2007) Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45(7):1558–1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.02.034
Jiang S, Yi B, Zhao Q, Yu H, Shao Z (2017) Palladium–nickel catalysts based on ordered titanium dioxide nanorod arrays with high catalytic performance for formic acid electro-oxidation. RSC Adv 7(19):11719–11723. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA00194K
Rai RK, Gupta K, Tyagi D, Mahata A, Behrens S, Yang X, Xu Q, Pathak B, Singh SK (2016) Access to highly active Ni–Pd bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for C-C coupling reactions. Catal Sci Technol 6(14):5567–5579. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CY00037A
Zamora Zeledón JA, Stevens MB, Gunasooriya G, Gallo A, Landers AT, Kreider ME, Hahn C, Nørskov JK, Jaramillo TF (2021) Tuning the electronic structure of Ag-Pd alloys to enhance performance for alkaline oxygen reduction. Nat Commun 12(1):620. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-20923-z
Coutanceau C, Baranton S, Napporn TW (2012) Platinum fuel cell nanoparticle syntheses: effect on morphology, structure and electrocatalytic behavior. INTECH Open Access Publisher, Rijeka
Hoshi N, Kida K, Nakamura M, Nakada M, Osada K (2006) Structural effects of electrochemical oxidation of formic acid on single crystal electrodes of palladium. J Phys Chem B 110(25):12480–12484. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0608372
El-Nagar GA, Mohammad AM, El-Deab MS, El-Anadouli BE (2012) Facilitated electro-oxidation of formic acid at nickel oxide nanoparticles modified electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 159(7):F249. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.043207jes
Hu S, Scudiero L, Ha S (2012) Electronic effect on oxidation of formic acid on supported Pd–Cu bimetallic surface. Electrochim Acta 83:354–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.06.111
She Y, Lu Z, Fan W, Jewell S, Leung MKH (2014) Facile preparation of PdNi/rGO and its electrocatalytic performance towards formic acid oxidation. J Mater Chem A 2(11):3894–3898. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14546H
Hu S, Scudiero L, Ha S (2014) Electronic effect of Pd-transition metal bimetallic surfaces toward formic acid electrochemical oxidation. Electrochem Commun 38:107–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2013.11.010
Zhang X, Fan H, Zheng J, Duan S, Huang Y, Cui Y, Wang R (2018) Pd–Zn nanocrystals for highly efficient formic acid oxidation. Catal Sci Technol 8(18):4757–4765. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CY01503A
Matin MA, Jang J-H, Kwon Y-U (2014) PdM nanoparticles (M = Ni Co, Fe, Mn) with high activity and stability in formic acid oxidation synthesized by sonochemical reactions. J Power Sources 262:356–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.03.109
Yang G, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Tang Y, Lu T (2010) Preparation of carbon supported Pd–P catalyst with high content of element phosphorus and its electrocatalytic performance for formic acid oxidation. Electrochem Commun 12(3):492–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2010.01.029
Wen W, Li C, Li W, Tian Y (2013) Carbon-supported Pd–Cr electrocatalysts for the electrooxidation of formic acid that demonstrate high activity and stability. Electrochim Acta 109:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.137
Gopalsamy K, Balamurugan J, Thanh TD, Kim NH, Hui D, Lee JH (2017) Surfactant-free synthesis of NiPd nanoalloy/graphene bifunctional nanocomposite for fuel cell. Compos B Eng 114:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.01.061
Yu X, Pickup PG (2008) Recent advances in direct formic acid fuel cells (DFAFC). J Power Sources 182(1):124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.03.075
Rice C, Ha S, Masel RI, Wieckowski A (2003) Catalysts for direct formic acid fuel cells. J Power Sources 115(2):229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00026-0
Zhang X, Yin H, Wang J, Chang L, Gao Y, Liu W, Tang Z (2013) Shape-dependent electrocatalytic activity of monodispersed palladium nanocrystals toward formic acid oxidation. Nanoscale 5(18):8392–8397. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR03100D
El-Refaei SM, El-Nagar GA, Mohammad AM, El-Anadouli BE (2015) Electro-oxidation of formic acid, glucose, and methanol at nickel oxide nanoparticle modified platinum electrodes. In: Dincer I, Colpan CO, Kizilkan O, Ezan MA (eds) Progress in clean energy. Analysis and Modeling, vol 1. Springer, Cham, pp 595–604
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Research Network NANOTEC-KU on Nanocatalysts and Nanomaterials for Sustainable Energy and Environment (RNN), Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand. This work has also been funded by the Kasetsart University Research Development Institute (KURDI). We also thank the Development and Promotion of Science Technology Talents Project (DPST) for the scholarship. We also acknowledge the facilities from the Research Network NANOTEC-KU, Synchrotron Light Research Institute for experimental instruments, and Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kankla, P., Butburee, T., Chanlek, N. et al. Enhanced Performance of Bimetallic Pd-based Electrocatalysts for Formic Acid Oxidation. Top Catal 66, 1608–1618 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-023-01821-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-023-01821-8