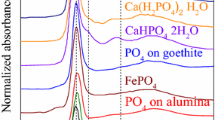
Abstract
The phosphorus (P) and cadmium (Cd) speciation was analyzed in a contaminated soil having a Cd concentration of 1,028 mg kg−1 in order to assess the value of bone char (BC) as a Cd immobilizing agent. The soil was incubated with BC and triple superphosphate (TSP, as control) in the dark at 60 to 70 % water holding capacity for time periods between 1 and 145 days. Samples from the various incubation periods were sequentially extracted and investigated by X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy. The sequential P extraction revealed that BC increased the H2SO4 extractable P fraction, mainly consisting of Ca- and Mg-phosphates, by 14 %, whereas TSP increased the water extractable P fraction by 7 % of total P at day 1. Subsequently, the proportions of these two P fractions decreased during incubation. The increase in these two P fractions is explained by the solubility of the main components of BC (hydroxylapatite (HAP)) and TSP (Ca(H2PO4)2). Furthermore, this finding was confirmed for BC by the P K-edge XANES spectra using partial least square regression that provided independent evidence for increased proportion of HAP after BC application. As a result of BC dissolution, the soil pH increased resulting in Cd immobilization as indicated by significantly reduced concentrations of mobile Cd in the sequential extraction up to 23 mg Cd kg−1. This observed immobilization was explained by the Cd L 3 -edge XANES spectra revealing an immediate increase in the proportion of insoluble Cd3(PO4)2. By contrast, none of the speciation methods indicated a Cd immobilizing capability of TSP. Thus, by using this multi-methodological approach, we could show that besides its potential as renewable and clean P fertilizer, BC is a superior immobilization agent for Cd compared to TSP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in the terrestrial environments—biochemistry, bioavailability and risk of metals (pp. 450–800). New York: Springer.
Ahnstrom, Z. S., & Parker, D. R. (1999). Development and assessment of a sequential extraction procedure for the fractionation of soil cadmium. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 63, 1650–1658.
Amini, M., Khademi, H., Afyuni, M., & Abbaspour, K. C. (2005). Variability of available cadmium in relation to soil properties and landuse in an arid region in central Iran. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 162, 205–218.
Antoniadis, V., & Alloway, B. J. (2000). Availability of Cd, Ni and Zn to ryegrass in sewage sludge-treated soils at different temperatures. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 132, 201–214.
Austrian Standards Institute. (1999). ÖNORM L 1084. Chemical analyses of soils: Determination of carbonate. Vienna: Österreichisches Normungsinstitut.
Beauchemin, S., Hesterberg, D., Chou, J., Beauchemin, M., Simard, R. R., & Sayers, E. (2003). Speciation of phosphorus in phosphorus-enriched agricultural soils using X-ray adsorption near-edge structure spectroscopy and chemical fractionation. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 1809–1819.
Blume, H. P., Stahr, K., & Leinweber, P. (2011). Bodenkundliches praktikum, vol 3. Heidelberg: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag.
Bolan, N. S., & Hedley, M. J. (1990). Dissolution of phosphate rocks in soils. 2. Effect of pH on the dissolution and plant availability of phosphate rock in soil with pH dependent charge. Fertilizer Research, 24, 125–134.
Bolan, N. S., Naidu, R., Khan, M. A. R., Tillman, R. W., & Syers, J. K. (1999). The effects of anions sorption on sorption and leaching of cadmium. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 3, 445–460.
Bolan, N. S., Adriano, D. C., Duraisamy, P., Mani, A., & Arulmozhiselvan, K. (2003). Immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium in variable charge soils. I. Effect of phosphate addition. Plant and Soil, 250, 83–94.
Chaiyarat, R., Suebsima, R., Putwattana, N., Kruatrachue, M., & Pokethitiyook, M. (2011). Effects of soil amendments on growth and metal uptake by Ocimum gratissimum grown in Cd/Zn-contaminated soil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 214, 383–392.
Dalal, R. C. (1977). Soil organic phosphorus. Advances in Agronomy, 29, 83–113.
Gilbert, N. (2009). The disappearing nutrient. Nature, 461, 716–718.
Hedley, M. J., Stewart, J. W. B., & Chauhan, B. S. (1982). Changes in organic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and laboratory incubations. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 46, 970–976.
Hesterberg, D., Zhou, W. Q., Hutchison, K. J., Beauchemin, S., & Sayers, D. E. (1999). XAFS study of adsorbed and mineral forms of phosphate. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 6, 636–638.
Hodson, M. E., Valsami-Jones, E., & Cotter-Howells, J. D. (2000). Bone meal additions as a remediation treatment for metal contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 3501–3507.
Isaure, M. P., Fayard, B., Sarret, G., Pairis, S., & Bourguignon, J. (2006). Localization and chemical forms of cadmium in plant samples by combining analytical electron microscopy and X-ray spectromicroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta, 12, 1242–1252.
Jalilehvand, F., Leung, B. O., & Mah, V. (2009). Cadmium(II) complex frmation with cysteine and penicillamine. Inorganic Chemistry, 48, 5758–5771.
Kolay, A. K. (2007). Manures and fertilizer. New Delhi: Atlantic Publisher and Distributors.
Kruse, J., Negassa, W., Appathurai, N., Zuin, L., & Leinweber, P. (2010). Phosphorus speciation in sequentially extracted agro-industrial by-products: evidence from X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy. Journal of Environmental Quality, 39, 2179–2184.
Lanfranco, A. M., Schofield, P. F., Murphy, P. J., Hodson, M. E., Mosselmans, J. F. W., & Valsami-Jones, E. (2003). Characterization and identification of mixed-metal phosphates in soils: the application, of Raman spectroscopy. Mineralogical Magazine, 67, 1299–1316.
Linquist, B. A., Singleton, P. W., & Cassman, K. G. (1997). Inorganic and organic phosphorus dynamics during a build-up and decline of available phosphorus in an ultisol. Soil Science, 162, 254–264.
Lombi, E., & Susini, J. (2009). Synchrotron-based techniques for plant and soil science: opportunities, challenges and future perspectives. Plant and Soil, 320, 1–35.
Madrid, L., & Diaz-Barrientos, E. (1992). Influence of carbonate on the reaction of heavy metals in soils. Journal of Soil Science, 43, 709–721.
McBride, M. B. (1980). Chemisorption of Cd2+ on calcite surfaces. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44, 26–28.
Naidu, R., Bolan, N. S., Kookana, R. S., & Tiller, K. G. (1994). Ionic strength and pH effects on the adsorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. European Journal of Soil Science, 45, 19–429.
Negassa, W., & Leinweber, P. (2009). How does the Hedley sequential phosphorus fractionation reflect impacts of land use and management on soil phosphorus: a review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 172, 305–325.
Pickering, I. J., Prince, R. C., George, G. N., Rauser, W. E., Wickramasinghe, W. A., Watson, A. A., et al. (1999). X-ray absorption spectroscopy of cadmium phytochelatin and model systems. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1429, 351–364.
Prieto, M., Cubillas, P., & Fernández-González, A. (2003). Uptake of dissolved cadmium by biogenic and abiogenic aragonite: a comparison with sorption onto calcite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67, 3859–3869.
R Development Core Team (2011). Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051_07_0, URL: http://www.R-project.org/.
Ravel, B., & Newville, M. (2005). Athena, Artemis, Hephaestus: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 12, 537–541.
Rowell, D. L. (1994). Soil science: Methods and applications. Harlow: Longman.
Seuntjens, P., Nowack, B., & Schulin, R. (2004). Root-zone modeling of heavy metal uptake and leaching in the presence of organic ligands. Plant and Soil, 265, 61–73.
Shober, A. L., Hesterberg, D. L., Thomas Sims, J., & Gardner, S. (2006). Characterization of phosphorus species in biosolids and manures using XANES spectroscopy. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1983–1993.
Siebers, N., & Leinweber, P. (2013). Bone char—a clean and renewable fertilizer with cadmium immobilizing capability. Journal of Environmental Quality. doi:10.2134/jeq2012.0363.
Siebers, N., Kruse, J., Eckhardt, K.-U., Hu, Y., & Leinweber, P. (2012). Solid-phase cadmium speciation in soil using L3-edge XANES spectroscopy with partial least-square regression. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 19, 579–585.
Soon, Y. K. (1981). Solubility and sorption of cadmium in soils amended with sewage sludge. Journal of Soil Science, 32, 85–95.
Stewart, J. W. B., & Tiessen, H. (1987). Dynamics of soil organic phosphorus. Biogeochemica, 4, 41–60.
Tiessen, H., Stewart, J. W. B., & Moir, J. O. (1983). Changes in organic and inorganic phosphorus composition of two grassland soils and their particle size fractions during 60–90 years of cultivation. Journal of Soil Science, 34, 815–823.
Toor, G. S., Peak, J. D., & Sims, J. T. (2005). Phosphorus speciation in broiler litter and turkey manure produced from modified diets. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 687–697.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1997). Method 305la: Microwave assisted acid dissolution of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils (2nd ed.). Washington: U.S. Gov. Print. Office.
Valsami-Jones, E., Ragnarsdottir, K. V., Putnis, A., Bosbach, D., Kemp, A. J., & Cressey, G. (1998). The dissolution of apatite in the presence of aqueous metal cations at pH 2–7. Chemical Geology, 151, 215–233.
Warren, G. P., Robinson, J. S., & Someus, E. (2009). Dissolution of phosphorus from animal bone char in 12 soils. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 84, 167–178.
Wehrens, R., & Mevik, B. H. (2007). R package version 2.1-0-http://mevik.net/work/software/pls.html.
Wuana, R. A., & Okieimen, F. E. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. International Scholarly Research Network Ecology. doi:10.5402/2011/402647.
Xiong, L. M. (1995). Influence of phosphate on cadmium adsorption by soils. Fertilizer Research, 40, 31–40.
Zeien, H., & Brümmer, G. W. (1989). Chemische Extraktionen zur Bestimmung von Schwermetallbindungsformen in Böden. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft, 59, 505–510.
Zheng, Z., MacLeod, J. A., Sanderson, J. B., & Lafond, J. (2004). Phosphorus dynamics after ten annual applications of mineral fertilizers and liquid dairy manure: fractionation and path analyses. Soil Science, 169, 449–456.
Zimmer, D., Kiersch, K., Baum, C., Meissner, R., Müller, R., Jandl, G., et al. (2011). Scale-dependent variability of As and heavy metals in a River Elbe floodplain. Clean - Soil, Air, Water, 39, 328–337.
Acknowledgments
Research described in this paper was performed in the scope of the Leibniz WissenschaftsCampus “Phosphor-Forschung-Rostock” and was done at the Canadian Light Source, which is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the National Research Council Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Province of Saskatchewan, Western Economic Diversification Canada, and the University of Saskatchewan. We thank Dr. Volkmar König, Thuringian State Research Centre for Agriculture (TLL), for providing the soil used in this study. N. Siebers also acknowledges a Ph.D. grant from the Federal State of Mecklenburg, Western Pommeria in Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siebers, N., Kruse, J. & Leinweber, P. Speciation of Phosphorus and Cadmium in a Contaminated Soil Amended with Bone Char: Sequential Fractionations and XANES Spectroscopy. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1564 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1564-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1564-7