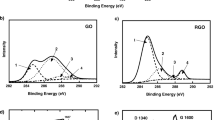
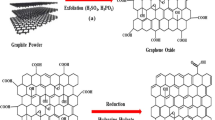
Abstract
This work addresses the synthesis of graphene oxide, its structural characterization, and its application in the removal of cationic surfactants from water. The synthesized graphene oxide was characterized by Raman, infrared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopies, scanning and transmission electron microscopies, and zeta potential. After the nanomaterial structural elucidation, optimization tests, studies of kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamics of adsorption were performed to study adsorbent/adsorbate interactions in the adsorption process of cationic surfactants on graphene oxide. Under optimized conditions, graphene oxide showed the highest removal potential for the pyridinium-containing surfactant (2083 mg/g), followed by the benzyl-containing surfactant (431 mg/g) and the tetrakyl surfactant (329 mg/g), suggesting that electrostatic, hydrophobic, and cation-π interactions are common in the process, but pyridinium-π and π-π interactions are stronger. In addition, the adsorbent, under optimized conditions, compared with other sorbents described in the literature, presented higher potential adsorption.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
125 Zur Theorie der sogenannten Adsorption gelöster Stoffe - Lagergreen, S., (Bihang A. K. Svenske Vet. Ak. Handl. 24, II. Nr. 4, S. 49; 1899; Z. physik. Ch. 32, 174–75; 1900.). Zeitschrift für Chemie und Ind der Kolloide 2:174–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01501332
Abdelkader, A. M., Kinloch, I. A., & Dryfe, R. A. W. (2014). High-yield electro-oxidative preparation of graphene oxide. Chemical Communications, 50, 8402–8404. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc03260h.
Abu-Jdayil, B., Ghannam, M., & Nasser, M. S. (2016). The modification of rheological properties of bentonite-water dispersions with cationic and anionic surfactants. International Journal of Chemical Engineering Application, 7, 75–80. https://doi.org/10.7763/ijcea.2016.v7.546.
Aiad, I., El-Sukkary, M. M., Soliman, E. A., et al. (2014). Characterization, surface properties and biological activity of new prepared cationic surfactants. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 1633–1640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.08.010.
Alam, S. N., Sharma, N., & Kumar, L. (2017). Synthesis of graphene oxide (GO) by modified Hummers method and its thermal reduction to obtain reduced graphene oxide (rGO)*. Graphene, 6, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.4236/graphene.2017.61001.
Arshadi, M., Amiri, M. J., & Mousavi, S. (2014). Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic investigations of Ni(II), Cd(II), Cu(II) and Co(II) adsorption on barley straw ash. Water Resour Ind, 6, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2014.06.001.
Aubourg, R., Bee, A., Cassaignon, S., et al. (2000). Adsorption isotherms of cetylpyridinium chloride with iron III salts at air/water and silica/water interfaces. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 230, 298–305. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.7044.
Awad, A. M., Shaikh, S. M. R., Jalab, R., et al. (2019). Adsorption of organic pollutants by natural and modified clays: a comprehensive review. Separation and Purification Technology, 228, 115719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115719.
Bae, S., Mannan, M. B., & Lee, W. (2012). Adsorption of cationic cetylpyridinium chloride on pyrite surface. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18, 1482–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.02.010.
Bai, Y., Lin, D., Wu, F., et al. (2010). Adsorption of Triton X-series surfactants and its role in stabilizing multi-walled carbon nanotube suspensions. Chemosphere, 79, 362–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.02.023.
Ban, F. Y., Majid, S. R., Huang, N. M., & Lim, H. N. (2012). Graphene oxide and its electrochemical performance. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 7, 4345–4351.
Başar, C. A. (2006). Applicability of the various adsorption models of three dyes adsorption onto activated carbon prepared waste apricot. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 135, 232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.055.
Bele, M., Kodre, A., Arčon, I., et al. (1998). Adsorption of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide on carbon black from aqueous solution. Carbon N Y, 36, 1207–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00099-2.
Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Mendoza-Castillo DI, Reynel-Ávila HE (2017) Adsorption processes for water treatment and purification.
Camesano, T. A., & Nagarajan, R. (2000). Micelle formation and CMC of gemini surfactants: a thermodynamic model. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp, 167, 165–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00473-2.
Cao, Y., & Li, X. (2014). Adsorption of graphene for the removal of inorganic pollutants in water purification: a review. Adsorption, 20, 713–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-014-9615-y.
Carosia, M. F., Okada, D. Y., Sakamoto, I. K., et al. (2014). Microbial characterization and degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate in an anaerobic reactor treating wastewater containing soap powder. Bioresource Technology, 167, 316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.06.002.
Carter, P. W., Dimagno, S. G., Porter, J. D., & Streitwieser, A. (1993). π-Stacking and aggregation of pyridinium-substituted indolizines. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 97, 1085–1096.
Chavez-Sumarriva, I., Van Steenberge, P. H. M., & D’Hooge, D. R. (2016). New insights in the treatment of waste water with graphene: dual-site adsorption by sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 55, 9387–9396. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02302.
Cheminski, T., De Figueiredo, N. T., Silva, P. M., et al. (2019). Insertion of phenyl ethyleneglycol units on graphene oxide as stabilizers and its application for surfactant removal. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 102976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102976.
Chen, H., & Zhao, J. (2009). Adsorption study for removal of Congo red anionic dye using organo-attapulgite. Adsorption, 15, 381–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-009-9155-z.
Chen, W., Duan, L., Wang, L., & Zhu, D. (2008). Adsorption of hydroxyl- and amino-substituted aromatics to carbon nanotubes. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 6862–6868. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8013612.
Chen, P., Li, H., Song, S., et al. (2017). Adsorption of dodecylamine hydrochloride on graphene oxide in water. Results Physics, 7, 2281–2288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.06.054.
da Silva, S. W., Klauck, C. R., Siqueira, M. A., & Bernardes, A. M. (2015). Degradation of the commercial surfactant nonylphenol ethoxylate by advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 282, 241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.014.
Deese, R. D., Leblanc, M. R., & Cook, R. L. (2016). Surfactant toxicity to Artemia franciscana and the influence of humic acid and chemical composition. Environment and Chemistry, 13, 507–516. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN15108.
Emiru, T. F., & Ayele, D. W. (2017). Controlled synthesis, characterization and reduction of graphene oxide: a convenient method for large scale production. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4, 74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2016.11.002.
Eng, Y. Y., Sharma, V. K., & Ray, A. K. (2012). Degradation of anionic and cationic surfactants in a monolithic swirl-flow photoreactor. Separation and Purification Technology, 92, 43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.03.009.
Flilissa, A., Méléard, P., & Darchen, A. (2016). Cetylpyridinium removal using phosphate-assisted electrocoagulation, electroreduction and adsorption on electrogenerated sorbents. Chemical Engineering Journal, 284, 823–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.135.
Freundlich, H. (1906). Concerning adsorption in solutions. Zeitschrift fur Phys chemie-stochiometrie und verwandtschaftslehre, 57, 385–470.
Gao, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2012). Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 368, 540–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.11.015.
Gargouri, Y., Julien, R., Bois, A. G., et al. (1983). Studies on the detergent inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. Journal of Lipid Research, 24, 1336–1342.
Ghadim, E. E., Manouchehri, F., Soleimani, G., et al. (2013). Adsorption properties of tetracycline onto graphene oxide: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. PLoS One, 8, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079254.
Ghiaci, M., Kia, R., & Kalbasi, R. J. (2004). Investigation of thermodynamic parameters of cetyl pyridinium bromide sorption onto ZSM-5 and natural clinoptilolite. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 36, 95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2003.09.002.
Giles, C. H., MacEwan, T. H., Nakhwa, S. N., & Smith, D. (1960). Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. Journal of the Chemical Society, 3973–3993. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9600003973.
Giles, C. H., Smith, D., & Huitson, A. (1974). A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 47, 755–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(74)90252-5.
Global Surfactants Market to 2022 | Industry Trends & Analysis | Smithers. https://www.smithers.com/services/market-reports/materials/the-future-of-surfactants-to-2022. Accessed 15 Oct 2019.
Gonalves, G., Marques, P. A. A. P., Barros-Timmons, A., et al. (2010). Graphene oxide modified with PMMA via ATRP as a reinforcement filler. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 20, 9927. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm01674h.
Gorkina A (2015) Transparent and conductive hybrid graphene/carbon nanotube films.
Guo, H. L., Wang, X. F., Qian, Q. Y., et al. (2009). A green approach to the synthesis of graphene nanosheets. ACS Nano, 3, 2653–2659. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900227d.
Gupta, V. K., Singh, P., & Rahman, N. (2004). Adsorption behavior of Hg(II), Pb(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solution on Duolite C-433: a synthetic resin. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 275, 398–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.046.
Gurunathan, S., Han, J. W., Kim, E., et al. (2014). Enhanced green fluorescent protein-mediated synthesis of biocompatible graphene. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-014-0041-9.
Hayati, B., Maleki, A., Najafi, F., et al. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of PAMAM/CNT nanocomposite as a super-capacity adsorbent for heavy metal (Ni2 +, Zn2 +, As3 +, Co2 +) removal from wastewater. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 224, 1032–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2016.10.053.
Hepperle J, Schüle E, Kolberg D, Scherbaum E (2013) Determination of quaternary ammonium compound residues in fruits and vegetables by QuEChERS following LC-MS/MS analysis. Asp food Control Anim Heal - eJournal.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998a). Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chemical Engineering Journal, 9, 70. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1385-8947(98)00076-X.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998b). A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Safety and Environment Protection, 76, 332–340. https://doi.org/10.1205/095758298529696.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5.
Hu, X., Lei, H., Zhang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Strong hydrophobic interaction between graphene oxide and supported lipid bilayers revealed by AFM. Microscopy Research and Technique, 79, 721–726. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22690.
Huang, C. C., Lin, Y. C., & Lu, F. C. (1999). Dynamic adsorption of organic solvent vapors onto a packed bed of activated carbon cloth. Separation Science and Technology, 34, 555–570. https://doi.org/10.1081/SS-100100666.
Hummers, W. S., & Offeman, R. E. (1958). Preparation of graphitic oxide. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 80, 1339. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01539a017.
Igwe, J. C., & Abia, A. A. (2007). Adsorption isotherm studies of Cd (II), Pb (II) and Zn (II) ions bioremediation from aqueous solution using unmodified and EDTA-modified maize cob. Eclet Quim, 32, 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702007000100005.
Jia, H., Lian, P., Leng, X., et al. (2019). Mechanism studies on the application of the mixed cationic/anionic surfactant systems to enhance oil recovery. Fuel, 258, 116–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116156.
Jing, G., Zhou, Z., & Zhuo, J. (2012). Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) study of toxicity of quaternary ammonium compounds on Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Chemosphere, 86, 76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.021.
John, N., & George, S. (2017). Raman spectroscopy. In Spectroscopic methods for nanomaterials characterization (pp. 92–127).
Johra, F. T., Lee, J. W., & Jung, W. G. (2014). Facile and safe graphene preparation on solution based platform. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 2883–2887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.11.022.
Kazi, S. N., Badarudin, A., Zubir, M. N. M., et al. (2015). Investigation on the use of graphene oxide as novel surfactant to stabilize weakly charged graphene nanoplatelets. Nanoscale Research Letters, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0882-7.
Khurana, I., Saxena, A., Bharti, et al. (2017). Removal of dyes using graphene-based composites: a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228, 180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3361-1.
Krivova, M. G., Grinshpan, D. D., & Hedin, N. (2013). Adsorption of CnTABr surfactants on activated carbons. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 436, 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.05.063.
Kyzas, G. Z., Peleka, E. N., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2013). Nanocrystalline akaganeite as adsorbent for surfactant removal from aqueous solutions. Materials (Basel), 6, 184–197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6010184.
Lagergreen, S. (1907). Zur Theorie der sogenannten Adsorption gelöster Stoffe. Zeitschr f Chem und Ind der Kolloide, 2(15), https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01501332.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004.
Leone, V., & Iovino, P. (2016). Sorption of a cationic surfactant benzyldimethyldodecyl ammonium chloride onto a natural zeolite. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227, 409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3108-4.
Li, M., Boggs, M., Beebe, T. P., & Huang, C. P. (2008). Oxidation of single-walled carbon nanotubes in dilute aqueous solutions by ozone as affected by ultrasound. Carbon N Y, 46, 466–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.12.012.
Li, Y., Umer, R., Samad, Y. A., et al. (2013). The effect of the ultrasonication pre-treatment of graphene oxide (GO) on the mechanical properties of GO/polyvinyl alcohol composites. Carbon N Y, 55, 321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.12.071.
Li, X.-b., Ye, J.-j., Qiu, Y.-q., et al. (2017). Adsorption of residual amine collector HAY from aqueous solution by refined carbon from coal fly ash and activated carbon. Journal of Central South University, 24, 30–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3405-0.
Lima, T. M. S., Procópio, L. C., Brandão, F. D., et al. (2011). Evaluation of bacterial surfactant toxicity towards petroleum degrading microorganisms. Bioresource Technology, 102, 2957–2964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.109.
Limousin, G., Gaudet, J. P., Charlet, L., et al. (2007). Sorption isotherms: a review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 249–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.09.010.
Lin, D., & Xing, B. (2008). Adsorption of phenolic compounds by carbon nanotubes: role of aromaticity and substitution of hydroxyl groups. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 7254–7259. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801297u.
Liney, K. E., Hagger, J. A., Tyler, C. R., et al. (2006). Health effects in fish of long-term exposure to effluents from wastewater treatment works. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114, 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8058.
Liu, Y. (2009). Is the free energy change of adsorption correctly calculated? Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 54, 1981–1985. https://doi.org/10.1021/je800661q.
Liu, H., Guan, Y., Wei, D., et al. (2016). Reinforcement of injectable calcium phosphate cement by gelatinized starches. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 104, 615–625. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.33434.
Liu, S.-S., Ge, H.-Y., Cheng, S.-L., et al. (2019). Synthesis of graphene oxide modified magnetic chitosan having skin-like morphology for methylene blue adsorption. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 19, 7993–8003. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2019.16872.
Ma, J., Liu, J., Zhu, W., & Qin, W. (2018). Solubility study on the surfactants functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 538, 79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.10.071.
Madadrang, C. J., Kim, H. Y., Gao, G., et al. (2012). Adsorption behavior of EDTA-graphene oxide for Pb (II) removal. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4, 1186–1193. https://doi.org/10.1021/am201645g.
Mezyk, S. P., Rickman, K. A., McKay, G., et al. (2011). Remediation of chemically-contaminated waters using sulfate radical reactions: kinetic studies. ACS Symposium Series, 1071, 247–263. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch012.
Miklos, D. B., Remy, C., Jekel, M., et al. (2018). Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment – a critical review. Water Research, 139, 118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.03.042.
Moleon, J. A., Ontiveros-Ortega, A., Gimenez-Martin, E., & Plaza, I. (2015). Effect of N-cetylpyridinium chloride in adsorption of graphene oxide onto polyester. Dyes and Pigments, 122, 310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2015.07.004.
Myśliwiec, D., Chylińska, M., Szymańska-Chargot, M., et al. (2016). Revision of adsorption models of xyloglucan on microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose, 23, 2819–2829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0995-x.
Obeid, L., El Kolli, N., Dali, N., et al. (2014). Adsorption of a cationic surfactant by a magsorbent based on magnetic alginate beads. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 432, 182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.06.027.
Ossonon, B. D., & Bélanger, D. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of sulfophenyl-functionalized reduced graphene oxide sheets. RSC Advances, 7, 27224–27234. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra28311j.
Park, C. J., Song, S. H., Kim, D. H., & Gye, M. C. (2016). Developmental and acute toxicity of cetylpyridinium chloride in Bombina orientalis (Amphibia: Anura). Aquatic Toxicology, 177, 446–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.06.022.
Patiha, Heraldy E, Hidayat Y, Firdaus M (2016) The langmuir isotherm adsorption equation: The monolayer approach. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. p 107.
Pavan, P. C., Crepaldi, E. L., De A. Gomes, G., & Valim, J. B. (1999). Adsorption of sodium dodecylsulfate on a hydrotalcite-like compound. Effect of temperature, pH and ionic strength. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 154, 399–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00847-4.
Perumbilavil, S., Sankar, P., Priya Rose, T., & Philip, R. (2015). White light Z-scan measurements of ultrafast optical nonlinearity in reduced graphene oxide nanosheets in the 400-700 nm region. Applied Physics Letters, 107(051), 104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4928124.
Prediger, P., Cheminski, T., de Figueiredo, N. T., et al. (2018). Graphene oxide nanomaterials for the removal of non-ionic surfactant from water. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 1536–1545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.01.072.
Qazi, M. J., Bonn, D., & Shahidzadeh, N. (2019). Drying of salt solutions from porous media: effect of surfactants. Transport in Porous Media, 128, 881–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1164-5.
Riaz, M. A., McKay, G., & Saleem, J. (2017). 3D graphene-based nanostructured materials as sorbents for cleaning oil spills and for the removal of dyes and miscellaneous pollutants present in water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 27731–27745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0606-x.
Rizzi, V., Longo, A., Fini, P., et al. (2014). Applicative study (part I): the excellent conditions to remove in batch direct textile dyes (direct red, direct blue and direct yellow) from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes on low-cost chitosan films under different conditions. Advances in Chemical Engineering and Science, 33, 399–447. https://doi.org/10.4236/aces.2014.44048.
Saleh, M. M., & Atia, A. A. (1999). Removal of some surfactants from dilute aqueous solutions using charcoal. Adsorption Science and Technology, 17, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/026361749901700106.
Schramm, L. L., Stasiuk, E. N., & Marangoni, D. G. (2003). Surfactants and their applications. Annual Reports on the Progress of Chemistry - Section C.
Shahriary, L., & Athawale, A. (2014). Graphene oxide synthesized by using modified Hummers approach. International Journal of Renewable Energy and Environmental Engineering, 2, 58–63.
Sheng JJ (2015) Status of surfactant EOR technology. Petroleum.
Sherlala, A. I. A., Raman, A. A. A., Bello, M. M., & Asghar, A. (2018). A review of the applications of organo-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites for heavy metal adsorption. Chemosphere, 193, 1004–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.093.
Shih, C. J., Lin, S., Sharma, R., et al. (2012). Understanding the pH-dependent behavior of graphene oxide aqueous solutions: a comparative experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Langmuir, 28, 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1021/la203607w.
Singhal, B., Porwal, A., Sharma, A., et al. (1997). Photocatalytic degradation of cetylpyridinium chloride over titanium dioxide powder. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 108, 85–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(97)00009-9.
Świercz, R., HaŁatek, T., Majcherek, W., et al. (2007). Toxic effect of benzalkonium chloride on animals and humans. Medycyna Pracy, 58, 139–142.
Tanada, M., Miyoshi, T., Nakamura, T., & Tanada, S. (1991). Adsorption removal of benzalkonium chloride by granular activated carbon for medical waste water treatment. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health, 5, 27–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/101053959100500108.
Tang, H., Zhao, Y., Shan, S., et al. (2018). Theoretical insight into the adsorption of aromatic compounds on graphene oxide. Environmental Science. Nano, 5, 2357–2367. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en00384j.
Tennouga, L., Mansri, A., Medjahed, K., et al. (2015). The micelle formation of cationic and anionic surfactants in aqueous medium: determination of CMC and thermodynamic parameters at different temperatures. Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 6, 2711–2716.
Tripathy, D. B., Mishra, A., Gupta, A., & Yadav, A. (2017). Biodegradability of laundry detergent surfactants., 5, 130–136.
Varga, M., Izak, T., Vretenar, V., et al. (2017). Diamond/carbon nanotube composites: Raman, FTIR and XPS spectroscopic studies. Carbon N Y, 111, 54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2016.09.064.
Wang, H., Zhou, A., Peng, F., et al. (2007). Mechanism study on adsorption of acidified multiwalled carbon nanotubes to Pb(II). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 316, 227–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.07.075.
Wang, Q., Han, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2008). Effect of surfactant structure on the stability of carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 112, 7227–7233. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp711816c.
Wang, X., Liu, Z., Ye, X., et al. (2015). A facile one-pot method to two kinds of graphene oxide-based hydrogels with broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties. Chemical Engineering Journal, 260, 331–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.102.
Wang, F. H., Bae, K., Huang, Z. W., & Xue, J. M. (2018a). Two-photon graphene quantum dot modified Gd 2 O 3 nanocomposites as a dual-mode MRI contrast agent and cell labelling agent. Nanoscale, 10, 5642–5649. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr08068a.
Wang, Y. Y., Liu, Y. X., Lu, H. H., et al. (2018b). Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 261, 53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2018.02.010.
Wang, B., Yang, X., Ma, L., et al. (2020). Ultra-high efficient pH induced selective removal of cationic and anionic dyes from complex coexisted solution by novel amphoteric biocomposite microspheres. Separation and Purification Technology, 231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115922.
Weber, W. J., & Carrell Morris, J. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division, 89, 31–60.
Wen, G., Qiang, C., Feng, Y., et al. (2018). Bromate formation during the oxidation of bromide-containing water by ozone/peroxymonosulfate process: Influencing factors and mechanisms. Chemical Engineering Journal, 352, 316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.186.
Wu, H., Lu, W., Shao, J. J., et al. (2013). pH-dependent size, surface chemistry and electrochemical properties of graphene oxide. Xinxing Tan Cailiao/New Carbon Mater, 28, 327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(13)60085-2.
Xiang, L., Wang, X. K., Li, Y. W., et al. (2015). Analysis of trace quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) in vegetables using ultrasonic-assisted extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 63, 6689–6697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01828.
Xiang, L., Sun, T. F., Zheng, M. J., et al. (2016). Sorption of dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride (DTAC) to agricultural soils. Science of the Total Environment, 48, 197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.235.
Xu, X. N., Guan, X. N., Zhou, H. H., & Zhu, Y. F. (2017). One-step reduction and surface modification of graphene oxide by 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid hydrazide and its polypropylene nanocomposites. Nanomaterials, 7, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7020025.
Yagub, M. T., Sen, T. K., Afroze, S., & Ang, H. M. (2014). Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 209, 172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002.
Yamada, S. (2018). Cation-π interactions in organic synthesis. Chemical Reviews, 118, 11353–11432. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00377.
Yamada, S., & Morita, C. (2002). Face-selective addition to a cation-π complex of a pyridinium salt: synthesis of chiral 1,4-dihydropyridines. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 124, 8184–8185. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0203317.
Yamada, S., Yamamoto, N., & Takamori, E. (2016). Synthesis of molecular seesaw balances and the evaluation of pyridinium- interactions. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 81, 11819–11830. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.6b02295.
Yao, Q., Fan, B., Xiong, Y., et al. (2017). 3D assembly based on 2D structure of cellulose nanofibril/graphene oxide hybrid aerogel for adsorptive removal of antibiotics in water. Scientific Reports, 7, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45914.
Ye, S., & Feng, J. (2016). The effect of sonication treatment of graphene oxide on the mechanical properties of the assembled films. RSC Advances, 46, 39681–39687. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra03996k.
Ye, C., Hu, N., & Wang, Z. (2013). Experimental investigation of Luffa cylindrica as a natural sorbent material for the removal of a cationic surfactant. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 44, 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.08.006.
Young, T. F. (2009). Statistical thermodynamics (Fowler, R. H.; Guggenheim, E. A.). Journal of Chemical Education, 18, 198. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed018p198.3.
Yusuf, M., Elfghi, F. M., Zaidi, S. A., et al. (2015). Applications of graphene and its derivatives as an adsorbent for heavy metal and dye removal: a systematic and comprehensive overview. RSC Advances, 5, 50392–50420. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra07223a.
Zhang, T. Y., & Zhang, D. (2011). Aqueous colloids of graphene oxide nanosheets by exfoliation of graphite oxide without ultrasonication. Bulletin of Materials Science, 34, 25–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0048-x.
Zhang, F., Li, S., Zhang, Q., et al. (2019). Adsorption of different types of surfactants on graphene oxide. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 276, 338–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.009.
Zhao, G., & Zhu, H. (2020). Cation-π interactions in graphene-containing systems for water treatment and beyond. Advanced Materials, 1905756, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201905756.
Zhao, J., Liu, X., Wu, Y., et al. (2019). Surfactants as promising media in the field of metal-organic frameworks. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 391, 30–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.04.002.
Zhu, M., Ge, F., Zhu, R., et al. (2010). A DFT-based QSAR study of the toxicity of quaternary ammonium compounds on Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere, 80, 46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.044.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Research Supporting Foundation of the State of São Paulo (FAPESP, proposal no. 2015/07033-7, 2018/10887-6, 2019/ 07822-2), LNNano, Brazilian Nanotechnology National Laboratory, CNPEM/MCTI for TEM and XPS analyses, Teaching, Research, and Extension Supporting Fund of the University of Campinas (FAEPEX), Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and the University of Campinas (UNICAMP). This research was supported by LNBR, Brazilian Biorenewables National Laboratory (CNPEM/MCTIC) during the use of the characterization of macromolecules (MAC) open-access facility. The authors thank to prof. Dr. Carlos Roque Duarte Correia for allowing us to use his laboratory facilities and to Espaço da Escrita, Coordenadoria Geral da Universidade, UNICAMP, for the language services provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
- The pyridinium-π and π-π interactions play important role for cationic surfactant adsorption onto GO.
- The kinetics of CPC, BZC, and DTAB adsorption onto GO was fast.
- High removal capacities of CPC (2083 mg/g), BZC (431 mg/g), and DTAB (329 mg/g) were achieved.
- GO was successfully used in three consecutive cycles, keeping high adsorption capacities.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Figueiredo Neves, T., Kushima Assano, P., Rodrigues Sabino, L. et al. Influence of Adsorbent/Adsorbate Interactions on the Removal of Cationic Surfactants from Water by Graphene Oxide. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04669-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04669-w