Abstract
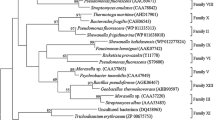
A functional screen of a metagenomic library from “Upo” swamp sediment in Korea identified a gene EstL28, the product of which displayed lipolytic properties on a tributyrin-supplemented medium. The EstL28 sequence encodes a 290 amino acid protein (designated as EstL28), with a predicted molecular weight of 31.3 kDa. The encoded EstL28 protein exhibited the highest sequence similarity (45 %) to a hydrolase found in Streptococcus sanguinis. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that EstL28 belongs to a currently uncharacterized family of esterases. Within the conserved α/β-hydrolase 6 domain, the EstL28 retains the catalytic triad Ser103–Asp248–His268 that is typical of esterases. The Ser103 residue in the catalytic triad is located in the consensus pentapeptide motif GXSXG. The purified EstL28 enzyme worked optimally at 35 °C and pH 8.5 and remained stable at temperatures lower than 20 °C. The catalytic activity of EstL28 was maximal with p-nitrophenyl butyrate, indicating that it was an esterase. This enzyme also exhibited stable activity in the presence of methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide. Therefore, the level of stability in organic solvents and cold temperature suggests that EstL28 has potential for many biotechnological applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343(Pt 1):177–183
Bornscheuer UT (2002) Microbial carboxyl esterases: classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:73–81
Chu X, He H, Guo C, Sun B (2008) Identification of two novel esterases from a marine metagenomic library derived from South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:615–625. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1566-3
Fan XJ, Liu XL, Huang R, Liu YH (2012) Identification and characterization of a novel thermostable pyrethroid-hydrolyzing enzyme isolated through metagenomic approach. Microb Cell Fact 11:33. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-11-33
Fernandez-Arrojo L, Guazzaroni ME, Lopez-Cortes N, Beloqui A, Ferrer M (2010) Metagenomic era for biocatalyst identification. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:725–733. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2010.09.006
Fu CZ et al (2011) Molecular cloning and characterization of a new cold-active esterase from a deep-sea metagenomic library. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:961–970
Georlette D et al (2004) Some like it cold: biocatalysis at low temperatures. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:25–42. doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2003.07.003
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:763–781. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1568-8
Heath C, Hu XP, Cary SC, Cowan D (2009) Identification of a novel alkaliphilic esterase active at low temperatures by screening a metagenomic library from Antarctic desert soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4657–4659
Hu XP, Heath C, Taylor MP, Tuffin M, Cowan D (2012) A novel, extremely alkaliphilic and cold-active esterase from Antarctic desert soil. Extremophiles 16:79–86. doi:10.1007/s00792-011-0407-y
Jiang X et al (2012) Identification and characterization of novel esterases from a deep-sea sediment metagenome. Arch Microbiol 194:207–214. doi:10.1007/s00203-011-0745-2
Jimenez DJ, Montana JS, Alvarez D, Baena S (2012) A novel cold active esterase derived from Colombian high Andean forest soil metagenome. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:361–370
Joseph B, Ramteke PW, Thomas G (2008) Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments. Biotechnol Adv 26:457–470. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.05.003
Kang CH, Oh KH, Lee MH, Oh TK, Kim BH, Yoon J (2011) A novel family VII esterase with industrial potential from compost metagenomic library. Microb Cell Fact 10:41. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-10-41
Kim SJ et al (2007) Screening and characterization of an enzyme with beta-glucosidase activity from environmental DNA. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:905–912
Kim EY, Oh KH, Lee MH, Kang CH, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2009) Novel cold-adapted alkaline lipase from an intertidal flat metagenome and proposal for a new family of bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:257–260. doi:10.1128/AEM.01400-08
Lee MH et al (2012) Novel metagenome-derived, cold-adapted alkaline phospholipase with superior lipase activity as an intermediate between phospholipase and lipase. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4959–4966. doi:10.1128/AEM.00260-12
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak S, von Heijne G (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng 10:1–6
Noguchi H, Taniguchi T, Itoh T (2008) MetaGeneAnnotator: detecting species-specific patterns of ribosomal binding site for precise gene prediction in anonymous prokaryotic and phage genomes. DNA Res 15:387–396. doi:10.1093/dnares/dsn027
Park HJ, Jeon JH, Kang SG, Lee JH, Lee SA, Kim HK (2007) Functional expression and refolding of new alkaline esterase, EM2L8 from deep-sea sediment metagenome. Protein Expr Purif 52:340–347. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2006.10.010
Pedersen AG, Baldi P, Brunak S, Chauvin Y (1996) Characterization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic promoters using hidden Markov models. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 4:182–191
Peng Q et al (2011) A novel esterase gene cloned from a metagenomic library from neritic sediments of the South China Sea. Microb Cell Fact 10:95. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-10-95
Roh C, Villatte F (2008) Isolation of a low-temperature adapted lipolytic enzyme from uncultivated micro-organism. J Appl Microbiol 105:116–123
Rondon MR et al (2000) Cloning the soil metagenome: a strategy for accessing the genetic and functional diversity of uncultured microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2541–2547
Taupp M, Mewis K, Hallam SJ (2011) The art and design of functional metagenomic screens. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:465–472. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2011.02.010
Virk AP, Sharma P, Capalash N (2011) A new esterase, belonging to hormone-sensitive lipase family, cloned from Rheinheimera sp. isolated from industrial effluent. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:667–674
Yu EY et al (2011) Isolation and characterization of cold-active family VIII esterases from an arctic soil metagenome. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:573–581
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the grant from National Academy of Agricultural Science, Rural Development Administration (Project Number PJ008604/PJ00864902) and IPET Project Number 110037-03-1-HD110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sohyeon Seo and Young-Seok Lee have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, S., Lee, YS., Yoon, SH. et al. Characterization of a novel cold-active esterase isolated from swamp sediment metagenome. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 879–886 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1496-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1496-9