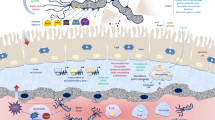
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori infection (H. pylori) is associated with chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. The present study provides information on the protective effects of Limosilactobacillus reuteri strain 2892 (L. reuteri 2892) isolated from camel’s milk against H. pylori-induced gastritis in the stomach tissue of animal models. Animal assays revealed that L. reuteri 2892 pretreatment significantly downregulated the virulence factor cagA gene expression. It upregulated the expression level of tight junction molecules [zona occludens (ZO-1), claudin-4] and suppressed metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 expressions. L. reuteri 2892 exhibited immunomodulatory effects on cytokine profile, as it reduced the serum concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and INF-γ and increased the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10. In addition, L. reuteri 2892 showed anti-oxidative stress activity by regulating the levels of oxidative stress-associated markers [superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA)]. Our findings suggest that L. reuteri 2892 attenuates H. pylori-induced gastritis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HP:
-
Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- L. acidophilus:
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus
- L. rhamnosus:
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- L. plantarum:
-
Lactobacillus plantarum
- LAB:
-
Lactic acid bacteria
- L. reuteri:
-
Limosilactobacillus reuteri
- cagA:
-
cytotoxin associated antigen A
- vacA:
-
vacuolization cytotoxin
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- MRS:
-
de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe
- Pb:
-
Probiotics
- rDNA:
-
ribosomal DNA
- RT-qPCR:
-
real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloproteinases
- ZO-1:
-
zona occludens
- PMNs:
-
Polymorphonuclears
References
Asgari B, Kermanian F, Hedayat Yaghoobi M, Vaezi A, Soleimanifar F, Yaslianifard S (2020) The anti-Helicobacter pylori effects of lactobacillus acidophilus, L. plantarum, and L. rhamnosus in stomach tissue of C57BL/6 mice. Visc Med 36:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1159/000500616
Azad MAK, Sarker M, Wan D (2018) Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics on cytokine profiles. Biomed Res. Int 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8063647
Bang CS, Baik GH (2014) Attempts to enhance the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 20:5252–5262. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5252
Butcher LD, den Hartog G, Ernst PB, Crowe SE (2017) Oxidative stress resulting from Helicobacter pylori infection contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.02.002
Cabral-Pacheco GA, Garza-Veloz I, Castruita-De la Rosa C, Ramirez-Acuña JM, Perez-Romero BA, Guerrero-Rodriguez JF, Martinez-Avila N, Martinez-Fierro ML (2020) The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci 21:9739
Caron TJ, Scott KE, Fox JG, Hagen SJ (2015) Tight junction disruption: Helicobacter pylori and dysregulation of the gastric mucosal barrier. World J Gastroenterol 21:11411–11427. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i40.11411
Chen M-J, Chen C-C, Huang Y-C, Tseng C-C, Hsu J-T, Lin Y-F, Fang Y-J, Wu M-S, Liou J-M, for the Taiwan Gastrointestinal Disease H C (2021) The efficacy of Lactobacillus acidophilus and rhamnosus in the reduction of bacterial load of Helicobacter pylori and modification of gut microbiota—a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Helicobacter 26:e12857. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12857
Corcoran BM, Stanton C, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP (2005) Survival of probiotic lactobacilli in acidic environments is enhanced in the presence of metabolizable sugars. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3060–3067. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.71.6.3060-3067.2005
Crabtree JE, Lindley IJ (1994) Mucosal interleukin-8 and Helicobacter pylori-associated gastroduodenal disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6(Suppl 1):S33–S38
de Moreno de LeBlanc A, LeBlanc JG, Perdigón G, Miyoshi A, Langella P, Azevedo V, Sesma F (2008) Oral administration of a catalase-producing Lactococcus lactis can prevent a chemically induced colon cancer in mice. J Med Microbiol 57:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.47403-0
Díaz P, Valenzuela Valderrama M, Bravo J, Quest AFG (2018) Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: adaptive cellular mechanisms involved in disease progression. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00005
Ding S-Z, Minohara Y, Fan XJ, Wang J, Reyes VE, Patel J, Dirden-Kramer B, Boldogh I, Ernst PB, Crowe SE (2007) Helicobacter pylori infection induces oxidative stress and programmed cell death in human gastric epithelial cells. Infect Immun 75:4030–4039. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00172-07
Dixon B, Hossain R, Patel RV, Algood HMS (2019) Th17 cells in Helicobacter pylori infection: a dichotomy of help and harm. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00363-19
Edalati E, Saneei B, Alizadeh M, Hosseini SS, Zahedi Bialvaei A, Taheri K (2019) Isolation of probiotic bacteria from raw camel’s milk and their antagonistic effects on two bacteria causing food poisoning. New Microbes New Infect 27:64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmni.2018.11.008
García A, Navarro K, Sanhueza E, Pineda S, Pastene E, Quezada M, Henríquez K, Karlyshev A, Villena J, González C (2017) Characterization of Lactobacillus fermentum UCO-979 C, a probiotic strain with a potent anti-helicobacter pylori activity. ELECTRON J BIOTECHN 25:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2016.11.008
Gebremariam HG, Qazi KR, Somiah T, Pathak SK, Sjölinder H, Sverremark Ekström E, Jonsson A-B (2019) Lactobacillus gasseri suppresses the production of proinflammatory cytokines in helicobacter pylori-infected macrophages by inhibiting the expression of ADAM17. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02326
Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, Suen MMY, Underwood FE, Tanyingoh D, Malfertheiner P, Graham DY, Wong VWS, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG, Ng SC (2017) Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol 153:420–429. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.022
Huang JQ, Zheng GF, Sumanac K, Irvine EJ, Hunt RH (2003) Meta-analysis of the relationship between cagA seropositivity and gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 125:1636–1644. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2003.08.033
Ierardi E, Giorgio F, Losurdo G, Di Leo A, Principi M (2013) How antibiotic resistances could change Helicobacter pylori treatment: A matter of geography? World J Gastroenterol 19:8168–8180. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8168
Ito F, Sono Y, Ito T (2019) Measurement and clinical significance of lipid peroxidation as a biomarker of oxidative stress: oxidative stress in diabetes, atherosclerosis, and chronic inflammation. Antioxidants 8:72
Ji J, Yang H (2020) Using probiotics as supplementation for Helicobacter pylori antibiotic therapy. Int J Mol Sci 21:1136
Ji J, Yang H (2021) In vitro effects of lactobacillus plantarum LN66 and antibiotics used alone or in combination on Helicobacter pylori mature biofilm. Microorganisms 9:424
Karamese M, Aydin H, Sengul E, Gelen V, Sevim C, Ustek D, Karakus E (2016) The Immunostimulatory Effect of Lactic acid Bacteria in a rat model. Iran J Immunol 13:220–228
Keikha M, Karbalaei M (2021) Probiotics as the live microscopic fighters against Helicobacter pylori gastric infections. BMC Gastroenterol 21:388. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-021-01977-1
Khaiboullina SF, Abdulkhakov S, Khalikova A, Safina D, Martynova EV, Davidyuk Y, Khuzin F, Faizullina R, Lombardi VC, Cherepnev GV, Rizvanov AA (2016) Serum cytokine signature that discriminates Helicobacter pylori positive and negative juvenile gastroduodenitis. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01916
Koyama S (2004) Significance of cell-surface expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors on gastric epithelium and infiltrating mucosal lymphocytes in progression of helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. Scand J Gastroenterol 39:1046–1053. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520410003245
Kusters JG, van Vliet AHM, Kuipers EJ (2006) Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Microbiol reviews 19: 449 – 90. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00054-05
Lamb A, Chen L-F (2013) Role of the Helicobacter pylori-Induced inflammatory response in the development of gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem 114:491–497. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24389
LeBlanc JG, del Carmen S, Miyoshi A, Azevedo V, Sesma F, Langella P, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Watterlot L, Perdigon G, de Moreno A (2011) Use of superoxide dismutase and catalase producing lactic acid bacteria in TNBS induced Crohn’s disease in mice. J Biotechnol 151:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.11.008
Li SL, Zhao JR, Ren XY, Xie JP, Ma QZ, Rong QH (2013) Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 associated with gastric ulcer recurrence. World J Gastroenterol 19:4590–4595. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4590
Lin C-C, Huang W-C, Su C-H, Lin W-D, Wu W-T, Yu B, Hsu Y-M (2020) Effects of multi-strain probiotics on immune responses and metabolic balance in Helicobacter pylori-Infected mice. Nutrients 12:2476
Lin W-Y, Lin J-H, Kuo Y-W, Chiang P-FR, Ho H-H (2022) Probiotics and their metabolites reduce oxidative stress in middle-aged mice. Curr Microbiol 79:1–12
Macfarlane GT, Cummings JH (1999) Probiotics and prebiotics: can regulating the activities of intestinal bacteria benefit health? BMJ 318:999–1003. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.318.7189.999
Mishra V, Shah C, Mokashe N, Chavan R, Yadav H, Prajapati J (2015) Probiotics as potential antioxidants: a systematic review. J Agric Food Chem 63:3615–3626. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf506326t
Panpetch W, Spinler JK, Versalovic J, Tumwasorn S (2016) Characterization of Lactobacillus salivarius strains B37 and B60 capable of inhibiting IL-8 production in Helicobacter pylori-stimulated gastric epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol 16:242. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-016-0861-x
Patel A, Shah N, Prajapati JB (2014) Clinical application of probiotics in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection—A brief review. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 47:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2013.03.010
Peña JA, Rogers AB, Ge Z, Ng V, Li SY, Fox JG, Versalovic J (2005) Probiotic Lactobacillus spp. diminish Helicobacter hepaticus-induced inflammatory bowel disease in interleukin-10-deficient mice. Infect Immun 73:912–920. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.73.2.912-920.2005
Piscione M, Mazzone M, Di Marcantonio MC, Muraro R, Mincione G (2021) Eradication of Helicobacter pylori and gastric Cancer: a controversial relationship. Front Microbiol 12:630852. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.630852
Ruggiero P (2014) Use of probiotics in the fight against Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 5:384–391. https://doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.384
Ruiz RLG, Mohamed F, Bleckwedel J, Medina R, De Vuyst L, Hebert EM, Mozzi F (2019) Diversity and functional properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from wild fruits and flowers present in Northern Argentina. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01091
Sgouras D, Maragkoudakis P, Petraki K, Martinez-Gonzalez B, Eriotou E, Michopoulos S, Kalantzopoulos G, Tsakalidou E, Mentis A (2004) In vitro and in vivo inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.70.1.518-526.2004
Sokolova O, Naumann M (2022) Matrix metalloproteinases in Helicobacter pylori–Associated gastritis and gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):1883
Sugimoto M, Yamaoka Y (2009) Virulence factor genotypes of Helicobacter pylori affect cure rates of eradication therapy. ARCH IMMUNOL THER EX 57:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-009-0007-z
Taverniti V, Guglielmetti S (2011) The immunomodulatory properties of probiotic microorganisms beyond their viability (ghost probiotics: proposal of paraprobiotic concept). Genes Nutr 6:261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-011-0218-x
Thung I, Aramin H, Vavinskaya V, Gupta S, Park JY, Crowe SE, Valasek MA (2016) Review article: the global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43:514–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13497
Verma S, Kesh K, Ganguly N, Jana S, Swarnakar S (2014) Matrix metalloproteinases and gastrointestinal cancers: impacts of dietary antioxidants. World J Biol Chem 5:355–376. https://doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i3.355
Wang Y, Wu Y, Wang Y, Xu H, Mei X, Yu D, Wang Y, Li W (2017) Antioxidant Properties of probiotic Bacteria. Nutrients 9:521
Westerik N, Reid G, Sybesma W, Kort R (2018) The probiotic lactobacillus rhamnosus for alleviation of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric pathology in East Africa. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01873
Zhou Q, Xue B, Gu R, Li P, Gu Q (2021) Lactobacillus plantarum ZJ316 attenuates Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastritis in C57BL/6 mice. J Agric Food Chem 69:6510–6523. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01070
WHO. Antimicrobial resistance global report on surveillance: 2014 summary (2014) (2014)
Wroblewski LE, Peek RM Jr, Wilson KT (2010) Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: factors that modulate disease risk. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:713–739. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00011-10
Wu Y, Zhu C, Chen Z, Chen Z, Zhang W, Ma X, Wang L, Yang X, Jiang Z (2016) Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on epithelial barrier disruption caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 172:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.03.005
Xia X, Zhang L, Wu H, Chen F, Liu X, Xu H, Cui Y, Zhu Q, Wang M, Hao H (2022) CagA+ Helicobacter pylori, not CagA–Helicobacter pylori, infection impairs endothelial function through exosomes-mediated ROS formation. Front Cardiovasc Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.881372
Yang Y-J, Chuang C-C, Yang H-B, Lu C-C, Sheu B-S (2012) Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates H. pylori-induced gastric inflammation by inactivating the Smad7 and NFκB pathways. BMC Microbiol 12:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-38
Yang KM, Jiang ZY, Zheng CT, Wang L, Yang XF (2014) Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum on diarrhea and intestinal barrier function of young piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. J Anim Sci 92:1496–1503. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2013-6619
Yarmohammadi M, Yadegar A, Ebrahimi MT, Zali MR (2021) Effects of a potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC 33323 on Helicobacter pylori-Induced Inflammatory Response and Gene expression in coinfected gastric epithelial cells. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13:751–764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09721-z
Zhang M (2015) High antibiotic resistance rate: a difficult issue for Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment. World J Gastroenterol 21:13432–13437. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13432
Zhang W, Lu H, Graham DY (2014) An update on Helicobacter pylori as the cause of gastric cancer. Gastrointest Tumors 1:155–165
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the staff at Islamic Azad University of Shiraz, Islamic Azad University of Neyshabur, and the Neyshabur University of Medical Sciences for their sincere assistance and efforts to make this project happen
Funding
This work was supported by Islamic Azad University of Shiraz (Grant numbers [162449566]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FFN and AR performed the experiments, analyzed data, prepared the figures, and drafted the manuscript. MA analyzed pathological data. JS designed the project and experiments. AG and MM conceived, designed and supervised all aspects of the work, critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose
Ethical approval
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Islamic Azad University of Shiraz under code number IR.IAU.SHIRAZ.REC.1401.015.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Forooghi Nia, F., Rahmati, A., Ariamanesh, M. et al. The Anti-Helicobacter pylori effects of Limosilactobacillus reuteri strain 2892 isolated from Camel milk in C57BL/6 mice. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 119 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03555-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03555-x