Abstract
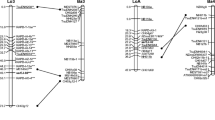
Linkage maps of the sweet cherry cultivar ‘Emperor Francis’ (EF) and the wild forest cherry ‘New York 54’ (NY) were constructed using primarily simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and gene-derived markers with known positions on the Prunus reference map. The success rate for identifying SSR markers that could be placed on either the EF or NY maps was only 26% due to two factors: a reduced transferability of other Prunus-species-derived markers and a low level of polymorphism in the mapping parents. To increase marker density, we developed four cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence markers (CAPS), 19 derived CAPS markers, and four insertion–deletion markers for cherry based on 101 Prunus expressed sequence tags. In addition, four gene-derived markers representing orthologs of a tomato vacuolar invertase and fruit size gene and two sour cherry sorbitol transporters were developed. To complete the linkage analysis, 61 amplified fragment length polymorphism and seven sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers were also used for map construction. This analysis resulted in the expected eight linkage groups for both parents. The EF and NY maps were 711.1 cM and 565.8 cM, respectively, with the average distance between markers of 4.94 cM and 6.22 cM. A total of 82 shared markers between the EF and NY maps and the Prunus reference map showed that the majority of the marker orders were the same with the Prunus reference map suggesting that the cherry genome is colinear with that of the other diploid Prunus species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott AG, Rajapakse S, Sosinski B, Lu ZX, Sossey-Alaoui K, Gannavarapu M, Reighard G, Ballard RE, Baird WV, Scorza R, Callahan A (1998) Construction of saturated linkage maps of peach crosses segregating for characters controlling fruit quality, tree architecture and pest resistance. Acta Hortic 465:41–49
Aranzana MJ, Garcia-Mas J, Carbo J, Arús P (2002) Development and variability analysis of microsatellite markers in peach. Plant Breed 121:87–92
Aranzana MJ, Pineda A, Cosson P, Dirlewanger E, Ascasibar J, Cipriani G, Ryder CD, Testolin R, Abbott A, King GJ, Iezzoni AF, Arús P (2003) A set of simple-sequence repeat markers covering the Prunus genome. Theor Appl Genet 106:819–825
Bliss FA, Arulsekar S, Foolad MR, Becerra V, Gillen AM, Warburton ML, Dandekar AM, Kocsisne GM, Mydin KK (2002) An expanded genetic linkage map of Prunus based on an interspecific cross between almond and peach. Genome 45:520–529
Bošković R, Tobutt KR (1998) Inheritance and linkage relationships of isoenzymes in two interspecific cherry progenies. Euphytica 103:273–286
Cantini C, Iezzoni AF, Lamboy WF, Boritzki M, Struss D (2001) DNA fingerprinting of tetraploid cherry germplasm using simple sequence repeats. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:205–209
Chaparro JX, Werner DJ, O’Malley D, Sederoff RR (1994) Targeted mapping and linkage analysis of morphological, isozyme, and RAPD markers in peach. Theor Appl Genet 87:805–815
Choi C, Kappel F (2004) Inbreeding, coancestry, and founding clones of sweet cherries in North America. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 129:535–543
Cipriani G, Lot G, Huang W-G, Marrazzo MT, Peterlunger E, Testolin R (1999) AC/GT and AG/CT microsatellite repeats in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch): isolation, characterisation and cross-species amplification in Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 99:65–72
Clarke JB, Tobutt KR (2003) Development and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites from Prunus avium ‘Napoleon’. Mol Ecol Notes 3:578–580
Decroocq V, Fave MG, Hagen L, Bordenave L, Decroocq S (2003) Development and transferability of apricot and grape EST microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor Appl Genet 106:912–922
Dettori MT, Quarta R, Verde I (2001) A peach linkage map integrating RFLPs, SSRs, RAPDs, and morphological markers. Genome 44:783–790
Dickson EE, Arumuganathan K, Kresovich S, Doyle JJ (1992) Nuclear DNA content variation within the Rosaceae. Am J Bot 79:1081–1086
Dirlewanger E, Pronier V, Parvery C, Rothan C, Guye A, Monet R (1998) A genetic linkage map of peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) using morphological, RFLP, isoenzyme, RAPD, and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:888–895
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Tavaud M, Aranzana MJ, Poizat C, Zanetto A, Arús P, Laigret R (2002) Development of microsatellite markers in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:127–138
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldere F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arús P (2004a) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:9891–9896
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Howad W, Capdeville G, Bosselut N, Claverie M, Voisin R, Poizat C, Lafargue B, Baron O, Laigret F, Kleinhentz M, Arús P, Esmenjaud D (2004b) Microsatellite genetic linkage maps of myrobalan plum and an almond-peach hybrid—location of root-knot nematode resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 109:827–838
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Boudehri K, Renaud C, Capdeville G, Tauzin Y, Laigret F, Moing A (2006) Development of a second-generation genetic linkage map for peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and characterization of morphological traits affecting flower and fruit. Tree Genet Genomes 3:1–13
Dondini L, Lain O, Geuna F, Banfi R, Gaiotti F, Tartarini S, Bassi D, Testolin R (2007) Development of a new SSR-based linkage map in apricot and analysis of synteny with existing Prunus maps. Tree Genet Genomes 3:239–249
Foolad MR, Arulsekar S, Becerra V, Bliss FA (1995) A genetic map of Prunus based on an interspecific cross between peach and almond. Theor Appl Genet 91:262–269
Foulongne M, Pascal T, Arús P, Kervella J (2003) The potential of Prunus davidiana for introgression into peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] assessed by comparative mapping. Theor Appl Genet 107:227–238
Frary A, Nesbitt TC, Frary A, Grandillo S, van der Knaap E, Cong B, Liu J, Meller J, Elber R, Alpert KB, Tanksley SD (2000) fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85–88
Fridman E, Pleban T, Zamir D (2000) A recombination hotspot delimits a wild-species quantitative trait locus for tomato sugar content to 484 bp within an invertase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4718–4723
Gao Z, Maurousset L, Lemoine R, Yoo S-D, van Nocker S, Loescher W (2003) Cloning, expression, and characterization of sorbitol transporters from developing sour cherry fruit and leaf sink tissues. Plant Physiol 131:1–10
Hagen LS, Chaib J, Fady B, Decroocq V, Bouchet JB, Lambert P, Audergon JM (2004) Genomic and cDNA microsatellites from apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Mol Ecol Notes 4:742–745
Hazen SP, Leroy P, Ward R (2002) AFLP in Triticum aestivum L.: patterns of genetic diversity and genome distribution. Euphytica 125:89–102
Horn R, Lecouls A-C, Callahan A, Dandekar A, Garay L, McCord P, Howad W, Chan H, Verde I, Main D, Jung S, Georgi L, Forrest S, Mook J, Zhebentyayeva T, Yu Y, Kim HR, Jesudurai C, Sosinski B, Arús P, Baird V, Parfitt D, Reighard G, Scorza R, Tomkins, Wing R, Abbott AG (2005) Candidate gene database and transcript map for peach, a model species for fruit trees. Theor Appl Genet 110:1419–1428
Howad W, Yamamoto T, Dirlewanger E, Testolin R, Cosson P, Cipriana G, Monforte AJ, Georgi L, Abbott AG, Arús P (2005) Mapping with a few plants: using selective mapping for microsatellite saturation of the Prunus reference map. Genetics 171:1305–1309
Hurtado MA, Vilanova S, Romero C, Abbott AG, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2002) Genetic linkage maps of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.) based on molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:182–191
Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Tao R, Hauck NR, Sebolt AM, Iezzoni AF (2005) Linkage and physical distances between the S-haplotype S-RNase and SFB genes in sweet cherry. Sex Plant Reprod 17:289–296
Joobeur T, Viruel MA, de Vicente MC, Jauregui B, Ballester J, Dettori MT, Verde I, Truco MJ, Messeguer R, Battle I, Quarta R, Dirlewanger E, Arús P (1998) Construction of a saturated linkage map for Prunus using an almond × peach F2 progeny. Theor Appl Genet 97:1034–1041
Joobeur T, Periam N, de Vicente MC, King GJ, Arús P (2000) Development of a second generation linkage map for almond using RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 43:649–688
Konieczny A, Ausubel F (1993) A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific PCR-based markers. Plant J 4:403–410
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lambert P, Hagen LS, Arús P, Audergon JM (2004) Genetic linkage maps of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.) compared with the almond ‘Texas’ × peach ‘Earlygold’ reference map for Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 108:1120–1130
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:445–461
Lopes MS, Sefc KM, Laimer M, Da Camara Machado A (2002) Identification of microsatellite loci in apricot. Mol Ecol Notes 2:24–26
Lu Z-X, Sosinski B, Reighard GL, Baird WV, Abbott AG (1998) Construction of a genetic linkage map and identification of AFLP markers or resistance to root-knot nematodes in peach rootstocks. Genome 41:199–207
Marchese A, Tobutt KR, Raimondo A, Motisi A, Bošković RI, Clarke J, Caruso T (2007) Morphological characteristics, microsatellite fingerprinting and determination of incompatibility genotypes of Sicilian sweet cherry cultivars. J Hortic Sci Biotech 82:41–48
Messina R, Lain O, Marrazzo MT, Cipriani G, Testolin R (2004) New set of microsatellite loci isolated in apricot. Mol Ecol Notes 4:432–434
Michaels SD, Amasino RM (1998) A robust method for detecting single-nucleotide changes as polymorphic markers by PCR. Plant J 14:381–385
Mnejja M, Garcia-Mas J, Howad W, Badenes ML, Arús P (2004) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers of Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) are highly polymorphic and transferable to peach and almond. Mol Ecol Notes 4:163–166
Mnejja M, Garcia-Mas J, Howad W, Arús P (2005) Development and transportability across Prunus species of 42 polymorphic almond microsatellites. Mol Ecol Notes 5:531–535
Neff MM, Neff JD, Chory J, Pepper AE (1998) dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J 14:387–392
Pedersen BH (2006) DNA fingerprints of 51 sweet and sour Prunus accessions using simple sequence repeats. J Hortic Sci Biotech 81:118–124
Quilot B, Wu BH, Kervella J, Genard M, Foulongne M, Moreau K (2004) QTL analysis of quality traits in an advanced backcross between Prunus persica cultivars and the wild related species P. davidiana. Theor Appl Genet 109:884–897
Rajapakse S, Belthoff LE, He G, Estager AE, Scorza R, Verde I, Ballard RE, Baird WV, Callahan A, Monet R, Abbott AG (1995) Genetic linkage mapping in peach using morphological, RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:503–510
Schueler S, Tusch A, Schuster M, Ziegenhagen B (2003) Characterization of microsatellites in wild and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.)—markers for individual identification and reproductive processes. Genome 46:95–102
Schueler S, Tusch A, Scholz F (2006) Comparative analysis of the within-population genetic structure in wild cherry (Prunus avium L.) at the self-incompatibility locus and nuclear microsatellites. Mol Ecol 15:3231–3243
Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat Biotechnol 18:233–234
Shaw J, Small RL (2004) Addressing the “hardest puzzle in American pomology”: phylogeny of Prunus sect. Prunocerasus (Rosaceae) based on seven noncoding chloroplast DNA regions. Am J Bot 91:985–996
Silva C, Garcia-Mas J, Sanchez AM, Arús P, Oliveira MM (2005) Looking into flowering time in almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill) D.A. Webb): the candidate gene approach. Theor Appl Genet 110:959–968
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Boskovic R, Tobutt KR (2001) Cloning of six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theor Appl Genet 102:1046–1055
Sosinski B, Gannavarapu M, Hager LD, Beck LE, King GJ, Ryder CD, Rajapakse S, Baird WV, Ballard RE, Abbott AG (2000) Characterization of microsatellite markers in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch). Theor Appl Genet 101:421–428
Stockinger EJ, Mulinix CA, Long CM, Brettin TS, Iezzoni AF (1996) A linkage map of sweet cherry based on RAPD analysis of a microspore-derived callus culture population. J Heredity 87:214–218
Stoeckel S, Grange J, Fernandez-Manjarres F, Bilger I, Frascaria-Lacoste N, Mariette S (2006) Heterozygote excess in a self-incompatible and partially clonal forest tree species—Prunus avium L. Mol Ecol 15:2109–2118
Struss D, Boritzki M, Karle R, Iezzoni AF (2002) Microsatellite markers differentiate eight Giessen cherry rootstocks. HortScience 37:191–193
Struss D, Ahmad R, Southwick SM, Boritzki M (2003) Analysis of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars using SSR and AFLP markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 128:904–909
Tao R, Yamane H, Sugiura A, Murayama H, Sassa H, Mori H (1999) Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification, characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 124:224–233
Testolin R, Marrazzo T, Cipriani G, Quarta R, Verde I, Dettori MT, Pancaldi M, Sansavini S (2000) Microsatellite DNA in peach (Prunus persica L. Batch) and its use in fingerprinting and testing the genetic origin of cultivars. Genome 43:512–520
Testolin R, Messina R, Lain O, Marrazzo MT, Huang WG, Cipriani G (2004) Microsatellites isolated in almond from an AC-repeat enriched library. Mol Ecol Notes 4:459–461
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Vaughan SP, Russell K (2004) Characterization of novel microsatellites and development of multiplex PCR for large-scale population studies in wild cherry, Prunus avium. Mol Ecol Notes 4:429–431
Vilanova S, Romero C, Abbott AG, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2003) An apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) F2 progeny linkage map based on SSR and AFLP markers, mapping plum pox virus resistance and self-incompatibility traits. Theor Appl Genet 107:239–247
Viruel MA, Messeguer R, de Vicente MC, Garcia-Mas J, Puigdomenech P, Vargas FJ, Arús P (1995) A linkage map with RFLP and isozyme markers for almond. Theor Appl Genet 91:964–971
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Heredity 93:77–78
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Rijans M, van der Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang D, Karle R, Brettin TS, Iezzoni AF (1998) Genetic linkage map in sour cherry using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:1217–1224
Wünsch A, Hormaza JI (2002) Molecular characterisation of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genotypes using peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] SSR sequences. Heredity 89:56–63
Yamamoto T, Shimada T, Imai T, Yaegaki H, Haji T, Matsuta N, Yamaguchi M, Hayashi T (2001) Characterization of morphological traits based on a genetic linkage map in peach. Breeding Sci 51:271–278
Yamamoto T, Mochida K, Imai T, Shi YZ, Ogiwara I, Hayashi T (2002) Microsatellite markers in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) derived from an enriched genomic and cDNA libraries. Mol Ecol Notes 2:298–301
Yamamoto T, Yamaguchi M, Hayashi T (2005) An integrated genetic linkage map of peach by SSR, STS, AFLP and RAPD. J Jpn Soc Hort Sci 74:203–213
Yamane H, Tao R, Sugiura A, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF (2001) Identification and characterization of S-RNases in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.). J Am Soc Hort Sci 126:661–667
Zhebentyayeva TN, Hort R, Mookj S, Lecouls A-C, Georgi L, Swire-Clark G, Reighard GL, Baird WV, Abbott AG (2006) A physical framework for the peach genome. Acta Hortic 713:83–88
Acknowledgement
This project was supported by the National Research Initiative Competitive Grant 2005-35300-15454 from the US Department of Agriculture Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Dirlewanger
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Table 1
Markers that did not amplify EF or NY DNA arranged by linkage groupa. Markers that identify multiple loci are in bold (DOC 29 kb)
Supplemental Table 2
Markers that were monomorphic for EF and NY arranged by linkage group position. Markers that identify multiple loci are identified in bolda (DOC 40 kb)
Supplemental Table 3
Markers that were “complex” or “difficult.” Bold identifies those SSRs that identified multiple loci (DOC 25.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olmstead, J.W., Sebolt, A.M., Cabrera, A. et al. Construction of an intra-specific sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genetic linkage map and synteny analysis with the Prunus reference map. Tree Genetics & Genomes 4, 897–910 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0161-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0161-1