Abstract
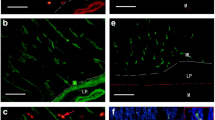
P2X2 receptors, with other P2X receptor subtypes, have an important role mediating synaptic transmission in regulating the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. Our recent work has found a new regulator of P2X receptor function, called phosphoinositide-interacting regulator of transient receptor potential channels (Pirt). In the present work, we have shown that Pirt immunoreactivity was localized in nerve cell bodies and nerve fibers in the myenteric plexus of the stomach, ileum, proximal, and distal colon and in the submucosal plexus of the jejunum, ileum, proximal, and distal colon. Almost all the Pirt-immunoreactive (ir) neurons were also P2X2-ir, and co-immunoprecipitation experiments have shown that Pirt co-precipitated with the anti-P2X2 antibody. This work provides detailed information about the expression of Pirt in the gut and its co-localization with P2X2, indicating its potential role in influencing P2X2 receptor function.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnstock G (2012) P2X receptors in the gut. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Membr Transport and Signaling 1(3):269–279
Burnstock G (2006) Pathophysiology and therapeutic potential of purinergic signaling. Pharmacol Rev 58(1):58–86
Galligan JJ (2004) Enteric P2X receptors as potential targets for drug treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome. Br J Pharmacol 141(8):1294–1302
Holzer P (2004) Gastrointestinal pain in functional bowel disorders: sensory neurons as novel drug targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets 8(2):107–123
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82(4):1013–1067
Castelucci P et al (2002) The distribution of purine P2X(2) receptors in the guinea-pig enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 117(5):415–422
Van Nassauw L et al (2002) Neurochemical identification of enteric neurons expressing P2X(3) receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Histochem Cell Biol 118(3):193–203
Poole DP et al (2002) The distribution of P2X3 purine receptor subunits in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Auton Neurosci 101(1–2):39–47
Galligan JJ (2002) Pharmacology of synaptic transmission in the enteric nervous system. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2(6):623–629
Hu HZ et al (2001) P2X(7) receptors in the enteric nervous system of guinea-pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol 440(3):299–310
Xiang Z, Burnstock G (2004) P2X2 and P2X3 purinoceptors in the rat enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 121(3):169–179
Yu Q et al (2009) Expression of P2X6 receptors in the enteric nervous system of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Histochem Cell Biol 133(2):177–188
Ruan HZ, Burnstock G (2005) The distribution of P2X5 purinergic receptors in the enteric nervous system of mouse. Cell Tissue Res 319(2):191–200
Koles L et al (2008) Interaction of P2 purinergic receptors with cellular macromolecules. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 377(1):1–33
Kim AY et al (2008) Pirt, a phosphoinositide-binding protein, functions as a regulatory subunit of TRPV1. Cell 133(3):475–485
Wang C et al (2015) Pirt contributes to uterine contraction-induced pain in mice. Mol Pain 11:57
Patel KN, Liu Q, Meeker S, Undem BJ, Dong X (2011) Pirt, a TRPV1 modulator, is required for histamine-dependent and -independent itch. PLoS One 6(e20559)
Tang Z et al (2013) Pirt functions as an endogenous regulator of TRPM8. Nat Commun 4:2179
Gao XF et al (2015) Pirt reduces bladder overactivity by inhibiting purinergic receptor P2X3. Nat Commun 6:7650
Ghosh AP et al (2012) CHOP potentially co-operates with FOXO3a in neuronal cells to regulate PUMA and BIM expression in response to ER stress. PLoS One 7(6), e39586
Mo G et al (2009) Subtype-specific regulation of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors by phosphoinositides in peripheral nociceptors. Molecular Pain 5(1):47
Zhao Q et al (2007) PIP(2) regulates the ionic current of P2X receptors and P2X(7) receptor-mediated cell death. Channels (Austin) 1(1):46–55
Zhao Q, Logothetis DE, Seguela P (2007) Regulation of ATP-gated P2X receptors by phosphoinositides. Pflugers Arch 455(1):181–185
Ase AR et al (2010) Modulation of heteromeric P2X1/5 receptors by phosphoinositides in astrocytes depends on the P2X1 subunit. J Neurochem 113(6):1676–1684
Fujiwara Y, Kubo Y (2006) Regulation of the desensitization and ion selectivity of ATP-gated P2X2 channels by phosphoinositides. J Physiol 576(Pt 1):135–149
Burnstock G (2001) Purine-mediated signalling in pain and visceral perception. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(4):182–188
Shinoda M, Feng B, Gebhart GF (2009) Peripheral and central P2X receptor contributions to colon mechanosensitivity and hypersensitivity in the mouse. Gastroenterology 137(6):2096–2104
Xiang Z, Burnstock G (2004) Development of nerves expressing P2X3 receptors in the myenteric plexus of rat stomach. Histochem Cell Biol 122(2):111–119
Guo W et al (2013) Developmental expression of P2X5 receptors in the mouse prenatal central and peripheral nervous systems. Purinergic Signal 9(2):239–248
Mizuno MS (2012) Expression of the P2X2 receptor in different classes of ileum myenteric neurons in the female obese ob/ob mouse. World J Gastroenterol 18(34):4693
Acknowledgments
We appreciated Dr. Xinzhong Dong and Zong-Xiang Tang for providing Pirt knockout (−/−) mice. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (81471260 to Z. Xiang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wei Guo and Qian-Qian Sui contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Sui, QQ., Gao, XF. et al. Co-localization of Pirt protein and P2X2 receptors in the mouse enteric nervous system. Purinergic Signalling 12, 489–496 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9515-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-016-9515-6