Abstract
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is linked to increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, not completely explained by traditional risk factors. Importantly, the increased risk occurs despite lower levels of total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Whilst systemic inflammation may be a factor, it is possible that changes in individual lipid species contribute to the increased cardiovascular risk.
Objectives
In the present study, we characterized plasma lipidomic profiles in patients with RA in comparison with healthy controls.
Methods
Patients with RA (n = 32) and age- and gender-matched healthy volunteers (n = 84) were recruited. Fasting plasma lipid profiles were measured using electrospray-ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. 24 lipid classes and subclasses were measured.
Results
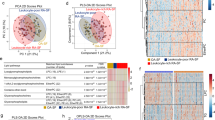
Patients with RA had normal total, low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but higher triglycerides than controls. Five lipid classes (dihydroceramides, alkylphosphatidylethanolamine, alkenylphosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine) differed between patients with RA and controls. Then we measured 36 lipid species within these 5 classes and found that 11 lipid species were different between patients with RA and controls. Three lipid classes (dihydroceramides, lysophosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine) and 10 lipid species remained significantly associated with RA after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, current smoking, systolic blood pressure and anti-hypertensive treatment in a binary logistic regression model.
Conclusion
This study has identified lipid alterations in RA. These alterations of lipids warrant further investigation as they may be associated with accelerated atherosclerosis and joint inflammation in patient with RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, H. M., Youssef, M., & Mosaad, Y. M. (2010). Antibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Rheumatology, 29(11), 1237–1243. doi:10.1007/s10067-010-1436-0.
Ajeganova, S., de Faire, U., Jogestrand, T., Frostegard, J., & Hafstrom, I. (2012). Carotid atherosclerosis, disease measures, oxidized low-density lipoproteins, and atheroprotective natural antibodies for cardiovascular disease in early rheumatoid arthritis—an inception cohort study. Journal of Rheumatology, 39(6), 1146–1154. doi:10.3899/jrheum.111334.
Arnett, F. C., Edworthy, S. M., Bloch, D. A., McShane, D. J., Fries, J. F., Cooper, N. S., et al. (1988). The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 31(3), 315–324.
Avina-Zubieta, J. A., Choi, H. K., Sadatsafavi, M., Etminan, M., Esdaile, J. M., & Lacaille, D. (2008). Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 59(12), 1690–1697. doi:10.1002/art.24092.
Avina-Zubieta, J. A., Thomas, J., Sadatsafavi, M., Lehman, A. J., & Lacaille, D. (2012). Risk of incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 71(9), 1524–1529. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200726.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 57(1), 289–300.
Camont, L., Lhomme, M., Rached, F., Le Goff, W., Negre-Salvayre, A., Salvayre, R., et al. (2013). Small, dense high-density lipoprotein-3 particles are enriched in negatively charged phospholipids: relevance to cellular cholesterol efflux, antioxidative, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic functionalities. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 33(12), 2715–2723. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301468.
Chung, C. P., Oeser, A., Raggi, P., Sokka, T., Pincus, T., Solus, J. F., et al. (2010). Lipoprotein subclasses determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and coronary atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology, 37(8), 1633–1638. doi:10.3899/jrheum.090639.
del Rincon, I. D., Williams, K., Stern, M. P., Freeman, G. L., & Escalante, A. (2001). High incidence of cardiovascular events in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort not explained by traditional cardiac risk factors. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 44(12), 2737–2745.
Dulioust, A., Hilliquin, P., Menkes, C. J., Benveniste, J., & Arnoux, B. (1992). Paf-acether acetylhydrolase activity is increased in patients with rheumatic diseases. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology, 21(4), 161–164.
El Alwani, M., Wu, B. X., Obeid, L. M., & Hannun, Y. A. (2006). Bioactive sphingolipids in the modulation of the inflammatory response. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 112(1), 171–183. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.04.004.
Engelmann, B. (2004). Plasmalogens: targets for oxidants and major lipophilic antioxidants. Biochemical Society Transactions, 32(Pt 1), 147–150.
Fan, F., Galvin, A., Fang, L., White, D. A., Moore, X. L., Sparrow, M., et al. (2014). Comparison of inflammation, arterial stiffness and traditional cardiovascular risk factors between rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Inflammation, 11(1), 29. doi:10.1186/s12950-014-0029-0.
Han, C., Robinson, D. W, Jr., Hackett, M. V., Paramore, L. C., Fraeman, K. H., & Bala, M. V. (2006). Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Journal of Rheumatology, 33(11), 2167–2172.
Heldenberg, D., Caspi, D., Levtov, O., Werbin, B., Fishel, B., & Yaron, M. (1983). Serum lipids and lipoprotein concentrations in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Rheumatology, 2(4), 387–391.
Hitchon, C. A., & El-Gabalawy, H. S. (2004). Oxidation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research and Therapy, 6(6), 265–278. doi:10.1186/ar1447.
Hokanson, J. E., & Austin, M. A. (1996). Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: a meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. Journal of Cardiovascular Risk, 3(2), 213–219.
Ifuku, M., Katafuchi, T., Mawatari, S., Noda, M., Miake, K., Sugiyama, M., et al. (2012). Anti-inflammatory/anti-amyloidogenic effects of plasmalogens in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in adult mice. J Neuroinflammation, 9, 197. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-197.
Kolodgie, F. D., Burke, A. P., Skorija, K. S., Ladich, E., Kutys, R., Makuria, A. T., et al. (2006). Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 protein expression in the natural progression of human coronary atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 26(11), 2523–2529. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000244681.72738.bc.
Maeba, R., Hara, H., Ishikawa, H., Hayashi, S., Yoshimura, N., Kusano, J., et al. (2008). Myo-inositol treatment increases serum plasmalogens and decreases small dense LDL, particularly in hyperlipidemic subjects with metabolic syndrome. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 54(3), 196–202.
Meikle, P. J., Wong, G., Tsorotes, D., Barlow, C. K., Weir, J. M., Christopher, M. J., et al. (2011). Plasma lipidomic analysis of stable and unstable coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 31(11), 2723–2732. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.234096.
Morel, O., Jesel, L., Freyssinet, J. M., & Toti, F. (2011). Cellular mechanisms underlying the formation of circulating microparticles. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 31(1), 15–26. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200956.
Moreno-Navarrete, J. M., Catalan, V., Whyte, L., Diaz-Arteaga, A., Vazquez-Martinez, R., Rotellar, F., et al. (2012). The L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol/GPR55 system and its potential role in human obesity. Diabetes, 61(2), 281–291. doi:10.2337/db11-0649.
Myasoedova, E., Crowson, C. S., Kremers, H. M., Roger, V. L., Fitz-Gibbon, P. D., Therneau, T. M., et al. (2011). Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 70(3), 482–487. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.135871.
Oka, S., Kimura, S., Toshida, T., Ota, R., Yamashita, A., & Sugiura, T. (2010). Lysophosphatidylinositol induces rapid phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and activating transcription factor 2 in HEK293 cells expressing GPR55 and IM-9 lymphoblastoid cells. Journal of Biochemistry, 147(5), 671–678. doi:10.1093/jb/mvp208.
Perk, J., De Backer, G., Gohlke, H., Graham, I., Reiner, Z., Verschuren, M., et al. 2012. European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012). The Fifth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts). European Heart Journal, 33(13):1635–1701. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehs092.
Peters, M. J., Voskuyl, A. E., Sattar, N., Dijkmans, B. A., Smulders, Y. M., & Nurmohamed, M. T. (2010). The interplay between inflammation, lipids and cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: why ratios may be better. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 64(10), 1440–1443. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02220.x.
Ruggeri, Z. M. (2002). Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nature Medicine, 8(11), 1227–1234. doi:10.1038/nm1102-1227.
Sattar, N., McCarey, D. W., Capell, H., & McInnes, I. B. (2003). Explaining how “high-grade” systemic inflammation accelerates vascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation, 108(24), 2957–2963. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000099844.31524.05.
Schimmel, E. K., & Yazici, Y. (2009). Increased lipid levels but unchanged atherogenic index in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs: published experience. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 27(3), 446–451.
Schmitz, G., & Ruebsaamen, K. (2010). Metabolism and atherogenic disease association of lysophosphatidylcholine. Atherosclerosis, 208(1), 10–18. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.05.029.
Semb, A. G., Kvien, T. K., Aastveit, A. H., Jungner, I., Pedersen, T. R., Walldius, G., et al. (2010). Lipids, myocardial infarction and ischaemic stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the apolipoprotein-related mortality risk (AMORIS) study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 69(11), 1996–2001. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.126128.
Skaff, O., Pattison, D. I., & Davies, M. J. (2008). The vinyl ether linkages of plasmalogens are favored targets for myeloperoxidase-derived oxidants: a kinetic study. Biochemistry, 47(31), 8237–8245. doi:10.1021/bi800786q.
Södergren, A., Karp, K., Bengtsson, C., Möller, B., Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S., & Wållberg-Jonsson, S. (2015). Is Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 a link between inflammation and subclinical atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis? Biomed Research International, 2015, 673018. doi:10.1155/2015/673018.
Toms, T. E., Panoulas, V. F., & Kitas, G. D. (2011). Dyslipidaemia in rheumatological autoimmune diseases. Open Cardiovascular Medicine Journal, 5, 64–75. doi:10.2174/1874192401105010064.
Van Vre, E. A., Ait-Oufella, H., Tedgui, A., & Mallat, Z. (2012). Apoptotic cell death and efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 32(4), 887–893. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.224873.
Wallner, S., & Schmitz, G. (2011). Plasmalogens the neglected regulatory and scavenging lipid species. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 164(6), 573–589. doi:10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2011.06.008.
Weir, J. M., Wong, G., Barlow, C. K., Greeve, M. A., Kowalczyk, A., Almasy, L., et al. (2013). Plasma lipid profiling in a large population-based cohort. Journal of Lipid Research, 54(10), 2898–2908. doi:10.1194/jlr.P035808.
Yamashita, A., Oka, S., Tanikawa, T., Hayashi, Y., Nemoto-Sasaki, Y., & Sugiura, T. (2013). The actions and metabolism of lysophosphatidylinositol, an endogenous agonist for GPR55. Prostaglandins and Other Lipid Mediators, 107, 103–116. doi:10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2013.05.004.
Yeom, M., Hahm, D. H., Sur, B. J., Han, J. J., Lee, H. J., Yang, H. I., et al. (2013). Phosphatidylserine inhibits inflammatory responses in interleukin-1beta-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes and alleviates carrageenan-induced arthritis in rat. Nutrition Research, 33(3), 242–250. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2013.01.006.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the clinic support staff in the Rheumatology Clinic of the Alfred Hospital and the Risk Evaluation Service of Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute for help with the clinical aspects of this study. The study was supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) program Grant to AMD and the Operational Infrastructure Support (OIS) Program of the Victorian Government, Australia. AMD is a Senior Principal Research Fellow (586656) and PJM is a NHMRC senior research fellow (1042095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Alfred Hospital.
Additional information
Lu Fang and Piyushkumar A Mundra have contributed to the work equally.
Peter Meikle and Anthony Michael Dart are Joint senior Authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, L., Mundra, P.A., Fan, F. et al. Plasma lipidomic profiling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Metabolomics 12, 136 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1086-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1086-6