Abstract
Introduction
Dogs with naturally occurring diabetes mellitus represent a potential model for human type 1 diabetes, yet significant knowledge voids exist in terms of the pathogenic mechanisms underlying the canine disorder. Untargeted metabolomic studies from a limited number of diabetic dogs identified similarities to humans with the disease.
Objective
To expand and validate earlier metabolomic studies, identify metabolites that differ consistently between diabetic and healthy dogs, and address whether certain metabolites might serve as disease biomarkers.
Methods
Untargeted metabolomic analysis via liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was performed on serum from diabetic (n = 15) and control (n = 15) dogs. Results were combined with those of our previously published studies using identical methods (12 diabetic and 12 control dogs) to identify metabolites consistently different between the groups in all 54 dogs. Thirty-two candidate biomarkers were quantified using targeted metabolomics. Biomarker concentrations were compared between the groups using multiple linear regression (corrected P < 0.0051 considered significant).
Results
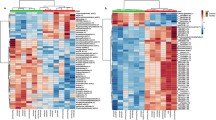
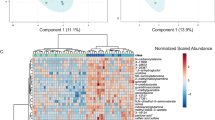
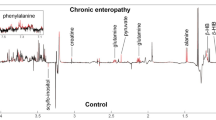
Untargeted metabolomics identified multiple persistent differences in serum metabolites in diabetic dogs compared with previous studies. Targeted metabolomics showed increases in gamma amino butyric acid, valine, leucine, isoleucine, citramalate, and 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid in diabetic versus control dogs while indoxyl sulfate, N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid, kynurenine, anthranilic acid, tyrosine, glutamine, and tauroursodeoxycholic acid were decreased.
Conclusion
Several of these findings parallel metabolomic studies in both human diabetes and other animal models of this disease. Given recent studies on the role of GABA and branched chain amino acids in human diabetes, the increase in serum concentrations in canine diabetes warrants further study of these metabolites as potential biomarkers, and to identify similarity in mechanisms underlying this disease in humans and dogs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available at the NIH Common Fund’s National Metabolomics Data Repository (NMDR) website, the Metabolomics Workbench, https://www.metabolomicsworkbench.org (Study ID ST001754, ST001742, and PR000396).
Change history
19 December 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01865-5
References
Allaway, D., Gilham, M., Wagner-Golbs, A., Maldonado, S. G., Haydock, R., Colyer, A., Stockman, J., & Watson, P. (2019). Metabolomic profiling to identify effects of dietary calcium reveal the influence of the individual and postprandial dynamics on the canine plasma metabolome. J Nutr Sci, 8, e13.
Bansal, P., Wang, S., Liu, S., Xiang, Y. Y., Lu, W. Y., & Wang, Q. (2011). GABA coordinates with insulin in regulating secretory function in pancreatic INS-1 beta-cells. PLoS One, 6, e26225.
Bhandage, A. K., Jin, Z., Korol, S. V., Shen, Q., Pei, Y., Deng, Q., Espes, D., Carlsson, P. O., Kamali-Moghaddam, M., & Birnir, B. (2018). GABA regulates release of inflammatory cytokines from peripheral blood mononuclear cells and CD4(+) T cells and is immunosuppressive in type 1 diabetes. eBioMedicine, 30, 283–294.
Bogner-Strauss, J. G. (2017). N-acetylaspartate metabolism outside the brain: Lipogenesis, histone acetylation, and cancer. Front Endocrinol (lausanne), 8, 240.
Braun, M., Ramracheya, R., Bengtsson, M., Clark, A., Walker, J. N., Johnson, P. R., & Rorsman, P. (2010). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an autocrine excitatory transmitter in human pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes, 59, 1694–1701.
Carlos, G., dos Santos, F. P., & Froehlich, P. E. (2020). Canine metabolomics advances. Metabolomics, 16, 16.
Cheng, F. P., Hsieh, M. J., Chou, C. C., Hsu, W. L., & Lee, Y. J. (2015). Detection of indoxyl sulfate levels in dogs and cats suffering from naturally occurring kidney diseases. The Veterinary Journal, 205, 399–403.
Chong, J., Soufan, O., Li, C., Caraus, I., Li, S., Bourque, G., Wishart, D. S., & Xia, J. (2018). MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 46, W486–W494.
Connor, S. C., Hansen, M. K., Corner, A., Smith, R. F., & Ryan, T. E. (2010). Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics data to aid biomarker discovery in type 2 diabetes. Molecular BioSystems, 6, 909–921.
Dong, H., Kumar, M., Zhang, Y., Gyulkhandanyan, A., Xiang, Y. Y., Ye, B., Perrella, J., Hyder, A., Zhang, N., Wheeler, M., Lu, W. Y., & Wang, Q. (2006). Gamma-aminobutyric acid up- and downregulates insulin secretion from beta cells in concert with changes in glucose concentration. Diabetologia, 49, 697–705.
Dutta, T., Kudva, Y. C., Persson, X. M., Schenck, L. A., Ford, G. C., Singh, R. J., Carter, R., & Nair, K. S. (2016). Impact of long-term poor and good glycemic control on metabolomics alterations in type 1 diabetic people. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 101, 1023–1033.
Gar, C., Rottenkolber, M., Prehn, C., Adamski, J., Seissler, J., & Lechner, A. (2018). Serum and plasma amino acids as markers of prediabetes, insulin resistance, and incident diabetes. Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences, 55, 21–32.
Gilor, C., Niessen, S. J., Furrow, E., & Dibartola, S. P. (2016). What’s in a name? Classification of diabetes mellitus in veterinary medicine and why it matters. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 30, 927–940.
Guasch-Ferré, M., Hruby, A., Toledo, E., Clish, C. B., Martínez-González, M. A., Salas-Salvadó, J., & Hu, F. B. (2016). Metabolomics in prediabetes and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 39, 833–846.
Han, G., Takahashi, H., Murao, N., Gheni, G., Yokoi, N., Hamamoto, Y., Asahara, S. I., Seino, Y., Kido, Y., & Seino, S. (2021). Glutamate is an essential mediator in glutamine-amplified insulin secretion. J Diabetes Investig, 12, 920–930.
Hansen, T. M., Brock, B., Juhl, A., Drewes, A. M., Vorum, H., Andersen, C. U., Jakobsen, P. E., Karmisholt, J., Frokjaer, J. B., & Brock, C. (2019). Brain spectroscopy reveals that N-acetylaspartate is associated to peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy in type 1 diabetes. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications, 33, 323–328.
Holle, J., Kirchner, M., Okun, J., Bayazit, A. K., Obrycki, L., Canpolat, N., Bulut, I. K., Azukaitis, K., Duzova, A., Ranchin, B., Shroff, R., Candan, C., Oh, J., Klaus, G., Lugani, F., Gimpel, C., Büscher, R., Yilmaz, A., Baskin, E., … Schaefer, F. (2020). Serum indoxyl sulfate concentrations associate with progression of chronic kidney disease in children. PLoS One, 15, e0240446.
Imazu, M., Fukuda, H., Kanzaki, H., Amaki, M., Hasegawa, T., Takahama, H., Hitsumoto, T., Tsukamoto, O., Morita, T., Ito, S., & Kitakaze, M. (2020). Plasma indoxyl sulfate levels predict cardiovascular events in patients with mild chronic heart failure. Science and Reports, 10, 16528.
Lamichhane, S., Ahonen, L., Dyrlund, T. S., Kemppainen, E., Siljander, H., Hyoty, H., Ilonen, J., Toppari, J., Veijola, R., Hyotylainen, T., Knip, M., & Oresic, M. (2018). Dynamics of plasma lipidome in progression to islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes - type 1 diabetes prediction and prevention study (DIPP). Science and Reports, 8, 10635.
Lamichhane, S., Kemppainen, E., Trost, K., Siljander, H., Hyoty, H., Ilonen, J., Toppari, J., Veijola, R., Hyotylainen, T., Knip, M., & Oresic, M. (2019). Circulating metabolites in progression to islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia, 62, 2287–2297.
Leong, S. C., & Sirich, T. L. (2016). Indoxyl sulfate-review of toxicity and therapeutic strategies. Toxins (Basel), 8.
Li, X., Xu, Z., Lu, X., Yang, X., Yin, P., Kong, H., Yu, Y., & Xu, G. (2009). Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry for metabonomics: Biomarker discovery for diabetes mellitus. Analytica Chimica Acta, 633, 257–262.
Liu, J. J., Raynal, S., Bailbe, D., Gausseres, B., Carbonne, C., Autier, V., Movassat, J., Kergoat, M., & Portha, B. (2015). Expression of the kynurenine pathway enzymes in the pancreatic islet cells. Activation by cytokines and glucolipotoxicity. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1852, 980–991.
Lloyd, A. J., Beckmann, M., Tailliart, K., Brown, W. Y., Draper, J., & Allaway, D. (2016). Characterisation of the main drivers of intra- and inter- breed variability in the plasma metabolome of dogs. Metabolomics, 12, 72.
Lloyd, A. J., Beckmann, M., Wilson, T., Tailliart, K., Allaway, D., & Draper, J. (2017). Ultra high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry plasma lipidomics can distinguish between canine breeds despite uncontrolled environmental variability and non-standardized diets. Metabolomics, 13, 15.
Mandrekar, J. N. (2010). Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 5, 1315–1316.
Menegaz, D., Hagan, D. W., Joana, A., Cianciaruso, C., Rodriguez-Diaz, R., Molina, J., Dolan, R. M., Becker, M. W., Schwalie, P. C., Nano, R., Lebreton, F., Kang, C., Sah, R., Gaisano, H. Y., Berggren, P.-O., Baekkeskov, S., Caicedo, A., & Phelps, E. A. (2019). Mechanism and effects of pulsatile GABA secretion from cytosolic pools in the human beta cell. Nature Metabolism, 1, 1110–1126.
Middleton, R. P., Lacroix, S., Scott-Boyer, M. P., Dordevic, N., Kennedy, A. D., Slusky, A. R., Carayol, J., Petzinger-Germain, C., Beloshapka, A., & Kaput, J. (2017). Metabolic differences between dogs of different body sizes. J Nutr Metab, 2017, 4535710.
Minuk, G. Y. (1993). Gamma-aminobutyric acid and the liver. Digestive Diseases, 11, 45–54.
Nelson, R. W., & Reusch, C. E. (2014). Animal models of disease: Classification and etiology of diabetes in dogs and cats. Journal of Endocrinology, 222, T1-9.
O’Kell, A. L., Garrett, T. J., Wasserfall, C., & Atkinson, M. A. (2017a). Untargeted metabolomic analysis in naturally occurring canine diabetes mellitus identifies similarities to human Type 1 Diabetes. Science and Reports, 7, 9467.
O’Kell, A. L., Garrett, T. J., Wasserfall, C., & Atkinson, M. A. (2019). Untargeted metabolomic analysis in non-fasted diabetic dogs by UHPLC-HRMS. Metabolomics, 15, 15.
O’Kell, A. L., Wasserfall, C., Catchpole, B., Davison, L. J., Hess, R. S., Jushner, J., & Atkinson, M. A. (2017b). Comparative pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes in humans, NOD mice, and canines: Has a valuable animal model of type 1 diabetes been overlooked? Diabetes, 66, 1443–1452.
Omori, K., Katakami, N., Arakawa, S., Yamamoto, Y., Ninomiya, H., Takahara, M., Matsuoka, T. A., Tsugawa, H., Furuno, M., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., & Shimomura, I. (2020). Identification of plasma inositol and indoxyl sulfate as novel biomarker candidates for atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. -Findings from metabolome analysis using GC/MS. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 27, 1053–1067.
Oresic, M., Simell, S., Sysi-Aho, M., Näntö-Salonen, K., Seppänen-Laakso, T., Parikka, V., Katajamaa, M., Hekkala, A., Mattila, I., Keskinen, P., Yetukuri, L., Reinikainen, A., Lähde, J., Suortti, T., Hakalax, J., Simell, T., Hyöty, H., Veijola, R., Ilonen, J., … Simell, O. (2008). Dysregulation of lipid and amino acid metabolism precedes islet autoimmunity in children who later progress to type 1 diabetes. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 205, 2975–2984.
Oxenkrug, G., van der Hart, M., & Summergrad, P. (2015). Elevated anthranilic acid plasma concentrations in type 1 but not type 2 diabetes mellitus. Integr Mol Med, 2, 365–368.
Rajani, C., & Jia, W. (2018). Bile acids and their effects on diabetes. Frontiers in Medicine, 12, 608–623.
Reetz, A., Solimena, M., Matteoli, M., Folli, F., Takei, K., & de Camilli, P. (1991). GABA and pancreatic beta-cells: Colocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA with synaptic-like microvesicles suggests their role in GABA storage and secretion. EMBO Journal, 10, 1275–1284.
Sen, S., Roy, S., Bandyopadhyay, G., Scott, B., Xiao, D., Ramadoss, S., Mahata, S. K., & Chaudhuri, G. (2016). gamma-aminobutyric acid is synthesized and released by the endothelium: Potential implications. Circulation Research, 119, 621–634.
Surendran, S., Matalon, R., & Tyring, S. K. (2006). Upregulation of aspartoacylase activity in the duodenum of obesity induced diabetes mouse: Implications on diabetic neuropathy. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 345, 973–975.
Tillakaratne, N. J., Medina-Kauwe, L., & Gibson, K. M. (1995). gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) metabolism in mammalian neural and nonneural tissues. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part a, Physiology, 112, 247–263.
Varga, T. V., Niss, K., Estampador, A. C., Collin, C. B., & Moseley, P. L. (2020). Association is not prediction: A landscape of confused reporting in diabetes - A systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 170, 108497.
Vendramini, T. H. A., Macedo, H. T., Zafalon, R. V. A., Macegoza, M. V., Pedrinelli, V., Risolia, L. W., Ocampos, F. M. M., Jeremias, J. T., Pontieri, C. F. F., Ferriolli, E., Colnago, L. A., & Brunetto, M. A. (2021). Serum metabolomics analysis reveals that weight loss in obese dogs results in a similar metabolic profile to dogs in ideal body condition. Metabolomics, 17, 27.
Vettorazzi, J. F., Ribeiro, R. A., Borck, P. C., Branco, R. C., Soriano, S., Merino, B., Boschero, A. C., Nadal, A., Quesada, I., & Carneiro, E. M. (2016). The bile acid TUDCA increases glucose-induced insulin secretion via the cAMP/PKA pathway in pancreatic beta cells. Metabolism, 65, 54–63.
Wewalka, M., Patti, M. E., Barbato, C., Houten, S. M., & Goldfine, A. B. (2014). Fasting serum taurine-conjugated bile acids are elevated in type 2 diabetes and do not change with intensification of insulin. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 99, 1442–1451.
Xia, J., Broadhurst, D. I., Wilson, M., & Wishart, D. S. (2013). Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: An introductory tutorial. Metabolomics, 9, 280–299.
Yi, Z., Waseemhani, M., Ghani, H., Jiang, W., Waseem Birmani, M., Ye, L., Bin, L., Cun, L. G., Lilong, A., & Mei, X. (2020). Gimmicks of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in pancreatic beta-cell regeneration through transdifferentiation of pancreatic alpha- to beta-cells. Cell Biol Int, 44, 926–936.
Yokoi, N., Beppu, M., Yoshida, E., Hoshikawa, R., Hidaka, S., Matsubara, T., Shinohara, M., Irino, Y., Hatano, N., & Seino, S. (2015). Identification of putative biomarkers for prediabetes by metabolome analysis of rat models of type 2 diabetes. Metabolomics, 11, 1277–1286.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., Yan, G., Wang, P., & Wang, X. (2015). Metabolomics for biomarker discovery: moving to the clinic. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 354671.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Dr. Amanda Posgai and Dr. Sara Williams (University of Florida) for editorial assistance and Dr. Rhonda Bacher (University of Florida) for her statistical expertise and advice.
Funding
This research was supported by Zomedica Inc. and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease of the National Institutes of Health (AO – K08DK116735). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ALO conceived of and designed the study, acquired the samples, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript; CW conceived of the study, interpreted the data, and reviewed/edited the manuscript; JGC analyzed the samples, analyzed the data, and contributed to the manuscript; BMWR performed data analysis and contributed to the manuscript; MAA conceived of the study and reviewed/edited the manuscript; TJG designed the study, analyzed the samples, analyzed and interpreted the data, and reviewed/edited the manuscript. Allison O’Kell is the guarantor of this work, had full access to all of the data in the study, and takes complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Zomedica Inc. provided financial support for the study, but had no influence on study design, data analysis, or the decision to publish. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Animal rights
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Kell, A.L., Wasserfall, C., Guingab-Cagmat, J. et al. Targeted metabolomic analysis identifies increased serum levels of GABA and branched chain amino acids in canine diabetes. Metabolomics 17, 100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01850-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-021-01850-y