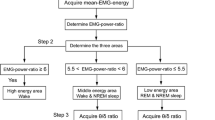
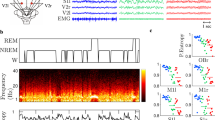
Abstract
Purpose
During the last decade, the reported prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults has been rapidly increasing. Therefore, automatic methods of sleep assessment are of particular interest. In a framework of translational neuroscience, this study introduces a reliable automatic detection system of behavioral sleep in laboratory rats based on the signal recorded at the cortical surface without requiring electromyography.
Methods
Experimental data were obtained in 16 adult male WAG/Rij rats at the age of 9 months. Electrocorticographic signals (ECoG) were recorded in freely moving rats during the entire day (22.5 ± 2.2 h). Automatic wavelet-based assessment of behavioral sleep (BS) was proposed. The performance of this wavelet-based method was validated in a group of rats with genetic predisposition to absence epilepsy (n=16) based on visual analysis of their behavior in simultaneously recorded video.
Results
The accuracy of automatic sleep detection was 98% over a 24-h period. An automatic BS assessment method can be adjusted for detecting short arousals during sleep (microarousals) with various duration.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that automatic wavelet-based assessment of behavioral sleep can be used for assessment of sleep quality. Current analysis indicates a temporal relationship between microarousals, sleep, and epileptic discharges in genetically prone subjects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonham AC (1995) Neurotransmitters in the CNS control of breathing. Respir Physiol 101(3):219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-5687(95)00045-F
Pavlov AN, Dubrovsky AI, Koronovskii AA Jr, Pavlova ON, Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya OV, Kurths J (2020) Extended detrended fluctuation analysis of sound-induced changes in brain electrical activity. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 139:109989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109989
Pavlov AN, Dubrovsky AI, Koronovskii AA Jr, Pavlova ON, Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya OV, Kurths J (2020) Extended detrended fluctuation analysis of electroencephalograms signals during sleep and the opening of the blood–brain barrier. Chaos 30(7):073138. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0011823
Milikovsky DZ, Ofer J, Senatorov VV, Friedman AR, Prager O, Sheintuch L, Elazari N, Veksler R, Zelig D, Weissberg I, Bar-Klein G, Swissa E, Hanael E, Ben-Arie G, Schefenbauer O, Kamintsky L, Saar-Ashkenazy R, Shelef I, Shamir MH, Goldberg I, Glik A, Benninger F, Kaufer D, Friedman A (2019) Paroxysmal slow cortical activity in Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy is associated with blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Sci Transl Med 11(521):eaaw8954. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw8954
Nunez P, Poza J, Gomez C, Barroso-Garcia V, Maturana-Candelas A, Tola Arribas MA, Cano M, Hornero R (2020) Characterization of the dynamic behavior of neural activity in Alzheimer’s disease: exploring the non-stationarity and recurrence structure of EEG resting-state activity. J Neural Eng 17(1):016071. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ab71e9
Gould RW, Russell JK, Nedelcovych MT, Bubser M, Blobaum AL, Bridges TM, Newhouse PA, Lindsley CW, Conn PJ, Nader MA, Jones CK (2020) Modulation of arousal and sleep/wake architecture by M 1 PAM VU0453595 across young and aged rodents and nonhuman primates. Neuropsychopharmacology 45(13):2219–2228. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00812-7
Ciric J, Lazic K, Petrovic J, Kalauzi A, Saponjic J (2016) Age-related disorders of sleep and motor control in the rat models of functionally distinct cholinergic neuropathology. Behav Brain Res 301:273–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.12.046
Bazilio DS, Bonagamba LG, Moraes DJ, Machado BH (2019) Cardiovascular and respiratory profiles during the sleep–wake cycle of rats previously submitted to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Exp Physiol 104(9):1408–1419. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP087784
Liu Y, Zhang N (2019) Propagations of spontaneous brain activity in awake rats. Neuroimage 202:116176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116176
Halász P, Terzano M, Parrino L, Bódizs R (2004) The nature of arousal in sleep. J Sleep Res 13(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2004.00388.x
Parrino L, Halasz P, Tassinari CA, Terzano MG (2006) CAP, epilepsy and motor events during sleep: the unifying role of arousal. Sleep Med Rev 10(4):267–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2005.12.004
Halász P, Kelemen A, Szűcs A (2013) The role of NREM sleep micro-arousals in absence epilepsy and in nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 107(1-2):9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.06.021
Halász P, Szűcs A (2020) Sleep and epilepsy link by plasticity. Front Neurol 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00911
Sitnikova E, Hramov AE, Grubov V, Koronovsky AA (2014) Time-frequency characteristics and dynamics of sleep spindles in WAG/Rij rats with absence epilepsy. Brain Res 1543:290–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2013.11.001
Sitnikova E, Hramov AE, Koronovsky AA, van Luijtelaar G (2009) Sleep spindles and spike–wave discharges in EEG: their generic features, similarities and distinctions disclosed with Fourier transform and continuous wavelet analysis. J Neurosci Methods 180(2):304–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.04.006
Sitnikova E, Hramov AE, Grubov V, Koronovsky AA (2016) Rhythmic activity in EEG and sleep in rats with absence epilepsy. Brain Res Bull 120:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.11.012
Van Luijtelaar ELJM, Coenen AML (1984) An EEG averaging technique for automated sleep-wake stage identification in the rat. Physiol Behav 33(5):837–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(84)90056-8
Chapotot F, Becq G (2010) Automated sleep–wake staging combining robust feature extraction, artificial neural network classification, and flexible decision rules. Int J Adapt Contr Signal Process 24(5):409–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/acs.1147
Sugi T, Kawana F, Nakamura M (2009) Automatic EEG arousal detection for sleep apnea syndrome. Biomed Sign Proces Contr 4(4):329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2009.06.004
Grubov VV, Nedaivozov VO (2018) Stream processing of multichannel EEG data using parallel computing technology with NVIDIA CUDA graphics processors. Tech Phys Lett 44(5):453–455. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785018050188
Coenen AML, van Luijtelaar ELJM (2003) Genetic animal models for absence epilepsy: a review of the WAG/Rij strain of rats. Behav Genet 33:635–655. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026179013847
Grubov VV, Sitnikova E, Pavlov AN, Koronovskii AA, Hramov AE (2017) Recognizing of stereotypic patterns in epileptic EEG using empirical modes and wavelets. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 486:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.05.091
van Luijtelaar G, Lüttjohann A, Makarov VV, Maksimenko VA, Koronovskii AA, Hramov AE (2016) Methods of automated absence seizure detection, interference by stimulation, and possibilities for prediction in genetic absence models. J Neurosci Methods 260:144–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.07.010
Ovchinnikov A, Lüttjohann A, Hramov A, Van Luijtelaar G (2010) An algorithm for real-time detection of spike-wave discharges in rodents. J Neurosci Methods 194(1):172–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.09.017
Abramovich F, Bailey TC, Sapatinas T (2000) Wavelet analysis and its statistical applications. J R Stat Soc 49(1):1–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9884.00216
Hramov AE, Koronovskii AA, Makarov VA, Pavlov AN, Sitnikova E (2015) Wavelets in neuroscience. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
ASDA (1992) EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples. Sleep 15:173–184
Gandolfo G, Romettino S, Gottesmann C, Van Luijtelaar G, Coenen A (1990) Genetically epileptic rats show a pronounced intermediate state of sleep. Physiol Behav 47(1):213–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(90)90063-a
Smyk MK, van Luijtelaar G (2020) Circadian rhythms and epilepsy: a suitable case for absence epilepsy. Front Neurol 11:245. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00245
Smyk MK, Sysoev IV, Sysoeva MV, van Luijtelaar G, Drinkenburg WH (2019) Can absence seizures be predicted by vigilance states? Advanced analysis of sleep–wake states and spike–wave discharges' occurrence in rats. Epilepsy Behav 96:200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.04.012
Borbély AA, Neuhaus HU (1978) Daily pattern of sleep, motor activity and feeding in the rat: effects of regular and gradually extended photoperiods. J Comp Physiol 124(1):1–14
van Luijtelaar G, Bikbaev A (2007) Midfrequency cortico-thalamic oscillations and the sleep cycle: genetic, time of day and age effects. Epilepsy Res 73(3):259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2006.11.002
Sitnikova E, Hramov AE, Grubov V, Koronovsky AA (2016) Rhythmic activity in EEG and sleep in rats with absence epilepsy. Brain Res Bull 120:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.11.012
Halász P (2013) How sleep activates epileptic networks? Epilepsy Res Treat 2013:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/425697
Arnaud C, Bochaton T, Pépin JL, Belaidi E (2020) Obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular consequences: pathophysiological mechanisms. Archiv Cardiovasc Dis 113(5):350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acvd.2020.01.003
Feige B, Baglioni C, Spiegelhalder K, Hirscher V, Nissen C, Riemann D (2013) The microstructure of sleep in primary insomnia: an overview and extension. Int J Psychophysiol 89(2):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.04.002
Engstrøm M, Hagen K, Bjørk M, Stovner LJ, Stjern M, Sand T (2014) Sleep quality, arousal and pain thresholds in tension-type headache: a blinded controlled polysomnographic study. Cephalalgia 34(6):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102413515339
Das S, Gupta R, Dhyani M, Goel D (2015) Headache secondary to sleep-related bruxism: a case with polysomnographic findings. J Neurosci Rural Pract 6(2):248–251. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-3147.150293
Ekstedt M, Åkerstedt T, Söderström M (2004) Microarousals during sleep are associated with increased levels of lipids, cortisol, and blood pressure. Psychosom Med 66(6):925–931. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.psy.0000145821.25453.f7
Agarwal R (2006) Automatic detection of micro-arousals. In 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference (pp. 1158-1161). IEEE. 10.1109/iembs.2005.1616628
Álvarez-Estévez D, Moret-Bonillo V (2011) Identification of electroencephalographic arousals in multichannel sleep recordings. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(1):54–63. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2010.2075930
Chaparro-Vargas R, Ahmed B, Penzel T, Cvetkovic D (2015) Searching arousals: a fuzzy logic approach. In 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) 2754-2757. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2015.7318962
Funding
This work has been supported by the RF Government Grant No. 075-15-2019-1885 in part of the biological interpretation. In the part of the development of new method of data analysis this work has been supported by the Council for Grants of the President of the Russian Federation for the State Support of Young Russian Scientists (project no. MD-645.2020.9). Experimental data has been obtained and visually analyzed with the financial support of Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant No. 19-015-00242).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Runnova, A., Zhuravlev, M., Kiselev, A. et al. Automatic wavelet-based assessment of behavioral sleep using multichannel electrocorticography in rats. Sleep Breath 25, 2251–2258 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-021-02357-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-021-02357-5