Abstract
Purpose
The main objective of this work was to develop and test a pilot scheme for decontaminating pesticide-containing water derived from pesticide mixtures used to protect vineyards, in which the scheme comprises adsorption by an organoclay and includes a system where an enhanced or rapid microbial degradation of the adsorbed residues can occur.
Methods
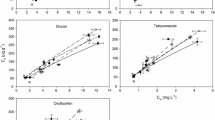
In laboratory experiments, the Freundlich adsorption coefficients of formulations of two fungicides, penconazole and cyazofamid, onto the organoclay Cloisite 20 A were measured in order to predict the efficiency of this organoclay in removing these fungicides from the waste spray-tank water. Subsequently, the adsorption tests were repeated in the pilot system in order to test the practical operation of the depuration scheme.
Results
The adsorption tests with the pilot system show 96% removal of both fungicides over a few hours, similar to the efficiency of removal predicted from the laboratory adsorption tests. The formulation type may influence the efficiency of clay recovered after adsorption. Regarding the waste disposal, for instance, the organoclay composted after the treatment, cyazofamid showed significant dissipation after 90 days, whereas the dissipation of penconazole was negligible.
Conclusion
The depuration scheme developed showed to be efficient for decontaminating pesticide-containing water derived from vineyards, but additional treatments for the adsorbed residues still appear to be necessary for persistent pesticides. However, future decontamination research should be attempted for water contaminated with pesticides containing antifoaming agents in their formulations, in which case the present pilot system could not be applied.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. ASA and SSSA, Madison, pp 595–624, Agronomy Monograph no. 9
Briggs GG (1981) Theoretical and experimental relationship between soil adsorption, octanol-water partition coefficient, water solubilities and bioconcentration factors and the parachlor. J Agric Food Chem 29:1050–1059
Castillo MP, Torstensson L, Stenström J (2008) Biobeds for environmental protection from pesticide use. J Agric Food Chem 56:6206–6219
Cruz-Guzman M, Celis R, Hermosin MC, Koskinen WC, Cornejo J (2005) Adsorption of pesticides from water by functionalized organobentonites. J Agric Food Chem 53:7502–7511
De Wilde T, Mertens J, Spanoghe P, Ryckeboer J, Jaeken P, Springael D (2008) Sorption kinetics and its effects on retention and leaching. Chemosphere 72:509–516
De Wilde T, Spanoghe P, Mertens J, Sniegowksi K, Ryckeboer J, Jaeken P, Springael D (2009) Characterizing pesticide sorption and degradation in macro scale biopurification systems using column displacement experiments. Environ Pollut 157:1373–1381
De Wilde T, Capri E, Husby J, Castillo MP, Karpouzas D, Nilsson E, Spliid NH (2010) 3rd European Biobed Workshop. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0407-y
Decoin M (2003) Where is the Fontaine-du-Theil. Phytoma 557:29–32, I (in French)
Fait G, Nicelli M, Fragoulis G, Trevisan M, Capri E (2007) Reduction of point contamination sources of pesticide from a vineyard farm. Environ Sci Technol 41:3302–3308
Giles CH, McEvans TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of adsorption isotherms and its use in diagnosis of desorption mechanism and measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc 3:3973–3993
Gupta VK, Ali I, Suhas SVK (2006) Adsorption of 2, 4-D and carbofuran pesticides using fertilizer and steel industry wastes. J Colloid Interface Sci 299:556–563
Hamadi NK, Swaminathan S, Chen XD (2004) Adsorption of Paraquat dichloride from aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from used tires. J Hazard Mater B112:133–141
Hameed BH, Din ATM, Ahmad AL (2007) Adsorption of methylene blue onto bamboo-based activated carbon: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 141:819–825
Jaeken P, Debaer C (2005) Risk of water contamination by plant production products (PPP) during pre-and post-treatment operations. Ann Rev Agric Eng 4:93–113
Kreuger J, Nilsson E (2001) Catchment scale risk-mitigation experiences—key issues for reducing pesticide transport to surface waters. In: Proceedings of the BCPC Conference. Pesticide Behaviour in Soil and Water, 78: 319–324
Kupper T, Bucheli TD, Brandli RC, Ortelli D, Edder P (2008) Dissipation of pesticides during composting and anaerobic digestion of source-separated organic waste at 15 full-scale plants. Bioresour Technol 99:7988–7994
Lombardy Region (2002) Recommended methods for microbiological analysis of food. Italy, pp 19–21(in Italian)
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Bigham JM (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3: chemical and microbiological properties. ASA, CSSA, SAAJ, Madison, pp 961–1010
Polubesova T, Nir S, Zadaka D, Rabinovitz O, Serban C, Groisman L, Rubin B (2005) Water purification from organic pollutants by optimized micelle-clay systems. Environ Sci Technol 39:2343–2348
Qu YH, Zeng GM, Huang JH, Xu K, Fang YY, Li X, Liu HL (2009) Treatment of the wastewater containing Cd2+ using micellar enhanced ultrafiltration combined with foam fractionation. Environ Eng Sci 26:761–766
Rodriguez-Cruz MS, Andrades MS, Sanchez-Martin MJ (2008) Significance of the long-chain organic cation structure in the sorption of the penconazole and metalaxyl fungicides by orano clays. J Hazard Mater 160:200–207
Suciu NA, Capri E (2009) Adsorption of chlorpyrifos, penconazole and metalaxyl from aqueous solution by modified clays. J Environ Sci Health B 44:525–532
Tajeddine L, Mountacer H, Sarrakha M (2010) Effect of iron and humic acid on photodegradation of some pesticides adsorbed on clay surfaces. Arabian J of Chem 3:73–78
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union (2009) Directive of the European parliament and of the council establishing a framework for Community action to achieve the sustainable use of pesticides, 2009/128/EC.
Vischetti C, Capri E, Trevisan M, Casucci C, Perucci P (2004) Biomassbed: a biological system to reduce pesticide point contamination at farm level. Chemosphere 55:823–828
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by the European Project “Mitigation of agricultural nonpoint - source pesticide pollution and phytoremediation in artificial wetland ecosystems” (LIFE06 ENV/F/000133). We like to thank Dr. Richard Bromilow for his useful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suciu, N.A., Ferrari, T., Ferrari, F. et al. Pesticide removal from waste spray-tank water by organoclay adsorption after field application to vineyards. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18, 1374–1383 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0494-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0494-4